7 5 Deflection By Moment Area Method Engineering Libretexts

7 5 Deflection By Moment Area Method Engineering Libr Vrog This page titled 7.5: deflection by moment area method is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by rené alderliesten (tu delft open) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. 7.4 using the moment area method, determine the deflection at point a of the cantilever beam shown in figure p7.11 through figure p7.12. fig. p7.11. cantilever beam. fig. p7.12. cantilever beam. 7.5 using the moment area method, determine the slope at point a and the slope at the midpoint c of the beams shown in figure p7.13 and figure p7.14.
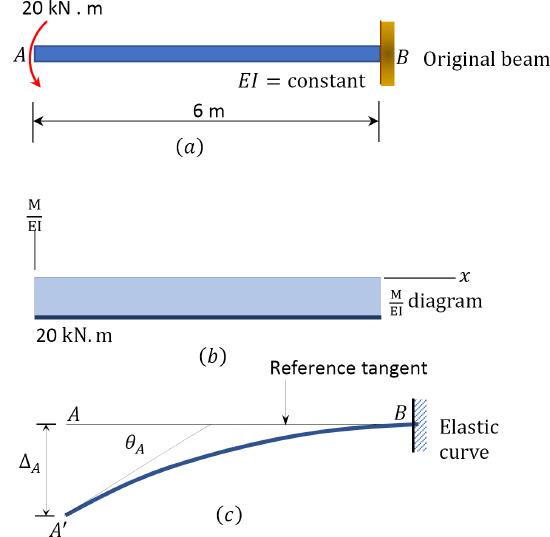
7 5 Deflection By Moment Area Method Engineering Libr Vrog 7.5: deflection by moment area method 7.6: deflection by the conjugate beam method this page titled 7: deflection of beams geometric methods is shared under a cc by nc sa 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by rené alderliesten ( tu delft open ) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts. This structural engineering video derives the moment area method, which is a quicker method to calculate the maximum deflection and slope in a beam.post your. The moment area method is based on two theorems, also called ' moment area theorems ' or ' mohr's theorems '. the first one correlates the slope change between any two points of the beam, while the second one is related with the deflection at a point of the beam. the two theorems will be presented after the following schematic, that will be. Maximum deflection to find the maximum deflection we first need to find the location at which this occurs. we know from beam theory that: d dx θ δ= hence, from basic calculus, the maximum deflection occurs at a rotation, 0θ= : to find where the rotation is zero: 1. calculate a rotation at some point, say support a, using mohr ii say; 2.

Comments are closed.