06 Proving The Logarithm Log Rules Understand Logarithm Rules Laws Of Logs

06 Proving The Logarithm Log Rules Understand Logarithm ођ More lessons: mathandscience twitter: twitter jasongibsonmath in this lesson, we will discuss at great length the logarithm laws t. Proofs of logarithm properties or rules. the logarithm properties or rules are derived using the laws of exponents. that’s the reason why we are going to use the exponent rules to prove the logarithm properties below. most of the time, we are just told to remember or memorize these logarithmic properties because they are useful.
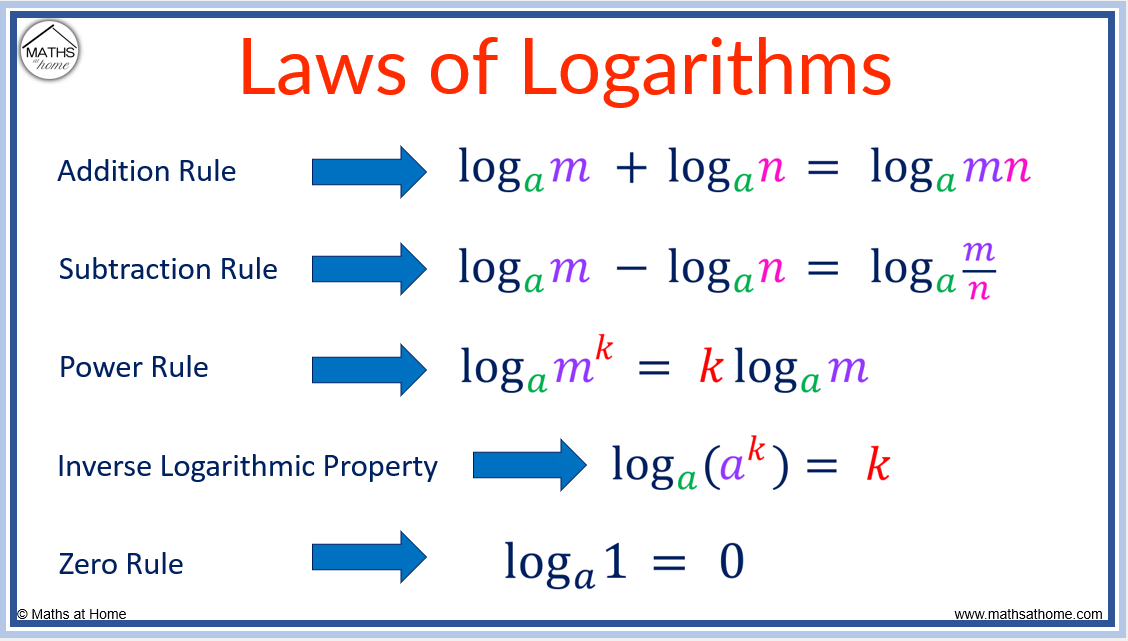
Logarithm Laws Made Easy A Complete Guide With Examples вђ Mathsathome Logarithm rules chilimath logarithm rules. The product rule of logarithm laws. the product rule of logarithms states that a single logarithm can be separated into the sum of individual logarithms which have inputs that multiply to make the input of the original logarithm. for example, log(21) = log(3) log(7). here are some examples of how to add logarithms using the addition log law. The logarithm properties are: the logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors. log a xy = log a x log a y. the logarithm of a quotient is the logarithm of the numerator minus the logarithm of the denominator. log a = log a x log a y. log a x n = nlog a x. where x and y are positive, and a > 0, a ≠ 1. Although technically a logarithm law, it is important to remember logarithms can be converted into exponentials: \(\log a(b) = x\) can be written as \(a^x = b\). law of logs proof. it is not necessary to be able to prove each logarithm law for the exam, but it is important to understand each step and why it occurs. product (addition) law.

Logarithm Rules Cheat Sheet The logarithm properties are: the logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors. log a xy = log a x log a y. the logarithm of a quotient is the logarithm of the numerator minus the logarithm of the denominator. log a = log a x log a y. log a x n = nlog a x. where x and y are positive, and a > 0, a ≠ 1. Although technically a logarithm law, it is important to remember logarithms can be converted into exponentials: \(\log a(b) = x\) can be written as \(a^x = b\). law of logs proof. it is not necessary to be able to prove each logarithm law for the exam, but it is important to understand each step and why it occurs. product (addition) law. Logarithm base change rule. the base b logarithm of x is base c logarithm of x divided by the base c logarithm of b. log b (x) = log c (x) log c (b) for example, in order to calculate log 2 (8) in calculator, we need to change the base to 10: log 2 (8) = log 10 (8) log 10 (2) see: log base change rule. Using the quotient rule for logarithms. for quotients, we have a similar rule for logarithms. recall that we use the quotient rule of exponents to combine the quotient of exponents by subtracting: \(x^{\frac{a}{b}}=x^{a−b}\). the quotient rule for logarithms says that the logarithm of a quotient is equal to a difference of logarithms.

Comments are closed.