Anatomy Lower Leg Muscles Medical Anatomy Muscle Anatomy о
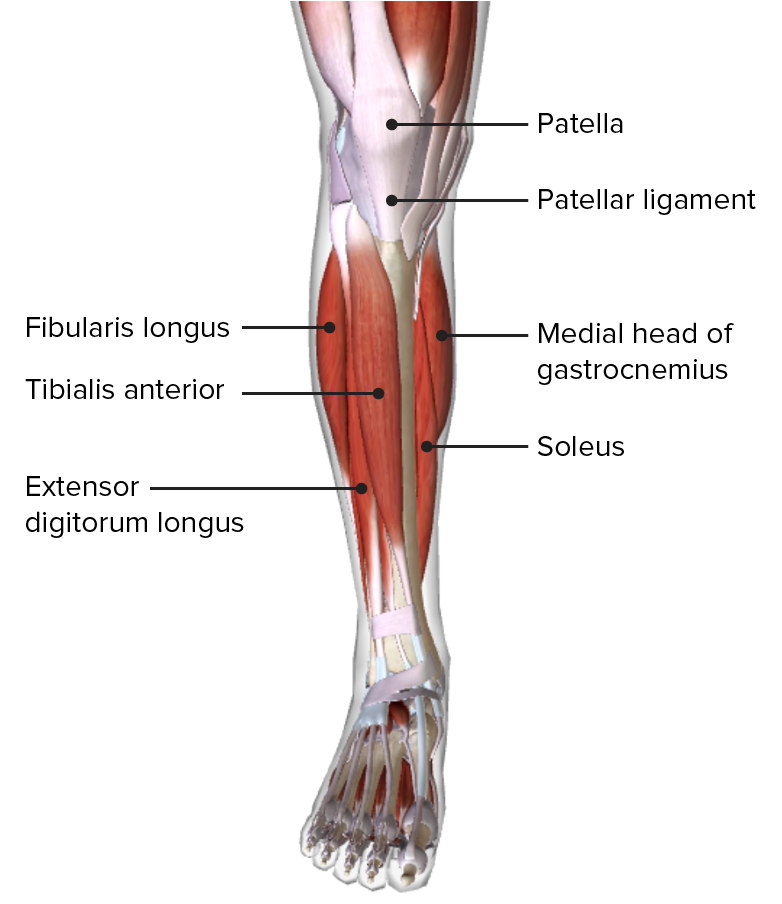
Diagram Of The Lower Leg Introduction. the leg is defined anatomically as the portion of the lower limb from the knee joint to the ankle joint. the muscles of the leg are divided into three compartments: the anterior compartment, the posterior compartment and the lateral compartment. in total, there are 13 separate muscles across these three compartments. The medical information on this site is provided as an information resource only, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. this information is intended for medical education, and does not create any doctor patient relationship, and should not be used as a substitute for professional diagnosis and treatment.

Lower Leg Muscle Diagram Labeled Anatomically, the leg is defined as the region of the lower limb below the knee. it consists of a posterior, anterior and lateral compartment. in accordance, the muscles of the leg are organized into three groups: anterior (dorsiflexor) group, which contains the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius and extensor. Leg muscles. your legs include many strong muscles. they allow you to do big and small movements. they also support your weight and stabilize your body so you can stand up straight. the muscles in your upper leg include your quadriceps and hamstrings. your calf muscles work with other muscles of the lower leg to help you move your feet. Anatomy of the lower leg. your muscles in the lower leg are supported by two very strong, long bones: the fibula and the tibia (shinbone). the tibia is stronger and more prominent than the fibula. it is located toward the middle of the lower leg. the fibula, or calf bone, is smaller and located on the lower leg's outside. It has an upper extremity, a shaft, and a lower extremity, all of which are full of various structural landmarks. several muscles attach to, and act on, the femur. they take full advantage of the mobility provided by two joints. the muscles of the thigh can be divided into three groups: anterior, medial, and posterior.
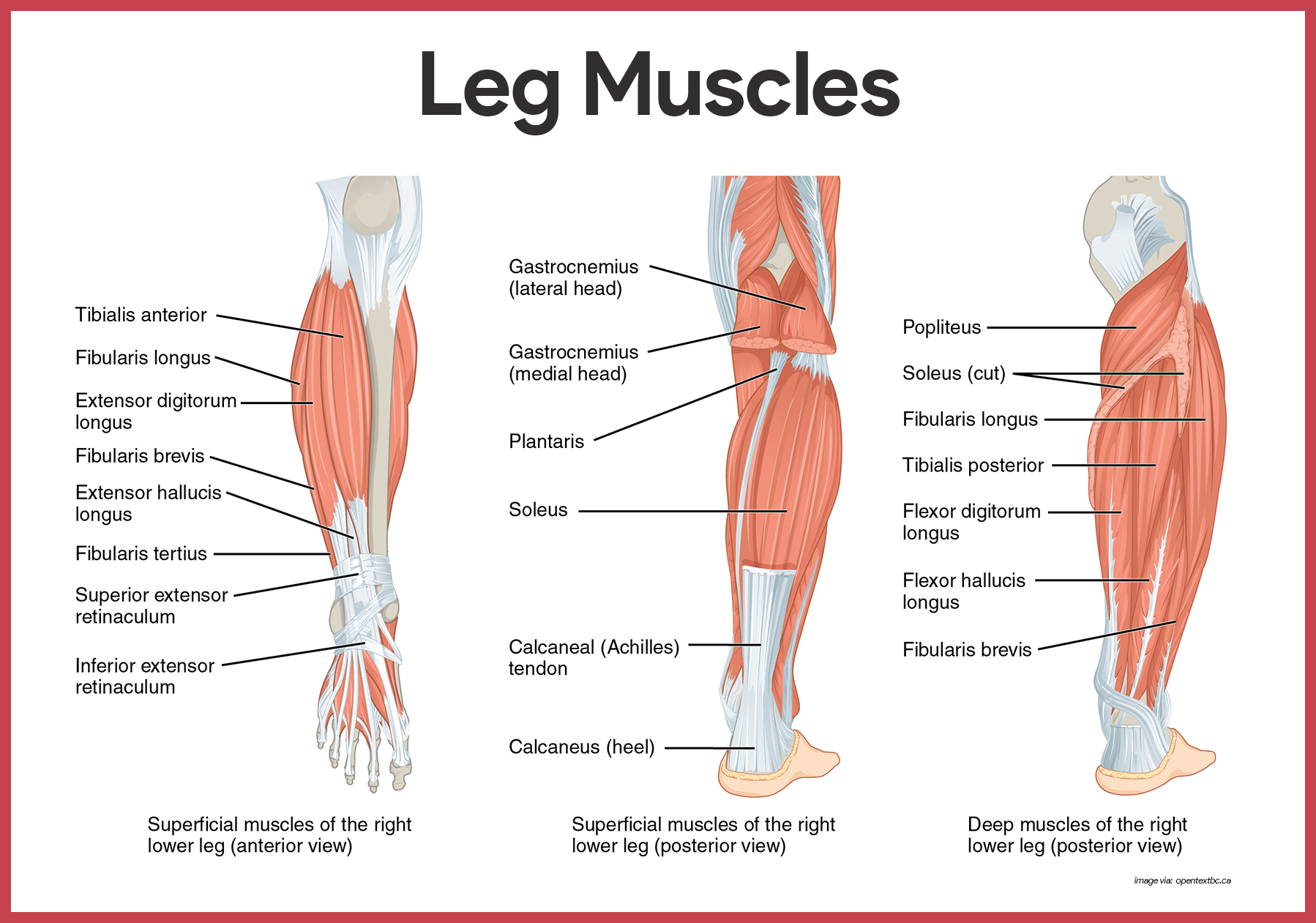
Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs Anatomy of the lower leg. your muscles in the lower leg are supported by two very strong, long bones: the fibula and the tibia (shinbone). the tibia is stronger and more prominent than the fibula. it is located toward the middle of the lower leg. the fibula, or calf bone, is smaller and located on the lower leg's outside. It has an upper extremity, a shaft, and a lower extremity, all of which are full of various structural landmarks. several muscles attach to, and act on, the femur. they take full advantage of the mobility provided by two joints. the muscles of the thigh can be divided into three groups: anterior, medial, and posterior. Gastrocnemius (calf muscle): one of the large muscles of the leg, it connects to the heel. it flexes and extends the foot, ankle, and knee. soleus: this muscle extends from the back of the knee to. Anterior tibial a. one of the muscles involved in anterior compartment syndrome. fibularis (peroneus) brevis. lower one third of the lateral surface of the fibula. tuberosity of the base of the 5th metatarsal. extends (plantar flexes) and everts the foot. superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve. fibular (peroneal) a.

Muscles Of Lower Leg Digman Fitness Gastrocnemius (calf muscle): one of the large muscles of the leg, it connects to the heel. it flexes and extends the foot, ankle, and knee. soleus: this muscle extends from the back of the knee to. Anterior tibial a. one of the muscles involved in anterior compartment syndrome. fibularis (peroneus) brevis. lower one third of the lateral surface of the fibula. tuberosity of the base of the 5th metatarsal. extends (plantar flexes) and everts the foot. superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve. fibular (peroneal) a.

Comments are closed.