Anesthetic Monitoring Interpreting The Readings
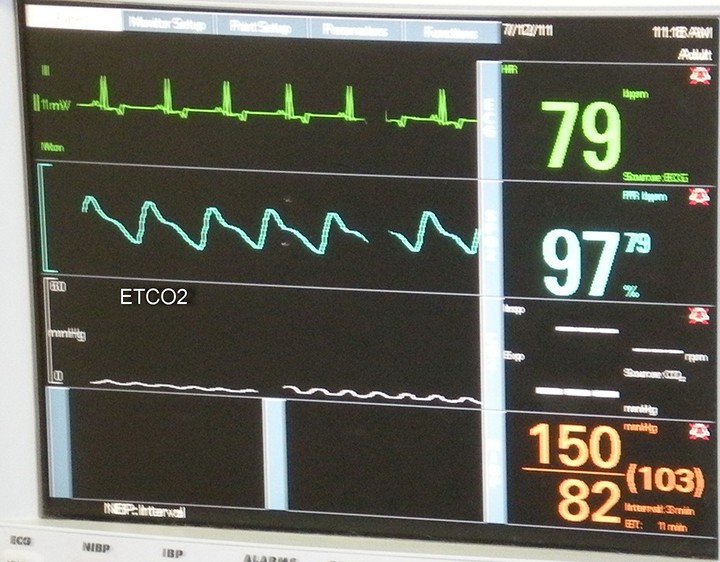
Anesthetic Monitoring Interpreting The Readings 51 Off However, a monitor cannot save a patient’s life unless the team member monitoring the patient understands the readings and can determine when the monitor is wrong. any values differing from normal parameters should be investigated to determine whether they are life threatening or merely glitches in the equipment or setup. (see table 1.). Introduction. monitoring is an essential component of’ anesthesia care. anesthesia clinicians must monitor patient physiologic variables and anesthesia equipment during all types of anesthesia, as anesthesia and surgery can cause rapid changes in vital functions. patient and equipment monitoring is used to titrate administration of anesthetic.

Anesthetic Monitoring Interpreting The Readings The word anesthesia originated from the greek term anaisthaesia, meaning “insensibility”; is used to describe the loss of sensation to the body in part or in its entirety. general anesthesia (ga) is defined as drug induced unconsciousness where cns depression is controlled but reversible. surgical anesthesia is the state plane of ga that. A “pop” may be felt and there should be no resistance to injection. y. considerations: (1) pelvic limb motor function is not blocked unless the volume of local anesthetic is large, causing cranial spread to the motor nerves of the pelvic limbs. stay at or below the 0.2 ml kg volume. The american society of anesthesiologists (asa) has developed standards for basic anesthetic monitoring, which was last updated in 2011. according to this document, an authorized anesthesia provider must remain with a patient throughout the duration of any general, regional, or monitored anesthesia care, to administer anesthesia and monitor the patient. Adequate supervision requires that an anaesthetist should be present throughout the conduct of anaesthesia or the administration of procedural sedation *.; general anaesthesia requires minimum monitoring of ecg, spo 2, nibp and capnography, which should be checked for correct function and begun before induction of anaesthesia and continue throughout anaesthesia, transfer to the post.

Comments are closed.