4 Of 7 Grounded Versus Ungrounded System Nec 2014 100 35min

4 Of 7 Grounded Versus Ungrounded System Nec 2014 100 35min This is part 4 of a 7 part series called electrical fundamentals – protection against electric shock (1hr:13min:19sec)visit mikeholt 14code to. Most of the electrical systems today are required by article 250 of the nec to be grounded, and the most commonly used system is the solidly grounded system. this type of grounding system is where the neutral is connected directly to the ground without intentional added resistance in the ground circuit.

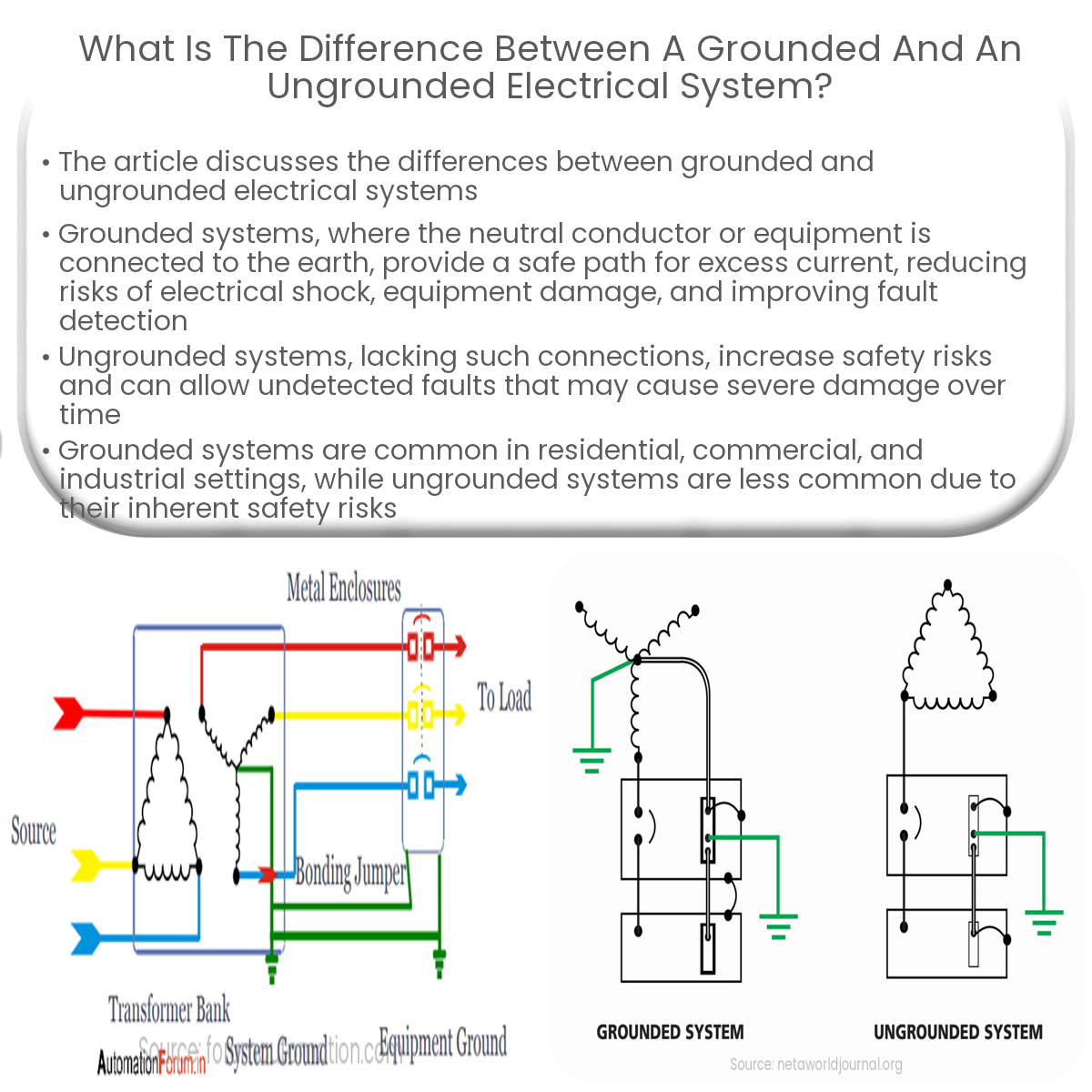
Advantage And Disadvantage Of Grounded And Ungrounded Neutral System An ungrounded system is a system grounded through capacitance. this natural capacitance is the result of electric charges traveling between energized conductors, through a dielectric medium including the ground. in overhead lines, the dielectric medium is the encircling air, and in cables, it is the insulation. Today, because grounded systems offer greater voltage stability, most of the systems described in article 250.20 of the nec require a grounded system, whether it is a solidly grounded system or an impedance grounded system. historically, the most commonly used system is the solidly grounded system (see figure 1). Upon the detection of a ground fault. this reduces system reliability and load availability compared to other grounding methods. because ground faults are 100 times more common than any other type of fault [8][9], having such a vulnerable design may not be the best choice for mission critical applications. figure 3. solidly grounded system. a. By taking these factors into consideration, electrical professionals can successfully implement a corner grounded delta diagram and enhance the reliability of the electrical system. video: 4 of 7 grounded versus ungrounded system, nec 2014 – [100], (35min:35sec).

Grounded Vs Ungrounded Electrical Systems Upon the detection of a ground fault. this reduces system reliability and load availability compared to other grounding methods. because ground faults are 100 times more common than any other type of fault [8][9], having such a vulnerable design may not be the best choice for mission critical applications. figure 3. solidly grounded system. a. By taking these factors into consideration, electrical professionals can successfully implement a corner grounded delta diagram and enhance the reliability of the electrical system. video: 4 of 7 grounded versus ungrounded system, nec 2014 – [100], (35min:35sec). 2014 2 of 7 electric shock (12min:14sec) 2014 3 of 7 preventing electric shock (3min:59sec) 2014 4 of 7 grounded versus ungrounded systems (35min:35sec) 2014 5 of 7 system and equipment grounding (13min:48sec). Grounding is the very foundation of a building or structure’s electrical system.
What Is The Difference Between A Grounded And An Ungrounded Electrical 2014 2 of 7 electric shock (12min:14sec) 2014 3 of 7 preventing electric shock (3min:59sec) 2014 4 of 7 grounded versus ungrounded systems (35min:35sec) 2014 5 of 7 system and equipment grounding (13min:48sec). Grounding is the very foundation of a building or structure’s electrical system.

Comments are closed.