2 2 Direct Variation

Ppt Section 2 2 вђ Direct Variation Powerpoint Presentation Free For example, if y represents the total cost of buying x items that cost $7 each, then the direct variation equation would be. y = 7x. in this direct variation equation, 7 is the constant of proportionality, which represents the cost per item. and, for example: when x=2, y=14. when x=3, y=21. when x=10, y=70. To write the equation of direct variation, we replace the letter [latex]k[ latex] by the number [latex]2[ latex] in the equation [latex]y = kx[ latex]. when an equation that represents direct variation is graphed in the cartesian plane, it is always a straight line passing through the origin.

2 2 Direct Variation Youtube It could be y is equal to 2 times 1 x, which is clearly the same thing as 2 x. it could be y is equal to 1 3 times 1 x, which is the same thing as 1 over 3x. it could be y is equal to negative 2 over x. and let's explore this, the inverse variation, the same way that we explored the direct variation. If you add a y intercept and change y=2x to, for example, y=2x 2, the x and the y will no longer be related by a constant ratio. if x is 1, y will be 4. if x is 2, y will be 6. though x has increased by a factor of 2, y has not. therefore, y=2x 2 is not direct variation. the same goes for inverse variation. When you have a direct variation, we say that as your variable changes, the resulting value changes in the same and proportional manner. a direct variation between y and x is typically denoted by. y = kx. where k ∈ r. this means that as x goes larger, y also tends to get larger. the opposite is also true. as x goes smaller, y tend to get smaller. Y = 48. therefore, 8 dozen oranges will cost $48. now, let us find the constant of direct variation by using the equation y = kx. where. y = the cost, x = the number of dozens, and. k = the constant of variation. k = 1 6. therefore, 1 6 or 0.1667 (approx) is the constant of direct variation.
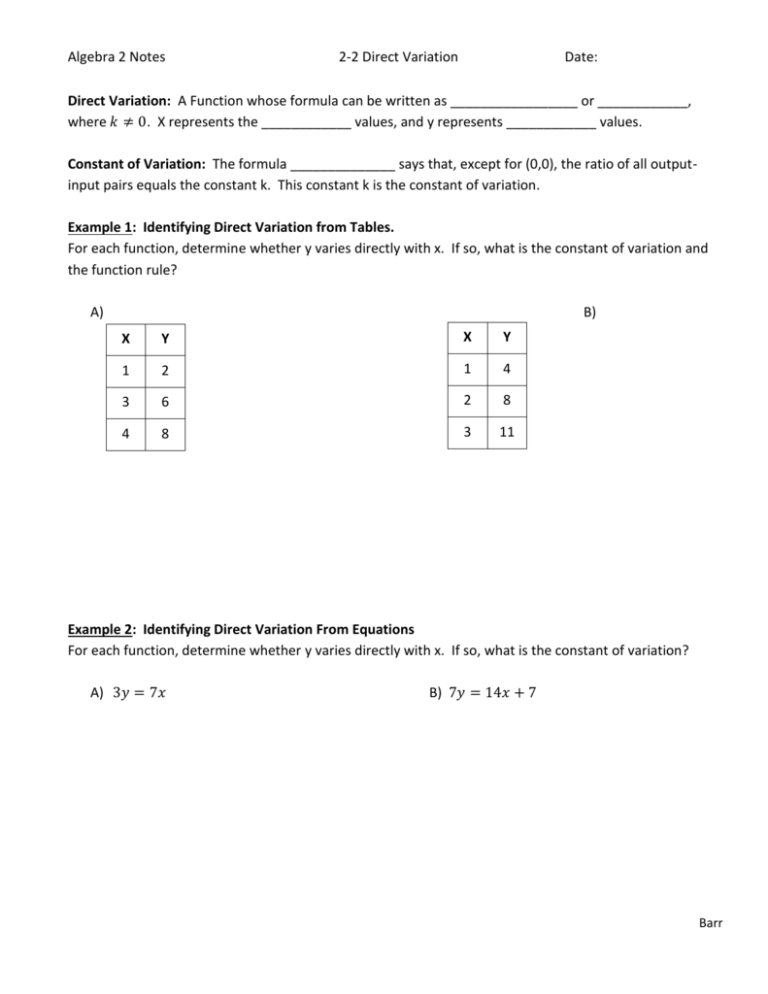
Algebra 2 Notes 2 2 Direct Variation Date Direct Variation A When you have a direct variation, we say that as your variable changes, the resulting value changes in the same and proportional manner. a direct variation between y and x is typically denoted by. y = kx. where k ∈ r. this means that as x goes larger, y also tends to get larger. the opposite is also true. as x goes smaller, y tend to get smaller. Y = 48. therefore, 8 dozen oranges will cost $48. now, let us find the constant of direct variation by using the equation y = kx. where. y = the cost, x = the number of dozens, and. k = the constant of variation. k = 1 6. therefore, 1 6 or 0.1667 (approx) is the constant of direct variation. When we say that a variable varies directly as another variable, or is directly proportionate to another variable, we mean that the variable changes with the same ratio as the other variable increases. also, if a variable decreases, then the other variable will decrease at the same rate. this is the most basic type of correlation, which can be applied to tons of daily real life situations. for. The sign “ ∝ ” is read “varies as” and is called the sign of variation. example: if y varies directly as x and given y = 9 when x = 5, find: a) the equation connecting x and y. b) the value of y when x = 15. c) the value of x when y = 6. solution: a) y ∝ x i.e. y = kx where k is a constant. substitute x = 5 and y = 9 into the equation:.

2 2 Direct Variation Youtube When we say that a variable varies directly as another variable, or is directly proportionate to another variable, we mean that the variable changes with the same ratio as the other variable increases. also, if a variable decreases, then the other variable will decrease at the same rate. this is the most basic type of correlation, which can be applied to tons of daily real life situations. for. The sign “ ∝ ” is read “varies as” and is called the sign of variation. example: if y varies directly as x and given y = 9 when x = 5, find: a) the equation connecting x and y. b) the value of y when x = 15. c) the value of x when y = 6. solution: a) y ∝ x i.e. y = kx where k is a constant. substitute x = 5 and y = 9 into the equation:.

Algebra 2 Solution Of 2 2 Direct Variation Youtube

Comments are closed.