Anatomy Of Cardiac Muscles Anatomy Book

Atlas Of Cardiac Anatomy Gratis Ebook вђ Cardiotext Publishing Cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. it is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle. the myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. coronary arteries supply to the cardiac muscle, and cardiac veins drain this blood. cardiomyocytes are the. The heart muscle is the myocardium or middle layer of the heart walls. the myocardium is responsible for the contractile function of the cardiac pump. composed of cardiomyocytes, the heart muscle has distinctive cellular and physiological features, allowing it to generate force to maintain adequate tissue and organ perfusion throughout the body. the heart muscle is one of the earliest.
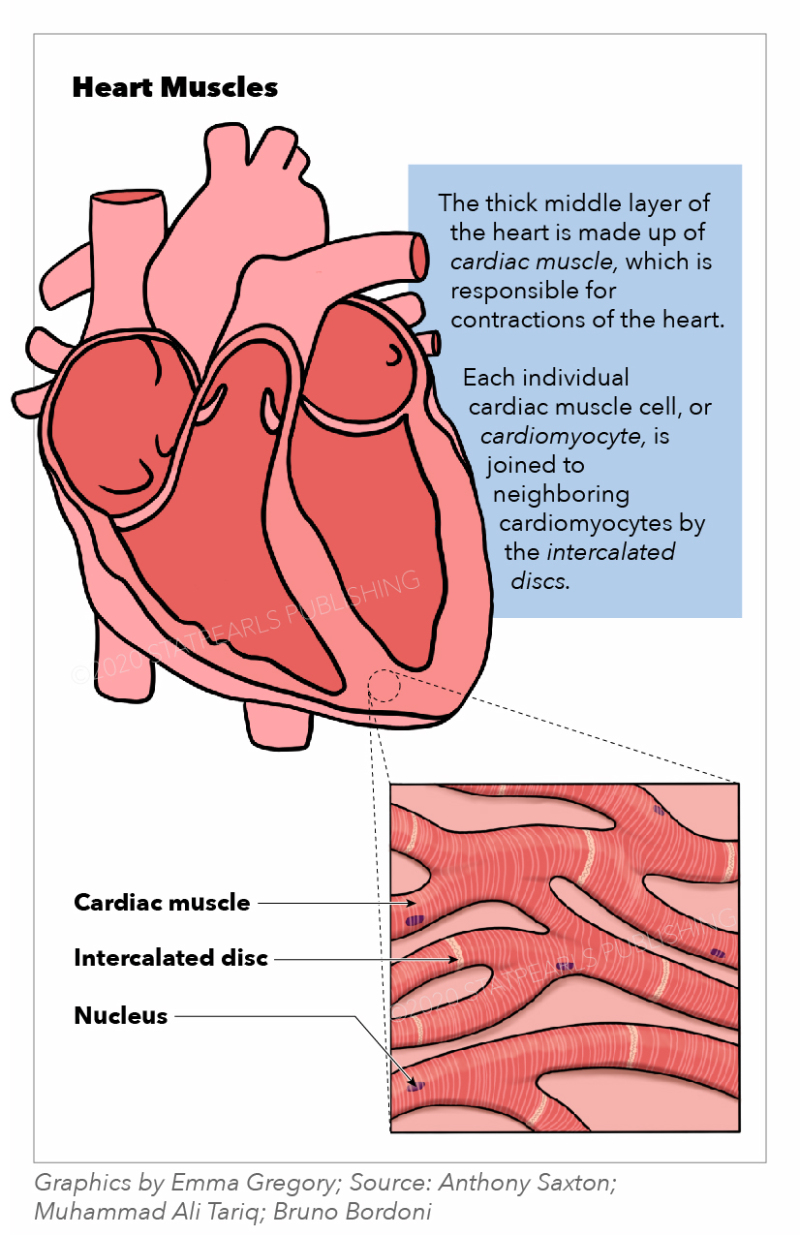
Figure Heart Muscles The Illustration Depicts The Statpearls Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle (figure 10.21). however, cardiac muscle fibers are shorter than skeletal muscle fibers and usually contain only one nucleus, which is located in the central region of the cell. 25.0 introduction. 25.1 internal and external anatomy of the kidney. 25.2 microscopic anatomy of the kidney: anatomy of the nephron. 25.3 physiology of urine formation: overview. 25.4 physiology of urine formation: glomerular filtration. 25.5 physiology of urine formation: tubular reabsorption and secretion. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle ( [link] ). The heart is a muscular organ situated in the center of the chest behind the sternum. it consists of four chambers: the two upper chambers are called the right and left atria, and the two lower chambers are called the right and left ventricles. the right atrium and ventricle together are often called the right heart, and the left atrium and left ventricle together functionally form the left.

Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity в Anatomy And Physiology Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle ( [link] ). The heart is a muscular organ situated in the center of the chest behind the sternum. it consists of four chambers: the two upper chambers are called the right and left atria, and the two lower chambers are called the right and left ventricles. the right atrium and ventricle together are often called the right heart, and the left atrium and left ventricle together functionally form the left. The walls of the ventricle are lined with trabeculae carneae, ridges of cardiac muscle covered by endocardium. in addition to these muscular ridges, a band of cardiac muscle, also covered by endocardium, known as the moderator band (see figure 19.9) reinforces the thin walls of the right ventricle and plays a crucial role in cardiac conduction. Figure 19.17 cardiac muscle (a) cardiac muscle cells have myofibrils composed of myofilaments arranged in sarcomeres, t tubules to transmit the impulse from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell, numerous mitochondria for energy, and intercalated discs that are found at the junction of different cardiac muscle cells. (b) a photomicrograph.

Anatomy Of Cardiac Muscles Anatomy Book The walls of the ventricle are lined with trabeculae carneae, ridges of cardiac muscle covered by endocardium. in addition to these muscular ridges, a band of cardiac muscle, also covered by endocardium, known as the moderator band (see figure 19.9) reinforces the thin walls of the right ventricle and plays a crucial role in cardiac conduction. Figure 19.17 cardiac muscle (a) cardiac muscle cells have myofibrils composed of myofilaments arranged in sarcomeres, t tubules to transmit the impulse from the sarcolemma to the interior of the cell, numerous mitochondria for energy, and intercalated discs that are found at the junction of different cardiac muscle cells. (b) a photomicrograph.

Comments are closed.