Anatomy Of Back Of Head

Lateral View Of The Brain Diagram Labeled The occipital bone is the bone at the back of the skull that protects the brain and connects to the spine. learn about its parts, function, and conditions that affect it. The occipital bone. the occipital bone is a flat, unpaired bone that forms a major part of the posterior wall and base of the skull. it is a complex structure that protects the cerebellum and occipital lobes of the cerebrum and provides attachment to several muscles and ligaments. in this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the occipital.

The Skull в Anatomy And Physiology In addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures: muscles of mastication. facial muscles. salivary glands. arteries. nerves. in this page, we are going to focus on the head anatomy and those five less evident features and learn more about them. Learn about the eight major and eight auxiliary bones of the cranium, the skull that protects the brain. the occipital bone forms the back of the head and connects with the spine and other bones. Occipital anatomy – external surface. if you need to describe where the occipital bone is located in as few words as possible, it extends from the bottom of the skull to approximately halfway up the back of the head, forming joints with the parietal bones, temporal bones, and sphenoid bone, as well as with the first cervical vertebra. Head and neck (anterior view) the head and neck are two examples of the perfect anatomical marriage between form and function, mixed with a dash of complexity. the neck is resilient enough to sustain a five kilogram weight 24 7, yet sufficiently mobile to move it in several directions.
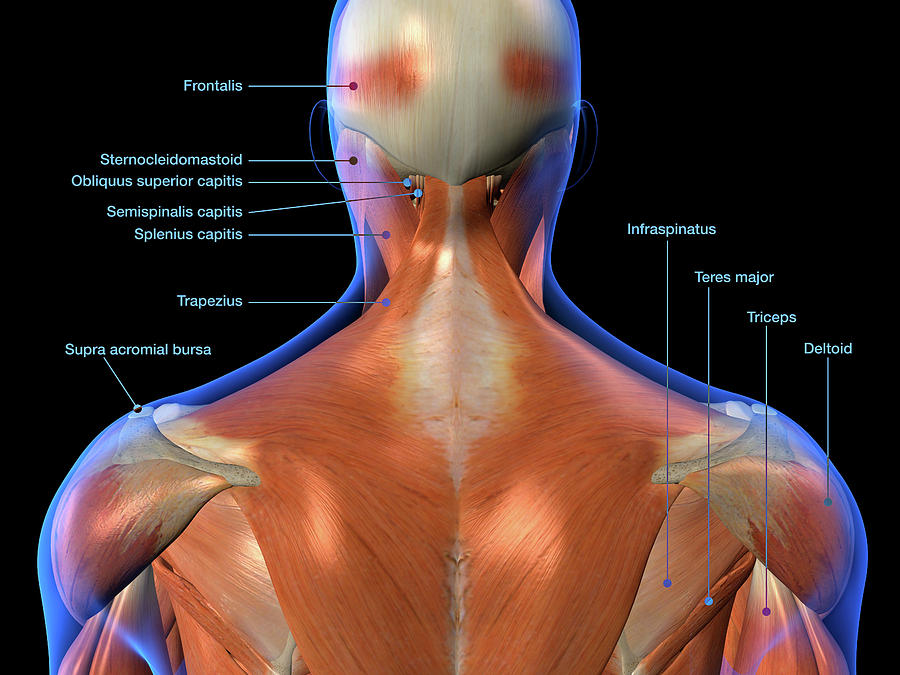
Anatomy Of Back Of Head Occipital anatomy – external surface. if you need to describe where the occipital bone is located in as few words as possible, it extends from the bottom of the skull to approximately halfway up the back of the head, forming joints with the parietal bones, temporal bones, and sphenoid bone, as well as with the first cervical vertebra. Head and neck (anterior view) the head and neck are two examples of the perfect anatomical marriage between form and function, mixed with a dash of complexity. the neck is resilient enough to sustain a five kilogram weight 24 7, yet sufficiently mobile to move it in several directions. 552. fma. 52735. anatomical terms of bone. [edit on wikidata] the occipital bone ( ˌɒkˈsɪpɪtəl ) is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). it is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. the occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. The skeletal section of the head and neck forms the top part of the axial skeleton and is made up of the skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, and cervical spine. the skull can be further subdivided into: the facial bones (14 bones: 2 zygomatic, 2 maxillary, 2 palatine, 2 nasal, 2 lacrimal, vomer, 2 inferior conchae, mandible).

The Skull Anatomy And Physiology I 552. fma. 52735. anatomical terms of bone. [edit on wikidata] the occipital bone ( ˌɒkˈsɪpɪtəl ) is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). it is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. the occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. The skeletal section of the head and neck forms the top part of the axial skeleton and is made up of the skull, hyoid bone, auditory ossicles, and cervical spine. the skull can be further subdivided into: the facial bones (14 bones: 2 zygomatic, 2 maxillary, 2 palatine, 2 nasal, 2 lacrimal, vomer, 2 inferior conchae, mandible).

Comments are closed.