An Overview Of How Human Memory Works

An Overview Of How Human Memory Works How memory works. memory is a continually unfolding process. initial details of an experience take shape in memory; the brain’s representation of that information then changes over time. with. There are three main processes that characterize how memory works. these processes are encoding, storage, and retrieval (or recall). encoding . encoding refers to the process through which information is learned. that is, how information is taken in, understood, and altered to better support storage (which you will look at in section 3.1.2).
An Overview Of How Human Memory Works The process of memory begins with encoding, then proceeds to storage and, eventually, retrieval. on the next page, you'll learn how encoding works and the brain activity involved in retrieving a memory. richard c. mohs "how human memory works" 1 january 1970. human memory is a complex, brain wide process that is essential to who we are. How psychologists define memory. memory refers to the psychological processes of acquiring, storing, retaining, and later retrieving information. memory involves three major processes: encoding, storage, and retrieval. human memory involves the ability to both preserve and recover information. however, this is not a flawless process. A memory engram, or memory trace, is a term for the set of changes in the brain on which a memory is based. these are thought to include changes at the level of the synapses that connect brain. Memory is the term given to the structures and processes involved in the storage and subsequent retrieval of information. memory is essential to all our lives. without a memory of the past, we cannot operate in the present or think about the future. we would not be able to remember what we did yesterday, what we have done today, or what we plan.
An Overview Of Human Memory And How It Works A memory engram, or memory trace, is a term for the set of changes in the brain on which a memory is based. these are thought to include changes at the level of the synapses that connect brain. Memory is the term given to the structures and processes involved in the storage and subsequent retrieval of information. memory is essential to all our lives. without a memory of the past, we cannot operate in the present or think about the future. we would not be able to remember what we did yesterday, what we have done today, or what we plan. Dementia (di men sha) : a loss of brain function that can be caused by a variety of disorders affecting the brain. symptoms include forgetfulness, impaired thinking and judgment, personality changes, agitation and loss of emotional control. alzheimer’s disease, huntington’s disease and inadequate blood flow to the brain can all cause dementia. Memories. humans retain different types of memories for different lengths of time. short term memories last seconds to hours, while long term memories last for years. we also have a working memory.

Human Memory A Basic Overview Of Human Memory Its Primary Functions Dementia (di men sha) : a loss of brain function that can be caused by a variety of disorders affecting the brain. symptoms include forgetfulness, impaired thinking and judgment, personality changes, agitation and loss of emotional control. alzheimer’s disease, huntington’s disease and inadequate blood flow to the brain can all cause dementia. Memories. humans retain different types of memories for different lengths of time. short term memories last seconds to hours, while long term memories last for years. we also have a working memory.
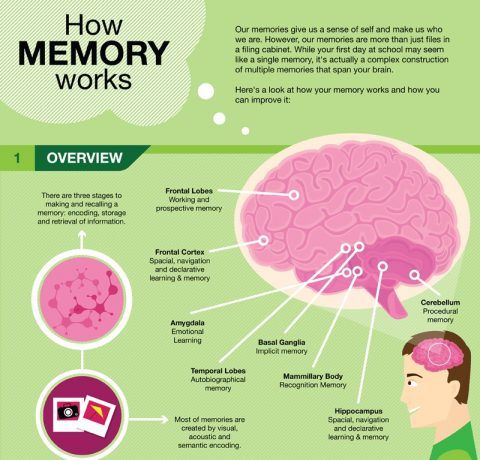
Memory Infographic Archives E Learning Infographics

Comments are closed.