Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Due To Endometrial Hyperplasia May Risk Factor Ka Ba
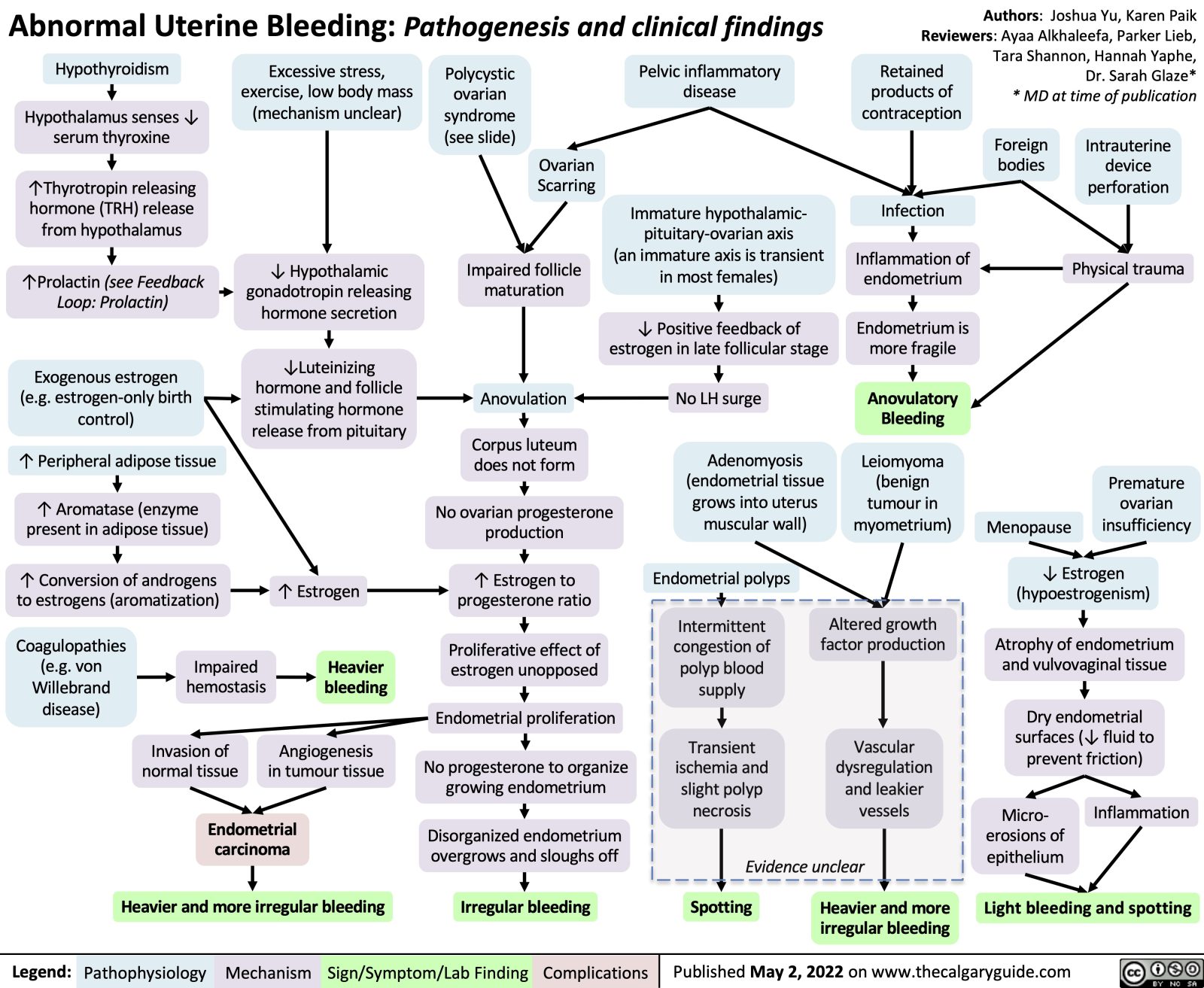
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Aub Pathogenesis And Clinical Findings Endometrial hyperplasia is a thickening of the lining of the uterus due to a hormonal imbalance. endometrial hyperplasia may lead to various symptoms, such as heavy menstrual periods, spotting, and post menopausal bleeding. while risk factors vary, some conditions that cause too much of the hormone estrogen can lead to endometrial hyperplasia. The most common causes of such bleeding are uterine fibroids, uterine adenomyosis, or endometrial polyps. fibroids are benign masses in the muscle layer of the uterus (myometrium), while adenomyosis is a condition in which the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows into the myometrium. endometrial polyps are fleshy (usually benign) growths of.

Investigating Abnormal Uterine Bleeding In Reproductive Aged Women Abnormal uterine bleeding (aub) in patients of reproductive age is a bleeding pattern that is not consistent with normal menstrual cycle parameters (frequency, regularity, duration, and volume). the palm coein system classifies causes of aub as structural (polyp, adenomyosis, leiomyoma [fibroid], or malignancy or hyperplasia) or nonstructural. Overview. endometrial hyperplasia is a precancerous condition in which there is an irregular thickening of the uterine lining. this may cause uncomfortable symptoms for women, including heavy menstrual periods, postmenopausal bleeding, and anemia due to the excess bleeding. endometrial hyperplasia is most common among women in their 50s and 60s. Abnormal uterine bleeding. abnormal uterine bleeding is bleeding between monthly periods, prolonged bleeding or an extremely heavy period. possible causes include fibroids, polyps, hormone changes and — in rare cases — cancer. contents overview symptoms and causes diagnosis and tests management and treatment prevention outlook prognosis. Abnormal uterine bleeding (aub) is a common condition that leads to increased health care costs and decreased quality of life. a systematic approach to aub evaluation can simplify management and enhance women’s well being. abnormal uterine bleeding describes any variation from normal bleeding patterns in nonpregnant, reproductive aged women beyond menarche lasting for at least 6 months.

Management Of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding And The Pathology Of Abnormal uterine bleeding. abnormal uterine bleeding is bleeding between monthly periods, prolonged bleeding or an extremely heavy period. possible causes include fibroids, polyps, hormone changes and — in rare cases — cancer. contents overview symptoms and causes diagnosis and tests management and treatment prevention outlook prognosis. Abnormal uterine bleeding (aub) is a common condition that leads to increased health care costs and decreased quality of life. a systematic approach to aub evaluation can simplify management and enhance women’s well being. abnormal uterine bleeding describes any variation from normal bleeding patterns in nonpregnant, reproductive aged women beyond menarche lasting for at least 6 months. Fig. 2. uterine evaluation. the uterine evaluation is, in part, guided by the medial history and other elements of the clinical situation, such as patient age, presence of an apparent chronic ovulatory disorder, or presence of other risk factors for endometrial hyperplasia or malignancy. Endometrial hyperplasia is more likely to occur in women with risk factors, including. age older than 35. never having been pregnant. older age at menopause. early age when menstruation started. history of certain conditions, such as diabetes mellitus, pcos, gallbladder disease, or thyroid disease. obesity. cigarette smoking.

Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Aub Endometriosis Free Sketchy Medical Fig. 2. uterine evaluation. the uterine evaluation is, in part, guided by the medial history and other elements of the clinical situation, such as patient age, presence of an apparent chronic ovulatory disorder, or presence of other risk factors for endometrial hyperplasia or malignancy. Endometrial hyperplasia is more likely to occur in women with risk factors, including. age older than 35. never having been pregnant. older age at menopause. early age when menstruation started. history of certain conditions, such as diabetes mellitus, pcos, gallbladder disease, or thyroid disease. obesity. cigarette smoking.

Pdf Risk Factors For Endometrial Hyperplasia And Cancer In Patients

Comments are closed.