Acyanotic Heart Disease Pdf Heart Congenital Heart Defect

Acyanotic Congenital Heart Defects Pathology Review Osmosis Management of congenital heart disease: state of the art. Acyanotic heart disease: causes, symptoms and treatment.

Acyanotic Heart Disease Pdf Heart Congenital Heart Defect The spectrum of congenital heart disease (chd) seen in the adult varies widely. malformations range from mild anomalies requiring no intervention to extremely complex pathologies characterized by the presence of multiple coexistent defects. echocardiography represents the primary noninvasive imaging modality in the assessment of these lesions. In the first paper [ 1 ], management of acyanotic congenital heart defects (chds) was discussed. in this paper, discussion of most common cyanotic chds will be included. cyanotic chds usually have multiple defects of the heart that result in right to left shunt. obstruction to pulmonary blood flow (for example tetralogy of fallot), complete. Acyanotic congenital heart diseases or left to right shunting lesions are the most common form of congenital heart disease. although most resolve spontaneously, many will remain hemodynamically significant, particularly in the premature infant. understanding the difference in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management between the term and preterm infant is imperative to minimize the risk of. This article discusses the four common congenital heart lesions associated with communications between the systemic circulation and the pulmonary circulation, as well as valvular pulmonic stenosis with intact ventricular septum. the incidence and description of each specific anatomical malformation is presented. the clinical findings on physical examination, electrocardiography, chest.
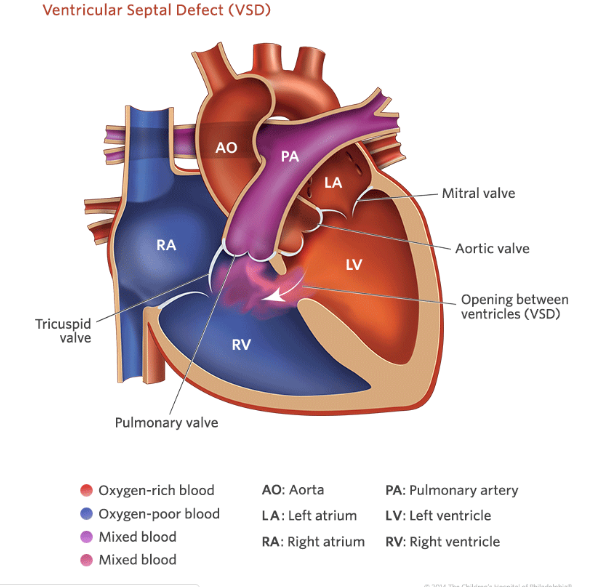
Ventricular Septal Defect Acyanotic congenital heart diseases or left to right shunting lesions are the most common form of congenital heart disease. although most resolve spontaneously, many will remain hemodynamically significant, particularly in the premature infant. understanding the difference in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management between the term and preterm infant is imperative to minimize the risk of. This article discusses the four common congenital heart lesions associated with communications between the systemic circulation and the pulmonary circulation, as well as valvular pulmonic stenosis with intact ventricular septum. the incidence and description of each specific anatomical malformation is presented. the clinical findings on physical examination, electrocardiography, chest. Congenital heart defects (chd) are the most common congenital anomaly with an incidence of around 8e10 per 1000 live born infants. up to a third of all the chds are of a critical type. a critical chd is fatal within 28 days of birth unless there is cardiac surgery or catheter inter vention. advances in diagnosis, pre operative intensive care. Abstract and figures. since the description of surgery for patent ductus arteriosus in late 1930s, an innumerable number of advances have taken place in the management of congenital heart defects.

Congenital Acyanotic Heart Disease Pdf Congenital Heart ођ Congenital heart defects (chd) are the most common congenital anomaly with an incidence of around 8e10 per 1000 live born infants. up to a third of all the chds are of a critical type. a critical chd is fatal within 28 days of birth unless there is cardiac surgery or catheter inter vention. advances in diagnosis, pre operative intensive care. Abstract and figures. since the description of surgery for patent ductus arteriosus in late 1930s, an innumerable number of advances have taken place in the management of congenital heart defects.

Congenital Heart Disease Acyanotic Department Of Cardiovascular

Comments are closed.