17 6 Circulation Through The Heart Biology Libretexts
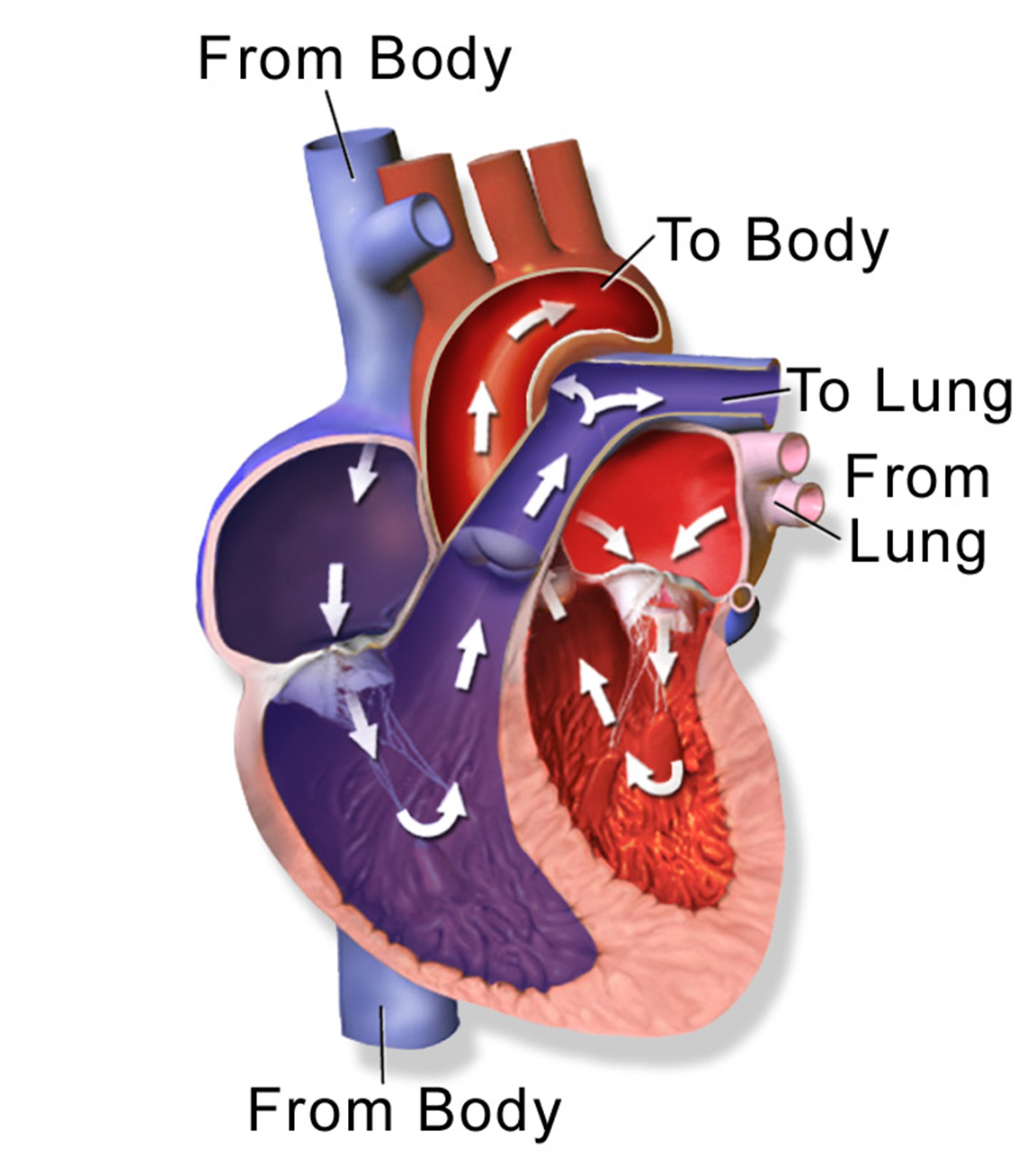
17 6 Circulation Through The Heart Biology Libretexts The function of the pulmonary circuit is to oxygenate (add oxygen to) the blood by transferring low oxygen blood to the lungs to acquire oxygen. once oxygenated, blood in the blood vessels of the pulmonary circuit returns to the heart to complete the circuit. the right side of the heart pumps blood through the systemic circuit. Figure 17.3.1 17.3. 1: listening to a heartbeat. the heart is a muscular organ behind the sternum (breastbone), slightly to the left of the center of the chest. a normal adult heart is about the size of a fist. the function of the heart is to pump blood through the blood vessels of the cardiovascular system.
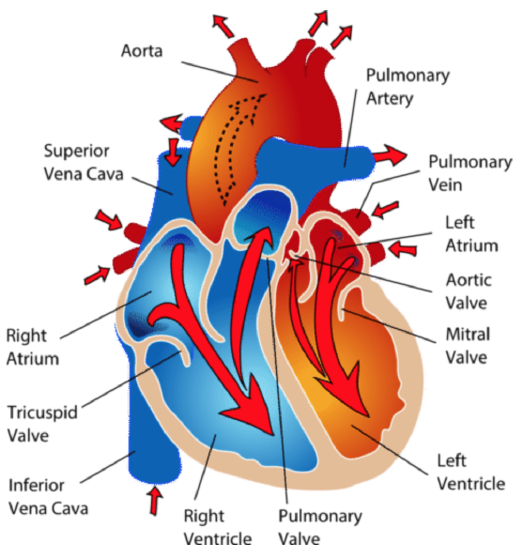
17 3 Heart Biology Libretexts 17.9: laboratory activities and assignment 17.10: collaborative study activities this page titled 17: cardiovascular system the heart is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by rosanna hartline . 17.1: the heart. 17.1a: anatomy of the heart; 17.1b: pericardium; 17.1c: layers of the heart walls; 17.1d: chambers of the heart; 17.1e: great vessels of the heart. The heart consists of four chambers separated into two sides. each side contains an atria which receives blood into the heart and flows it into a ventricle, which pumps the blood out of the heart. the atria and ventricle on each side of the heart are linked together by valves that prevent backflow of blood. the wall that separates the left and. The heart. the heart is a muscular organ in the chest. it consists mainly of cardiac muscle tissue and pumps blood through blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. the heart has four chambers, as shown in figure below: two upper atria (singular, atrium) and two lower ventricles.

Blood Flow In The Heart вђ Mcat Biology Medschoolcoach The heart consists of four chambers separated into two sides. each side contains an atria which receives blood into the heart and flows it into a ventricle, which pumps the blood out of the heart. the atria and ventricle on each side of the heart are linked together by valves that prevent backflow of blood. the wall that separates the left and. The heart. the heart is a muscular organ in the chest. it consists mainly of cardiac muscle tissue and pumps blood through blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. the heart has four chambers, as shown in figure below: two upper atria (singular, atrium) and two lower ventricles. Pulmonary circulation is the part of the circulatory system that carries blood between the heart and lungs (the term “pulmonary” means “of the lungs”). it is illustrated in figure below. deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle through pulmonary arteries, which transport it to the lungs. in the lungs, the blood gives up carbon. Heart. the heart is a muscular organ in the chest. it consists mainly of cardiac muscle tissue and pumps blood through blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. as shown in figure 17.2.3 17.2. 3, the heart has four inner chambers: a right atrium and ventricle and a left atrium and ventricle.
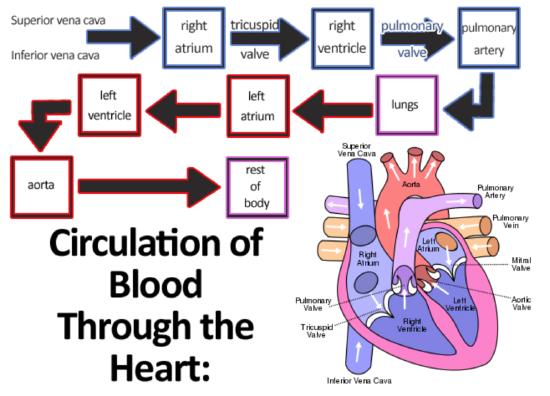
17 3 Heart Biology Libretexts Pulmonary circulation is the part of the circulatory system that carries blood between the heart and lungs (the term “pulmonary” means “of the lungs”). it is illustrated in figure below. deoxygenated blood leaves the right ventricle through pulmonary arteries, which transport it to the lungs. in the lungs, the blood gives up carbon. Heart. the heart is a muscular organ in the chest. it consists mainly of cardiac muscle tissue and pumps blood through blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. as shown in figure 17.2.3 17.2. 3, the heart has four inner chambers: a right atrium and ventricle and a left atrium and ventricle.

40 9 Mammalian Heart And Blood Vessels Structures Of The Heart

Comments are closed.