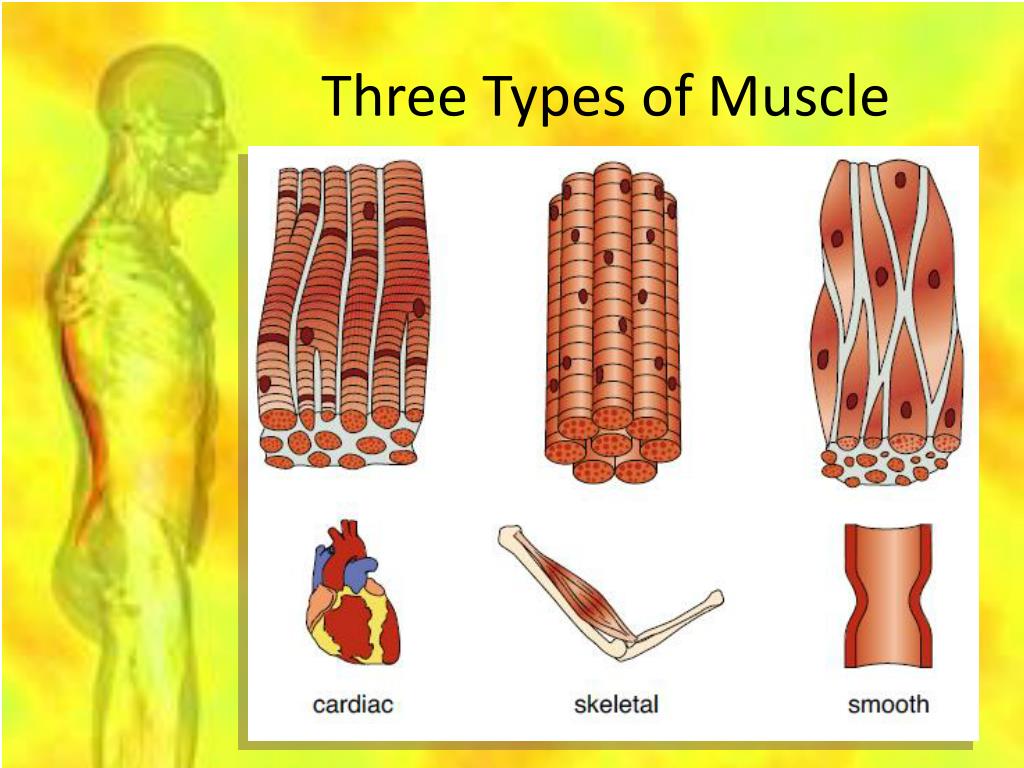
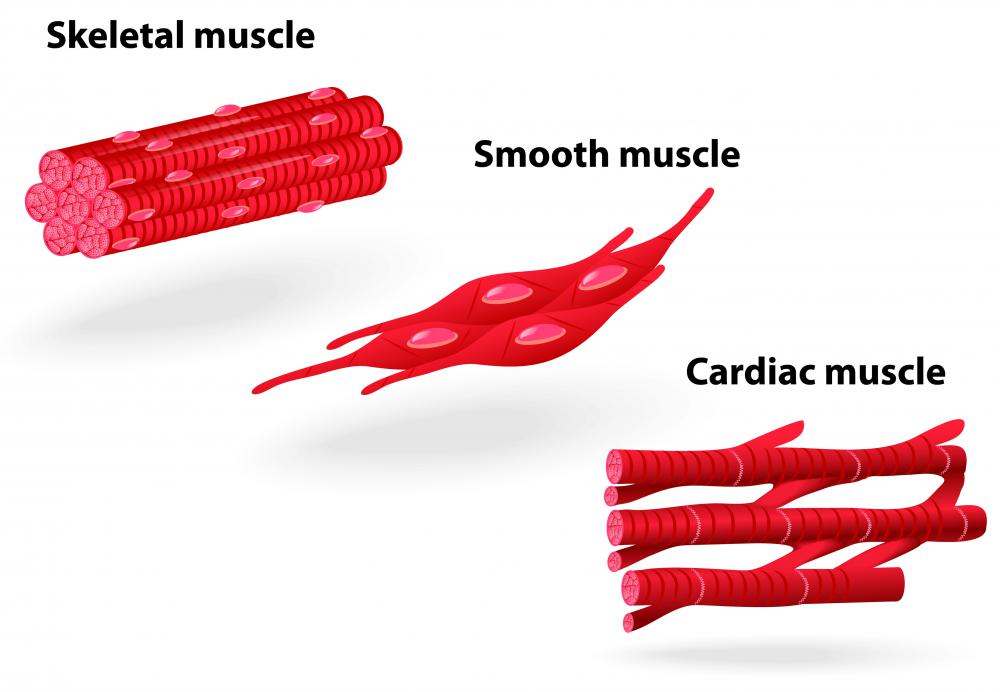
3 Types Of Skeletal Muscle
Muscle Tissue Types Learn Muscular Anatomy Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles that connect to bones and allow you to move. learn about their structure, function, location and common disorders. Learn about the structure and function of skeletal muscle fibers, myofibrils, and sarcomeres. see how the sliding filament process of contraction involves actin and myosin proteins and changes the sarcomere length.

Structure Of Three Basic Muscle Types Muscle System Mcat Content Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the other being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. they are part of the voluntary muscular system [1] and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. [2][3] the skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of. Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscles in the human body the others being visceral and cardiac muscles. in this lesson, skeletal muscles, its definition, structure, properties, functions, and types are explained in an easy and detailed manner. Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external. The musculoskeletal system comprises one of the body's major tissue organ systems. the three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle groups.[1][2][3] skeletal muscle attaches to the bone by tendons, and together they produce all body movements. the skeletal muscle fibers are crossed with a regular pattern of fine red and white lines, giving the muscle a distinctive.
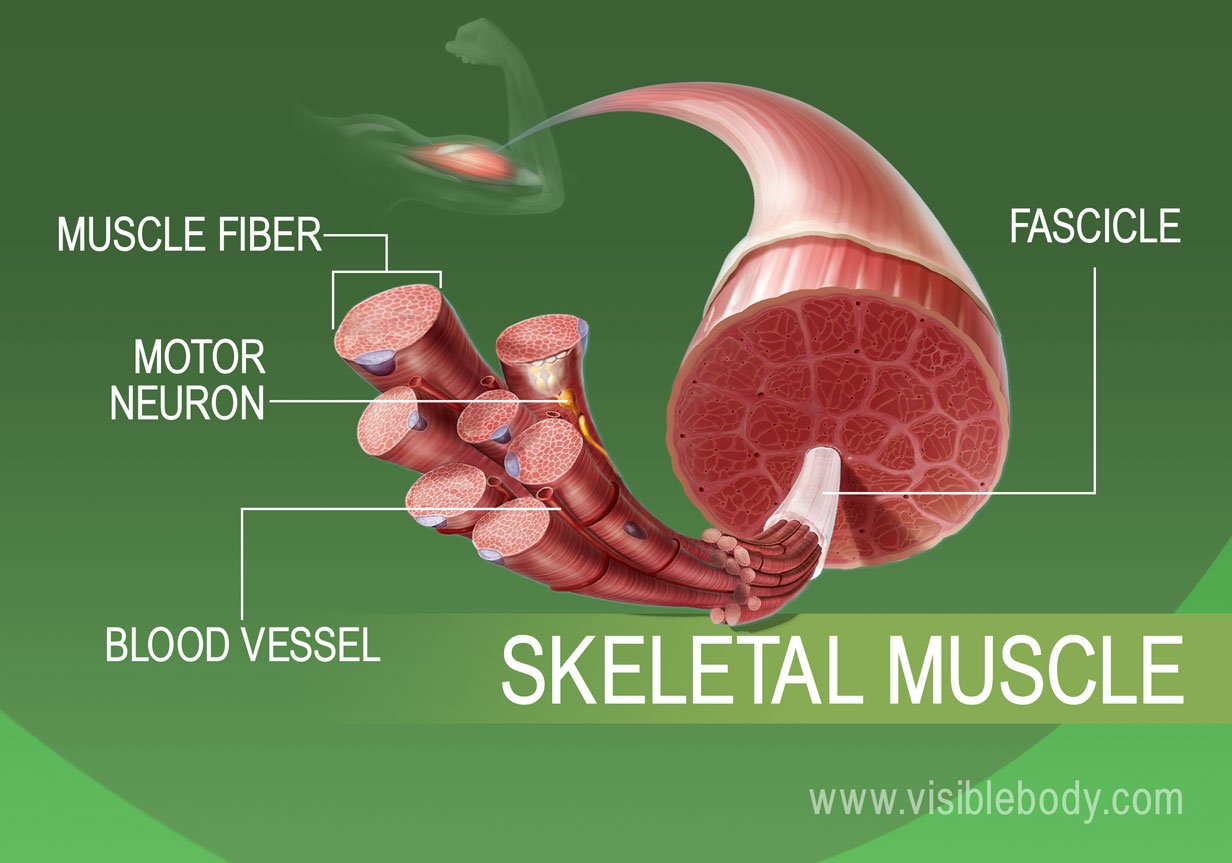
What Are The Different Types Of Muscles Muscles and muscle tissue. this type of tissue is found in skeletal muscles and is responsible for the voluntary movements of bones. muscle is defined as a tissue primarily composed of specialized cells fibers which are capable of contracting in order to effect movement. this can relate to movement of the body or body parts with our external. The musculoskeletal system comprises one of the body's major tissue organ systems. the three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle groups.[1][2][3] skeletal muscle attaches to the bone by tendons, and together they produce all body movements. the skeletal muscle fibers are crossed with a regular pattern of fine red and white lines, giving the muscle a distinctive. Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. this article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue (called “mysia”) that enclose it and provide structure to the muscle as a whole, and also compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (figure 10.3).
What Is The Anatomy Of The Skeletal Muscles With Pictures Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. this article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions. These tissues include the skeletal muscle fibers, blood vessels, nerve fibers, and connective tissue. each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue (called “mysia”) that enclose it and provide structure to the muscle as a whole, and also compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (figure 10.3).

Comments are closed.