3 Decommissioning Wind Turbine Monopiles And Foundations
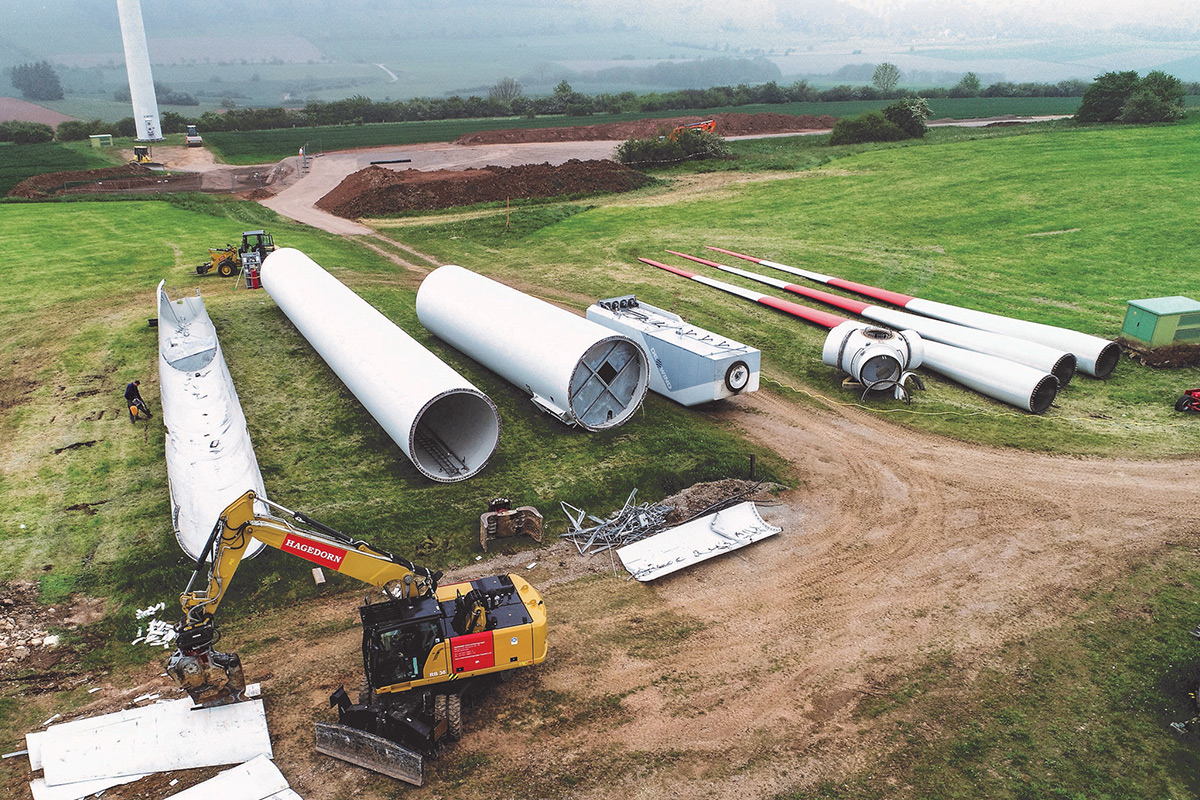

Decommissioning Of Onshore Wind Turbines Windeurope This is an excerpt from ore catapult's film exploring scenarios for a circular economy in offshore wind. you can view the full film or scenarios for individu. Monopiles remain the most widely used foundation structure for offshore wind turbines: by 2020, roughly 80% of all new and cumulative installations in europe had adopted this technology.25 it is a popular solution due to its tubular structure, making it relatively easy to design and manufacture.26.
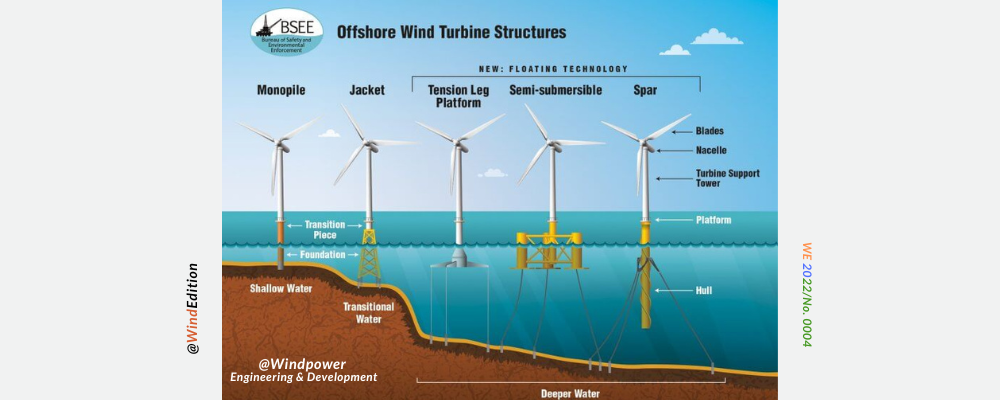
Introducing Different Types Of Offshore Wind Turbine Foundations Fixed The limited lifetime of offshore wind farms requires an efficient and safe decommissioning. the project hydraulic pile extraction scale tests (hype st) studied the option of removal of offshore wind turbine foundations (monopiles) in a sustainable way. hype st project aimed at both the fundamental understanding and the demonstration of the. [3] c. moore, “warning that increasingly large offshore wind turbines risk getting too big for their foundations,” new civil engineer, 10 11 2021. [online]. Monopile foundations are usually steel pipe piles with large diameters and thick walls that are driven (hammered) into the seabed. carlo (ortolani 2017) and byrne reported commonly used monopile foundations with large diameter (d) of 4–7 m (fig. 3), sometimes even up to 10 m in diameter with their lengths of 40–50 m (while in china, the length of several monopiles is as long as 70 m, i.e. The design envelope for the empire wind project estimates the footprint for each gbs foundation would cover 3.7 hectares (9.1 acres), including the scour protection. with the minimum design spacing of 1.2 km (0.65 nm), the maximum seabed disturbance from the turbine foundations would be about 2.5% of the windfarm area.

3 Decommissioning Wind Turbine Monopiles And Foundations Youtube Monopile foundations are usually steel pipe piles with large diameters and thick walls that are driven (hammered) into the seabed. carlo (ortolani 2017) and byrne reported commonly used monopile foundations with large diameter (d) of 4–7 m (fig. 3), sometimes even up to 10 m in diameter with their lengths of 40–50 m (while in china, the length of several monopiles is as long as 70 m, i.e. The design envelope for the empire wind project estimates the footprint for each gbs foundation would cover 3.7 hectares (9.1 acres), including the scour protection. with the minimum design spacing of 1.2 km (0.65 nm), the maximum seabed disturbance from the turbine foundations would be about 2.5% of the windfarm area. 1. introduction. offshore wind turbines (owts) are subjected to a variety of environmental loads such as the dynamic lateral loads with a predominant frequency of 0.01 hz (bhattacharya and adhikari, 2011) arising from wind acting on the tower and turbine assembly, and wave and water current loads with a frequency typically ranging over 0.1–0.3 hz (kallehave et al., 2015) acting on the tower. Offshore wind turbine (owt) structures are usually supported by various types of foundations and its selection depends on several factors such as water depth, economic costs, construction methodologies, seabed bathymetry, soil characteristics, and load characteristics.
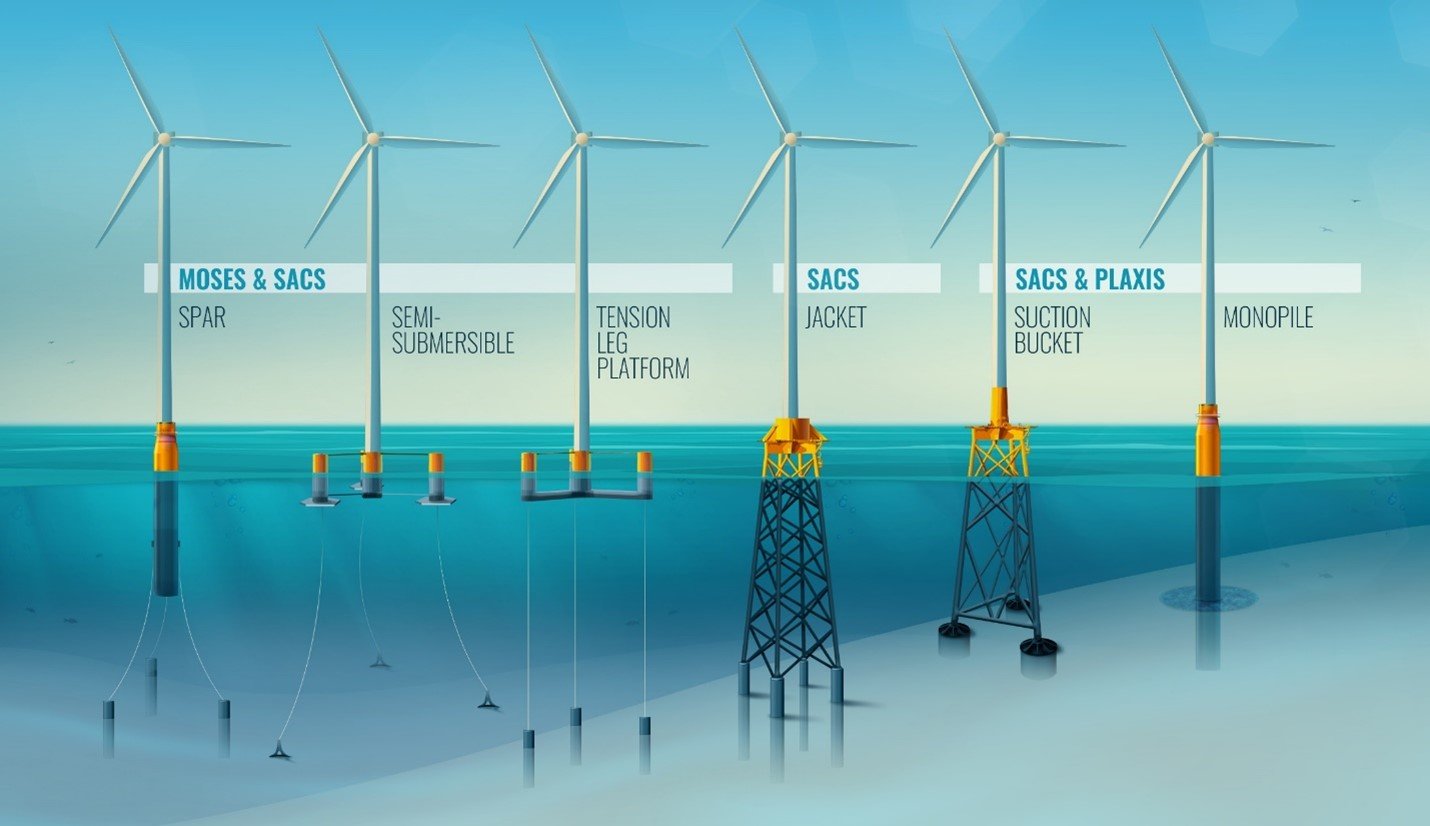

All About Offshore Wind Turbine Foundations 1. introduction. offshore wind turbines (owts) are subjected to a variety of environmental loads such as the dynamic lateral loads with a predominant frequency of 0.01 hz (bhattacharya and adhikari, 2011) arising from wind acting on the tower and turbine assembly, and wave and water current loads with a frequency typically ranging over 0.1–0.3 hz (kallehave et al., 2015) acting on the tower. Offshore wind turbine (owt) structures are usually supported by various types of foundations and its selection depends on several factors such as water depth, economic costs, construction methodologies, seabed bathymetry, soil characteristics, and load characteristics.
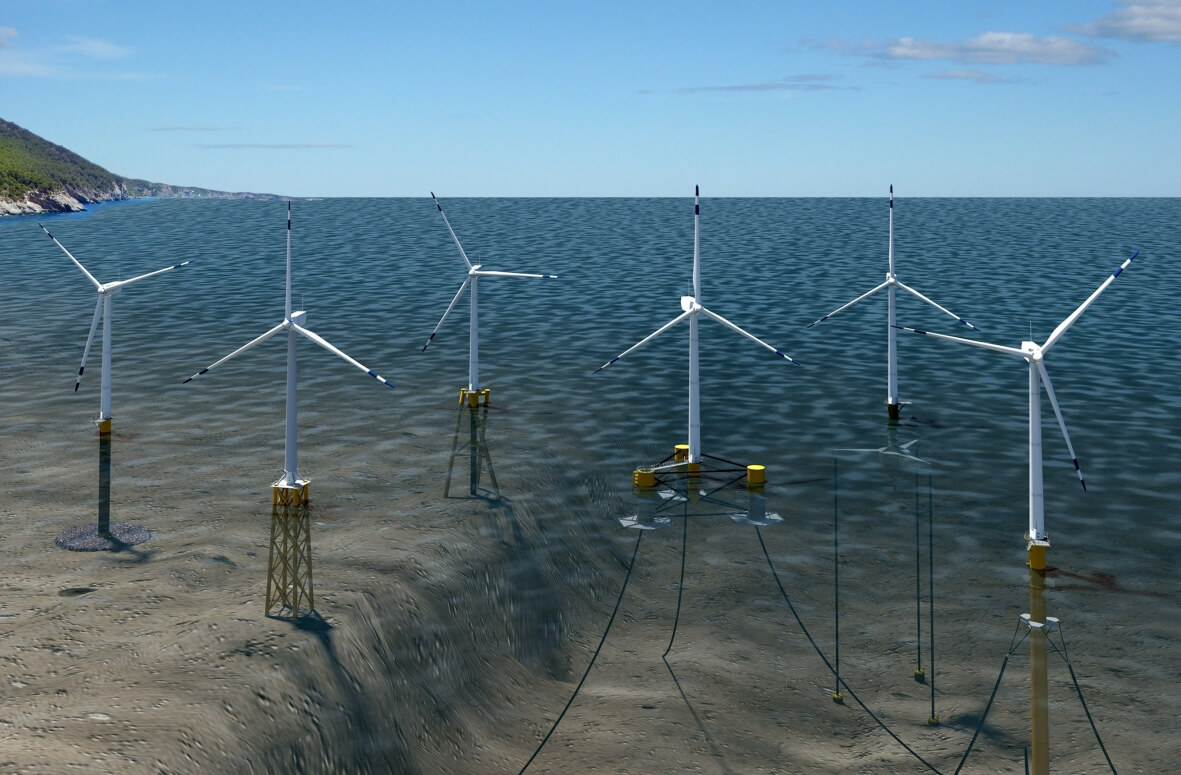

в дно водоема вбита свая длиной 82 фото

Comments are closed.