A1 2 Climate Smart Agriculture Climate Smart Agricultur
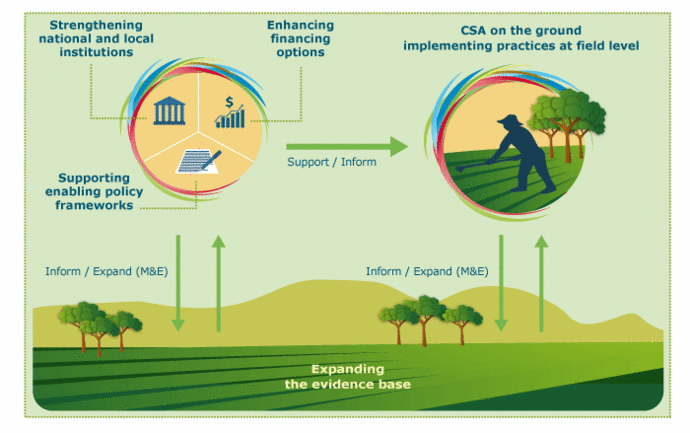
A1 2 Climate Smart Agriculture Climate Smart Agricultur Designing a national climate smart agriculture approach requires the coordination of activities of a wide range of stakeholders. this clearly includes the private sector, as it will be individual agricultural producers, both large scale and small scale, who will need to adopt climate smart agriculture practices, as will other enterprises involved in the food value chain. A1 overview. a1 1 sustainability, food security and climate change: three intertwined challenges. a1 2 climate smart agriculture. a1 3 climate smart agriculture implementation in agricultural production systems and food systems. a1 4 enabling environment for climate smart agriculture: policies, institutions and finances.
Climate Smart Agriculture Bferst Bferst It will take long term coordinated effort by all stakeholders to make the transition to climate smart agriculture. since fao introduced the concept of climate smart agriculture at the 2010 hague conference on agriculture, food security and climate change, there has been growing support at international and national levels for this approach. Introduction. this section introduces a range of climate smart agriculture (csa) practices and technologies within seven entry points for csa; soil management, crop management, water management, livestock management, forestry, fisheries and aquaculture, and energy management. practices are understood broadly as ways of doing things, for example. Introduction. climate smart agriculture (csa) may be defined as an approach for transforming and reorienting agricultural development under the new realities of climate change (lipper et al. 2014). 1 the most commonly used definition is provided by the food and agricultural organisation of the united nations ( fao ), which defines csa as. Source: ccafs big facts: climate impact on production. the relationship between agriculture and climate change is a two way street: agriculture is not only affected by climate change but has a significant effect on it in return. globally, agriculture, land use change and forestry are responsible for 19 29% of greenhouse gas (ghg) emissions.

Why We Must Scale Up Climate Smart Agriculture To Feed The World Introduction. climate smart agriculture (csa) may be defined as an approach for transforming and reorienting agricultural development under the new realities of climate change (lipper et al. 2014). 1 the most commonly used definition is provided by the food and agricultural organisation of the united nations ( fao ), which defines csa as. Source: ccafs big facts: climate impact on production. the relationship between agriculture and climate change is a two way street: agriculture is not only affected by climate change but has a significant effect on it in return. globally, agriculture, land use change and forestry are responsible for 19 29% of greenhouse gas (ghg) emissions. This course analyses climate change impacts on agriculture, food security and food systems and provides an overview of the main climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies in agriculture. it also introduces the climate smart agriculture (csa)approach and describes the 5 step process to implement it. this course addresses the subject matter from a technical perspective, but is written. The world bank has significantly scaled up its engagement and investment in climate smart agriculture (csa). in its climate change action plan (2021 2025), the world bank has identified agriculture, food, water and land as one of the five key transitions needed to tackle the paris agreement. since the adoption of the paris agreement, the world.

Climate Smart Agriculture Building Resilience To Climate Change This course analyses climate change impacts on agriculture, food security and food systems and provides an overview of the main climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies in agriculture. it also introduces the climate smart agriculture (csa)approach and describes the 5 step process to implement it. this course addresses the subject matter from a technical perspective, but is written. The world bank has significantly scaled up its engagement and investment in climate smart agriculture (csa). in its climate change action plan (2021 2025), the world bank has identified agriculture, food, water and land as one of the five key transitions needed to tackle the paris agreement. since the adoption of the paris agreement, the world.

Comments are closed.