12 Passive Design Strategies For Cold Climate Architecture Mud Plaster

12 Passive Design Strategies For Cold Climate Architecture Mud Plaster The design strategies that can be followed for cold climate architecture. the below mentioned strategies help in the reduction of energy consumption and increase comfort for users living in sites situated in cold climates. 1. building orientation. orient the building more to the south for maximum winter sun penetration into the building openings. Here are some of the key features of passive design strategies: optimal building orientation: it is one of the key features for cold weather architecture. it begins with strategic building orientation, harnessing the sun’s path to maximize the solar gain during colder weather conditions. effective insulation: sufficient insulation is a.
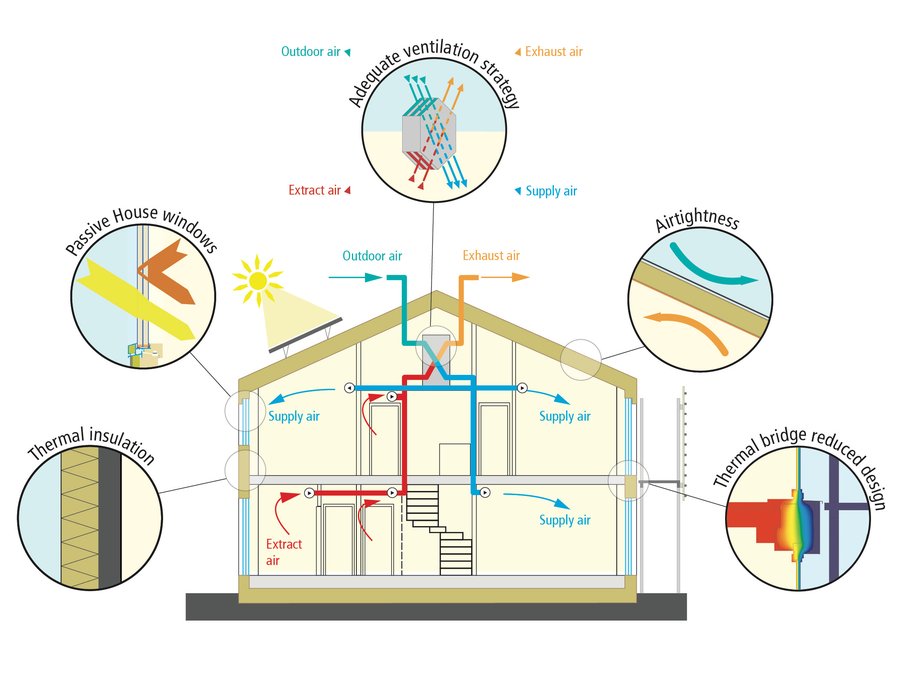
Enerphit Quality By using natural ventilation and shading. – passive cooling systems can help to reduce the amount of pollutants in the air. – passive cooling systems can help to reduce noise levels. by using sound absorbing materials and insulation. – passive cooling systems can help to create a more peaceful and quiet environment. In winter, the values range from 7 to 8 degrees celsius during the day and 14 to 0 degrees celsius in the dark. winters thus are extremely cold. the low relative humidity, ranging from about 10–50%, and less precipitation than 200 mm per year, marks this type of climate. the sky is fairly clear throughout the year with a cloudiness of but 50%. The thickness of external wall is 50–60 cm and internal wall is 30 cm. the adobe blocks, used for wall construction, are laid in course using mud mortar and covered with mud plaster. the mud plaster is made up of mud, cow dung and use of reinforcing material. cupboard for storage were provided in the 50–60 cm thick walls with a depth of 30 cm. Passive design strategies use the natural climate conditions to control the indoor environment of a house. they are the opposite of active design strategies such as mechanical heating, cooling and ventilation. for some passive design strategies to work, you, the occupant, need to be active instead. the more passive design strategies you can use.

12 Passive Cooling Strategies For Hot Climate Architecture Dessert The thickness of external wall is 50–60 cm and internal wall is 30 cm. the adobe blocks, used for wall construction, are laid in course using mud mortar and covered with mud plaster. the mud plaster is made up of mud, cow dung and use of reinforcing material. cupboard for storage were provided in the 50–60 cm thick walls with a depth of 30 cm. Passive design strategies use the natural climate conditions to control the indoor environment of a house. they are the opposite of active design strategies such as mechanical heating, cooling and ventilation. for some passive design strategies to work, you, the occupant, need to be active instead. the more passive design strategies you can use. 8. cool roofs. cool roofs is one of the most compelling passive design strategies that holds immense potential to transform conventional rooftops into energy efficient surfaces. the central idea of cool roofs is based on utilizing roofing materials and coatings with high solar reflectance and thermal emittance. Most efficient passive cooling and heating strategies based on the climate and location of a building site. fig.2 bioclimatic chart for shimla . throughout the year the temperature is low, so solar passive heating strategy is needed to bring it in comfort zone. design strategies for cold and cloudy climate.

12 Passive Design Strategies For Cold Climate Architecture 8. cool roofs. cool roofs is one of the most compelling passive design strategies that holds immense potential to transform conventional rooftops into energy efficient surfaces. the central idea of cool roofs is based on utilizing roofing materials and coatings with high solar reflectance and thermal emittance. Most efficient passive cooling and heating strategies based on the climate and location of a building site. fig.2 bioclimatic chart for shimla . throughout the year the temperature is low, so solar passive heating strategy is needed to bring it in comfort zone. design strategies for cold and cloudy climate.

Comments are closed.