1 The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Neck Ento Key

1 The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Neck Ento Key 10.1055 b 0034 75356 1 the anatomy and physiology of the neckmiller philip j., zoumalan richard a., carron michael a. a well contoured neck is a hallmark of youth, health, and attractiveness. the neck is a highly complex anatomical structure, and a complete working knowledge of the anatomy of the neck is therefore essential for any surgeon who. The anatomy and physiology of the neck. philip j. miller, richard a. zoumalan, and michael a. carron. a well contoured neck is a hallmark of youth, health, and attractiveness. the neck is a highly complex anatomical structure, and a complete working knowledge of the anatomy of the neck is therefore essential for any surgeon who seeks to.

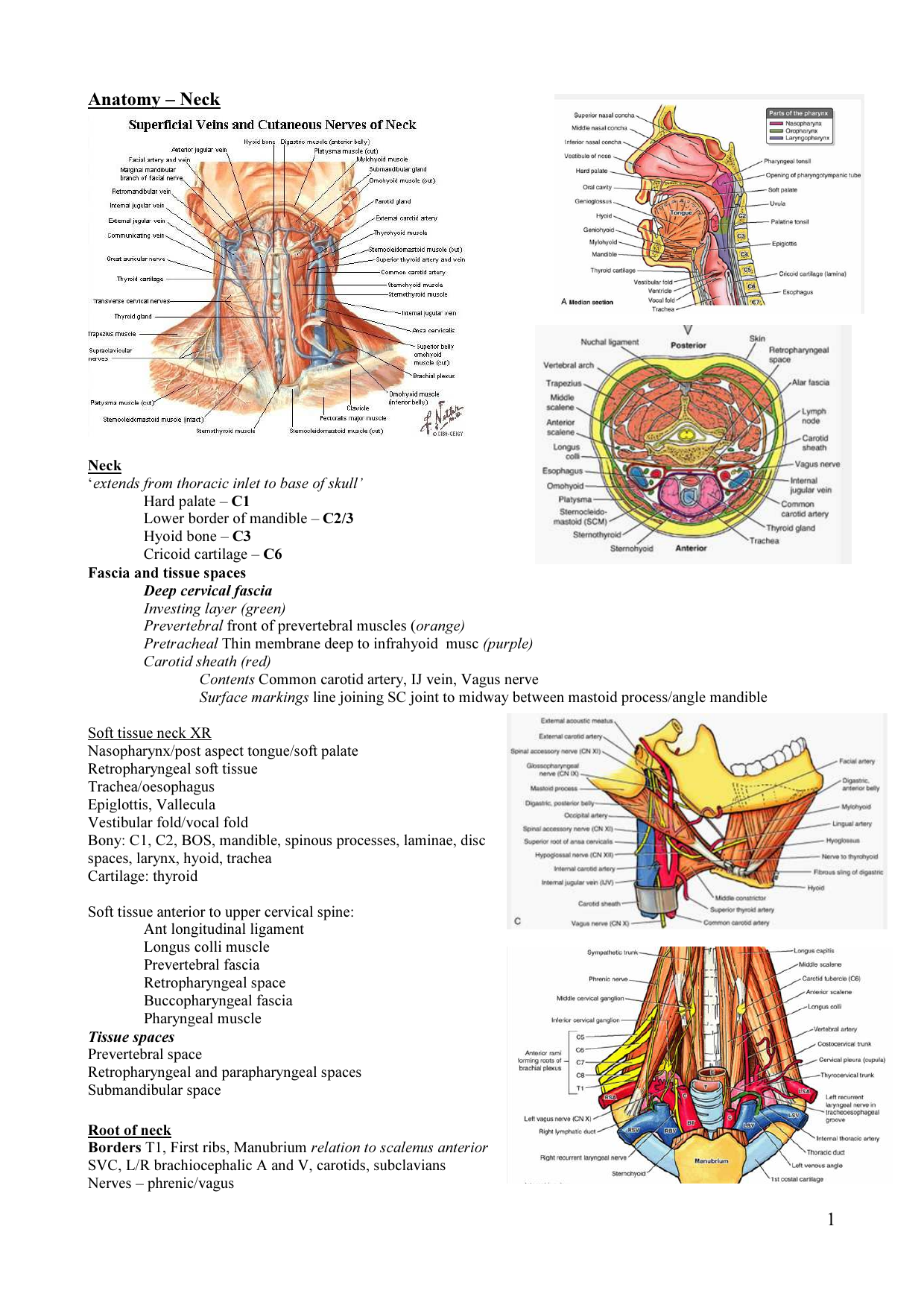
1 The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Neck Ento Key Chapter 131. anatomy and physiology of the eustachian tube. • the eustachian tube is involved in pressure equalization, mucociliary clearance, and middle ear protection. • the principal dilator of the eustachian tube is the tensor veli palatini muscle. • anatomic changes in the tube with growth and development include increased length and. This chapter discusses the clinical anatomy and physiology of the hearing and balance systems. the focus is on the clinically relevant information that impacts the ability to reach a working diagnosis and to institute physiologically based treatments. this chapter is divided into two sections: the auditory system and the vestibular system. Main nerves: maxillary nerve (cn v2), mandibular nerve (cn v3), vagus nerve (cn x), hypoglossal nerve (cn xii), and facial nerve (cn vii) neck. contains hyoid bone, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pharynx and larynx; externally divided into triangles, internally divided into compartments. main arteries: common carotid, external carotid. The neck is the bridge between the head and the rest of the body. it is located in between the mandible and the clavicle, connecting the head directly to the torso, and contains numerous vital structures. it contains some of the most complex and intricate anatomy in the body and is comprised of numerous organs and tissues with essential structure and function for normal physiology. structures.

1 The Anatomy And Physiology Of The Neck Ento Key Main nerves: maxillary nerve (cn v2), mandibular nerve (cn v3), vagus nerve (cn x), hypoglossal nerve (cn xii), and facial nerve (cn vii) neck. contains hyoid bone, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pharynx and larynx; externally divided into triangles, internally divided into compartments. main arteries: common carotid, external carotid. The neck is the bridge between the head and the rest of the body. it is located in between the mandible and the clavicle, connecting the head directly to the torso, and contains numerous vital structures. it contains some of the most complex and intricate anatomy in the body and is comprised of numerous organs and tissues with essential structure and function for normal physiology. structures. The content of the neck is grouped into 4 neck spaces, called the compartments. vertebral compartment: contains cervical vertebrae and postural muscles. visceral compartment: contains glands ( thyroid, parathyroid, and thymus ), the larynx, pharynx and trachea. two vascular compartments: contain the common carotid artery, internal jugular vein. Makes up the main axis of our body, includes the head, neck, and trunk. fundamental division of our body. relating to the limbs and their attachments to the axis. runs horizontally from right to left, dividing the body into superior and inferior parts.

Anatomy Of The Neck Trial Exhibits Inc The content of the neck is grouped into 4 neck spaces, called the compartments. vertebral compartment: contains cervical vertebrae and postural muscles. visceral compartment: contains glands ( thyroid, parathyroid, and thymus ), the larynx, pharynx and trachea. two vascular compartments: contain the common carotid artery, internal jugular vein. Makes up the main axis of our body, includes the head, neck, and trunk. fundamental division of our body. relating to the limbs and their attachments to the axis. runs horizontally from right to left, dividing the body into superior and inferior parts.
The Neck Anatomy

Comments are closed.