10 Types Of Pricing Strategies Design Talk
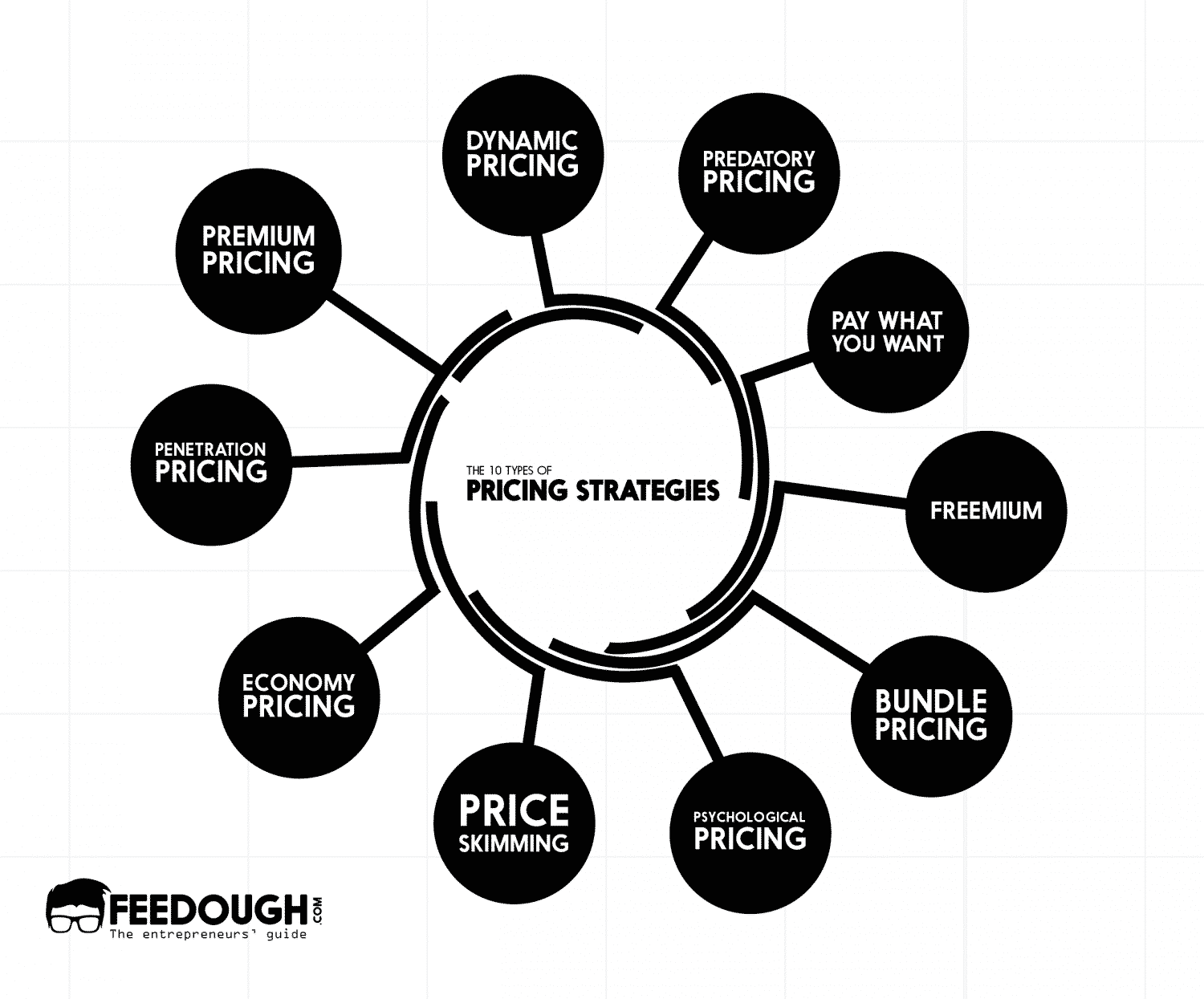
The 10 Types Of Pricing Strategies Feedough Such strategies come in the form of: charm pricing: this involves reducing the price by a minimal amount (say 1 cent) which makes the customer perceive the price to be less. for example – the price of a $3 product is set as $2.99 in supermarkets as customers’ brains process $2.99 to be nearer to $2 and not $3. Overall, promotional pricing is a common marketing tactic businesses use to generate sales and attract customers. a pricing strategy is a plan or approach that a company uses to set the price of its products or services. common pricing strategies are cost plus, skimming, penetration, value based, promotional & dynamic.

What Is Pricing Strategy Top 5 Types Examples And Template вђ Boredmonday Here are 13 different types of pricing strategies with their pros and cons highlighted alongside. 1. penetration pricing. penetration pricing is a planned pricing strategy whereby the prices of a product are initially set low to quickly reach a wide range of audience. 2. cost plus pricing strategy. the cost plus pricing strategy involves adding a fixed percentage markup to the production cost of a product. this straightforward approach ensures that all costs, including production, labor, and overheads, are covered, and a consistent profit margin is achieved. A pricing strategy is a method used to determine the optimal price for a product or service. it involves considering various factors, such as production costs, competition, customer perception, and market demand, to set a price. a pricing strategy aims to strike a balance between generating a profit and remaining attractive to consumers. Studies show that a pricing increase of just 1% can induce profit growth of more than 11%. of course, by setting prices too high, you’ll alienate certain market segments and risk pricing yourself out of the market. you need to find the right price, or prices, to maximize market penetration.

Pricing Strategies A pricing strategy is a method used to determine the optimal price for a product or service. it involves considering various factors, such as production costs, competition, customer perception, and market demand, to set a price. a pricing strategy aims to strike a balance between generating a profit and remaining attractive to consumers. Studies show that a pricing increase of just 1% can induce profit growth of more than 11%. of course, by setting prices too high, you’ll alienate certain market segments and risk pricing yourself out of the market. you need to find the right price, or prices, to maximize market penetration. The production cost of a jar of wild blueberry jelly is $1.50 per 250 ml. the company is going to add a markup of 40%. thus, the price of the jelly in the shop will be $2.10. target pricing strategy. target pricing strategy is a method used by companies to establish the product price on the basis of market prices. Most common pricing strategies: 1. cost plus pricing: this strategy involves setting the price of a product or service by adding a markup to the cost of producing it. examples: a bakery adding a 20% markup to the cost of ingredients when selling a loaf of bread.

11 Different Types Of Pricing And When To Use Them Vrogue Co The production cost of a jar of wild blueberry jelly is $1.50 per 250 ml. the company is going to add a markup of 40%. thus, the price of the jelly in the shop will be $2.10. target pricing strategy. target pricing strategy is a method used by companies to establish the product price on the basis of market prices. Most common pricing strategies: 1. cost plus pricing: this strategy involves setting the price of a product or service by adding a markup to the cost of producing it. examples: a bakery adding a 20% markup to the cost of ingredients when selling a loaf of bread.

Comments are closed.