33 Construct An Orbital Diagram To Show The Electron

33 Construct An Orbital Diagram To Show The Electron This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. it explains how to write the orbital diagram n. In this case, 2 2 6 2 6 2 10 6 2 1= 39 and z=39, so the answer is correct. a slightly more complicated example is the electron configuration of bismuth (symbolized bi, with z = 83). the periodic table gives the following electron configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p65s2 4d10 5p6 6s2 4f14 5d10 6p3.
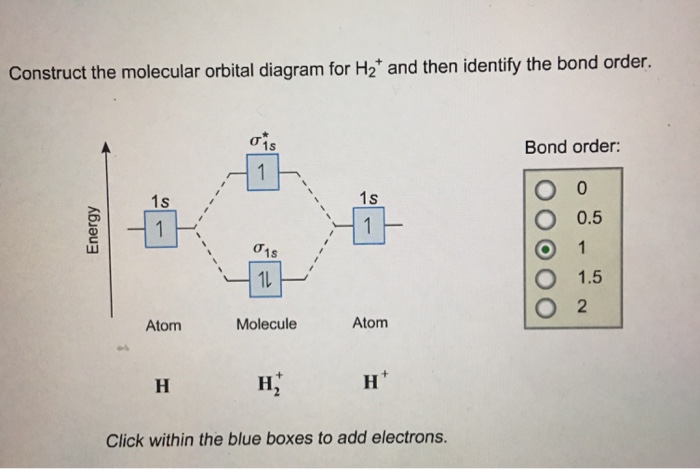
33 Construct An Orbital Diagram To Show The Electron Shown below is a qualitative diagram of the atomic orbital energies for an na atom. the number of orbitals in each subshell is not shown. (d) a sodium vapor lamp (figure 7.23) operates by using electricity to excite the highest energy electron to the next highest energy level. light is produced when the excited electron drops back to the lower. The first two electrons in lithium fill the 1 s orbital and have the same sets of four quantum numbers as the two electrons in helium. the remaining electron must occupy the orbital of next lowest energy, the 2 s orbital (figure 5.1.3 or 5.1.4 ). thus, the electron configuration and orbital diagram of lithium are:. The electron configuration for carbon is 1s22s22p2. an orbital box diagram can be written as well. boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin–one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The electron configuration for phosphorus is 1s 2 2s 2 2p6 3 s2 3p3 and the orbital diagram is drawn below. 1.4: electron configurations and electronic orbital diagrams (review) is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the electron configuration of an atom indicates the number of valence electrons.
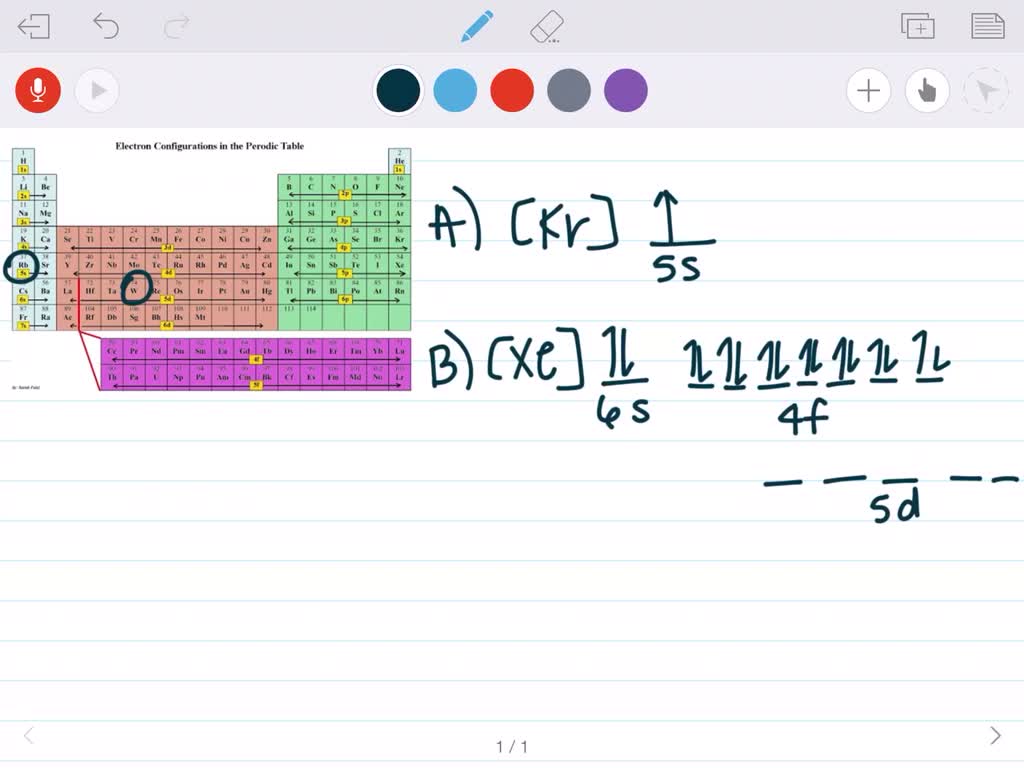
33 Construct An Orbital Diagram To Show The Electron The electron configuration for carbon is 1s22s22p2. an orbital box diagram can be written as well. boxes, or horizontal lines represent the orbitals, arrows represent the electrons, and if an orbital is full, the electrons must be of opposite spin–one arrow pointing up and the other one pointing down. The electron configuration for phosphorus is 1s 2 2s 2 2p6 3 s2 3p3 and the orbital diagram is drawn below. 1.4: electron configurations and electronic orbital diagrams (review) is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the electron configuration of an atom indicates the number of valence electrons. Electron orbital diagrams are diagrams used to show the energy of electrons within the sublevels of an atom or atoms when used in bonding. single atom diagrams (atomic orbital diagrams) consist of horizontal lines or boxes for each sublevel. within orbitals, arrows indicate the spin direction of the occupant electrons. The remaining electron must occupy the orbital of next lowest energy, the 2s orbital (figure 6.26 or figure 6.27). thus, the electron configuration and orbital diagram of lithium are: an atom of the alkaline earth metal beryllium, with an atomic number of 4, contains four protons in the nucleus and four electrons surrounding the nucleus.

Comments are closed.