Aerodynamics The Theory Of Lift Owlcation
The Importance Of Aerodynamics Research For Aviation The theory states that the air molecules have to reach the trailing edge at the same time, and in order to do that the molecules going over the top of the wing must travel faster than the molecules moving under the wing. because the upper flow is faster, the pressure is lower, as known by bernoulli's equation, and thus the difference in. Drag: drag is the force generated by air resistance. the air blows in the opposite direction of a fast moving airplane on the runway. it produces drag, which is the polar opposite of propulsion. lift: it is the force that elevates the airplane. the wing's airfoil form creates a pressure difference.

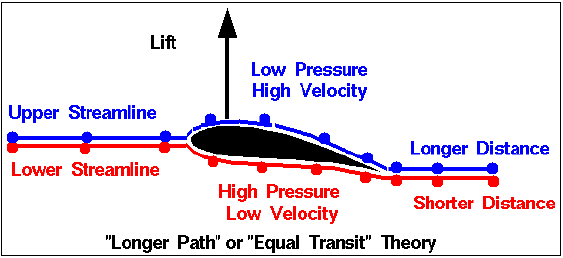
Aerodynamics Basics Know The Fundamentals Engineeringclicks These concepts are depicted in the figure below. let us review all of these concepts to understand the core theory of airfoil aerodynamics. figure: basic components of the lift model relevant to airfoil theory. background theory and concepts airfoil. airfoils are the cross sections of a wing or lifting surface (i.e., propellers and fins). these. The most popular incorrect theory of lift arises from a mis application of bernoulli’s equation. the theory is known as the “equal transit time” or “longer path” theory which states that wings are designed with the upper surface longer than the lower surface, to generate higher velocities on the upper surface because the molecules of. Lift by pressure differential is based on the theory of daniel bernoulli (bernoulli’s theorem)—the faster a fluid flows (including air), the lower will be the pressure surrounding it; given the difference of the camber of the upper and lower surfaces, the air passing over the foil has greater distance to travel than the air passing under. Bernoulli's theorem: explains lift as a function of the high and low air velocities generated on upper and lower surfaces due to the airfoil profile. it also relies on the theory of equal transit, which s tates that due to the upper and lower surfaces of an aerofoil having different lengths, air must travel faster over the longer surface in order to meet airflow flowing from the shorter.

Aerodynamics The Theory Of Lift Owlcation Lift by pressure differential is based on the theory of daniel bernoulli (bernoulli’s theorem)—the faster a fluid flows (including air), the lower will be the pressure surrounding it; given the difference of the camber of the upper and lower surfaces, the air passing over the foil has greater distance to travel than the air passing under. Bernoulli's theorem: explains lift as a function of the high and low air velocities generated on upper and lower surfaces due to the airfoil profile. it also relies on the theory of equal transit, which s tates that due to the upper and lower surfaces of an aerofoil having different lengths, air must travel faster over the longer surface in order to meet airflow flowing from the shorter. No motion, no lift. lift is the force that directly opposes the weight of an airplane and holds the airplane in the air. lift is generated by every part of the airplane, but most of the lift on a normal airliner is generated by the wings. lift is a mechanical aerodynamic force produced by the motion of the airplane through the air. Theory of flight. theory of flight. flight is a phenomenon that has long been a part of the natural world. birds fly not only by flapping their wings, but by gliding with their wings outstretched for long distances. smoke, which is composed of tiny particles, can rise thousands of feet into the air. both these types of flight are possible.
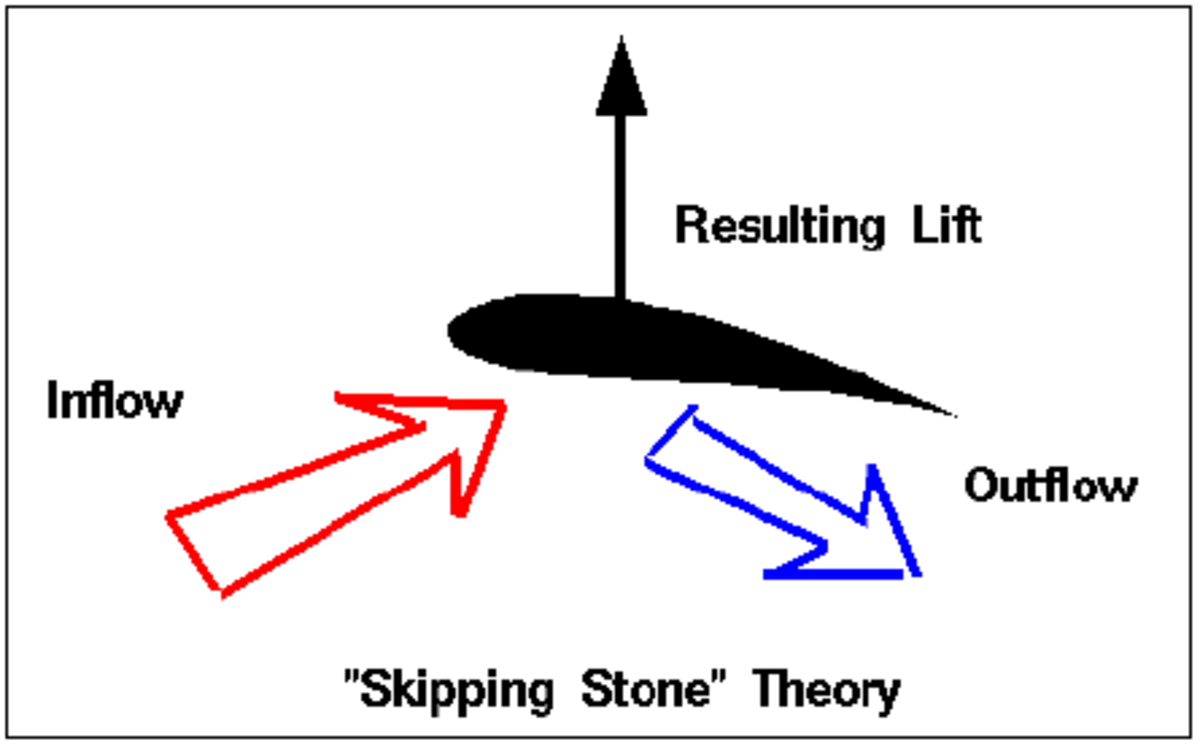
Aerodynamics The Theory Of Lift Owlcation No motion, no lift. lift is the force that directly opposes the weight of an airplane and holds the airplane in the air. lift is generated by every part of the airplane, but most of the lift on a normal airliner is generated by the wings. lift is a mechanical aerodynamic force produced by the motion of the airplane through the air. Theory of flight. theory of flight. flight is a phenomenon that has long been a part of the natural world. birds fly not only by flapping their wings, but by gliding with their wings outstretched for long distances. smoke, which is composed of tiny particles, can rise thousands of feet into the air. both these types of flight are possible.
Aerodynamics The Theory Of Lift Owlcation

Comments are closed.