A P Lab Chapter 13 Anatomy Of Muscular System Muscles Of Thorax

A P Lab Chapter 13 Anatomy Of Muscular System Muscles Of Thorax Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like thorax and shoulder superficial, pectoralis major, pectoralis minor and more. A&p lab chapter 13: anatomy of muscular system: muscles of shoulder and thorax (movements of humerus) q chat; get a hint. muscles of the shoulder and thorax.
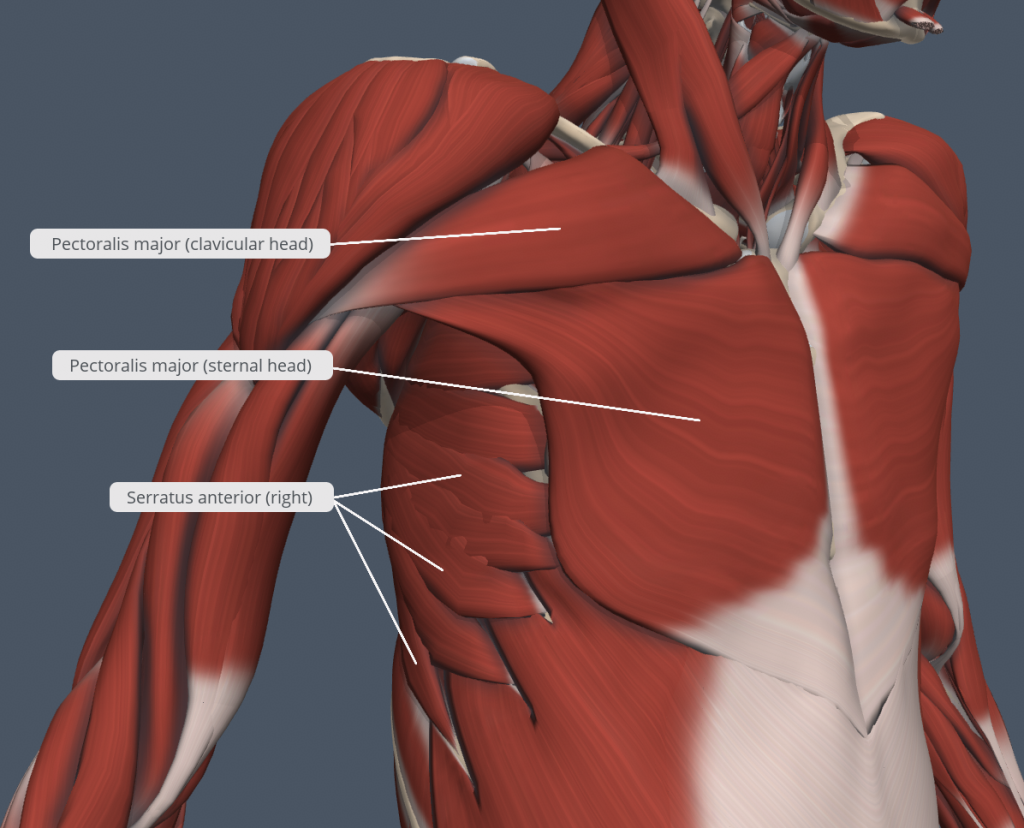
Thorax Muscles Anatomy What is highlighted? layer 4. upper: quadratus lumborum muscle, unilateral lateral flexion of trunk, bilateral extension of trunk, on ilium crest. lower: iliacus muscle, flexion of thigh, ilium fossa, sacrum pelvic surface of ala. right: psoas major muscle, flexion of high, lateral rotation of thigh, lateral flexion of trunk. Muscles of the thorax. the muscles of the thorax include both the diaphragm as well as the muscles of the thoracic cage. the diaphragm can be located below the lungs and consists of a sheet of skeletal muscle which displays a double domed structure. the diaphragm is important as it separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and. Figure 13.7. overview of the muscular system. on the anterior and posterior views of the muscular system above, superficial muscles (those at the surface) are shown on the right side of the body while deep muscles (those underneath the superficial muscles) are shown on the left half of the body. Thoracic muscle. the transversus thoracic muscle is a thin muscle consisting of four to five slips arising from the lower sternum and xiphoid and passing superolaterally to the second to sixth costal cartilage [1]. discover the intricate muscle structure of the thoracic region, their origins, insertions, and functions.

Muscle System Of Human Thorax Royalty Free Vector Image Figure 13.7. overview of the muscular system. on the anterior and posterior views of the muscular system above, superficial muscles (those at the surface) are shown on the right side of the body while deep muscles (those underneath the superficial muscles) are shown on the left half of the body. Thoracic muscle. the transversus thoracic muscle is a thin muscle consisting of four to five slips arising from the lower sternum and xiphoid and passing superolaterally to the second to sixth costal cartilage [1]. discover the intricate muscle structure of the thoracic region, their origins, insertions, and functions. A&p 13: the peripheral nervous system & reflex activity; a&p 14: the autonomic nervous system; a&p 15: the special senses; organic 8: nucleophilic substitution; a&pii lab 1: the endocrine system; a&p 16: the endocrine system; organic 11: arenes & aromaticity; a&pii lab 2: blood histology; a&pii: lab 3: the lymphatic system; a&p 20: the. Muscles of the thorax. the muscles of the chest serve to facilitate breathing by changing the size of the thoracic cavity . when you inhale, your chest rises because the cavity expands. alternately, when you exhale, your chest falls because the thoracic cavity decreases in size.

Axial Muscles Of The Abdominal Wall And Thorax Anatomy And Physiology I A&p 13: the peripheral nervous system & reflex activity; a&p 14: the autonomic nervous system; a&p 15: the special senses; organic 8: nucleophilic substitution; a&pii lab 1: the endocrine system; a&p 16: the endocrine system; organic 11: arenes & aromaticity; a&pii lab 2: blood histology; a&pii: lab 3: the lymphatic system; a&p 20: the. Muscles of the thorax. the muscles of the chest serve to facilitate breathing by changing the size of the thoracic cavity . when you inhale, your chest rises because the cavity expands. alternately, when you exhale, your chest falls because the thoracic cavity decreases in size.

Comments are closed.