Aphthous Ulcer Stomatitis Vs Traumatic Ulcer

Western University Oral Ulcers Osmosis Video Library Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (ras), commonly called "canker sores," is a perplexing oral condition characterized by the recurrent development of painful aphthous ulcers on non keratinized oral mucous membranes. this condition poses a significant challenge to patients and healthcare professionals due to its uncertain etiology. Aphthous ulcers are a common and painful problem. benign aphthae tend to be small (less than 1 cm in diameter) and shallow. aphthous ulcers that occur in conjunction with symptoms of uveitis.
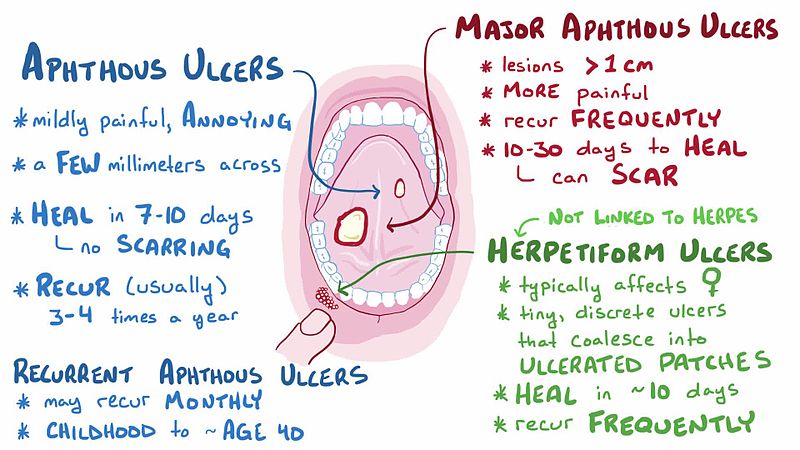
Aphthous Ulcer What To Do Aphthous ulcer stomatitis vs traumatic ulcerthis video explained how to differentiate aphthous ulcer stomatitis and traumatic ulcer clinically. Typical symptoms of minor aphthous ulcers include: a small round or oval lesion with a yellow or white center and a red border. located inside the mouth – either on or under the tongue, inside the cheeks or lips, at the base of the gums, or on the roof of your mouth. tingling in the area may be noticed a day or two before the sores appear. Introduction. recurrent aphthous stomatitis (ras) is considered as the most common oral mucosal lesion. these present as recurrent, multiple, small, or ovoid ulcers, having yellow floors and are surrounded by erythematous haloes, present first in childhood or adolescence.1 aphthous ulcers affect up to 25% of the general population, and 3 month recurrence rates are as high as 50%.1 it is more. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (ras), also known as "canker sores," is a common disease of unknown etiology that affects the oral mucosa and is characterized by the repeated development of one to many discrete, painful ulcers that usually heal within 7 to 14 days [ 1 6 ]. the lesions are typically 3 to 5 mm, round to oval ulcers with a.
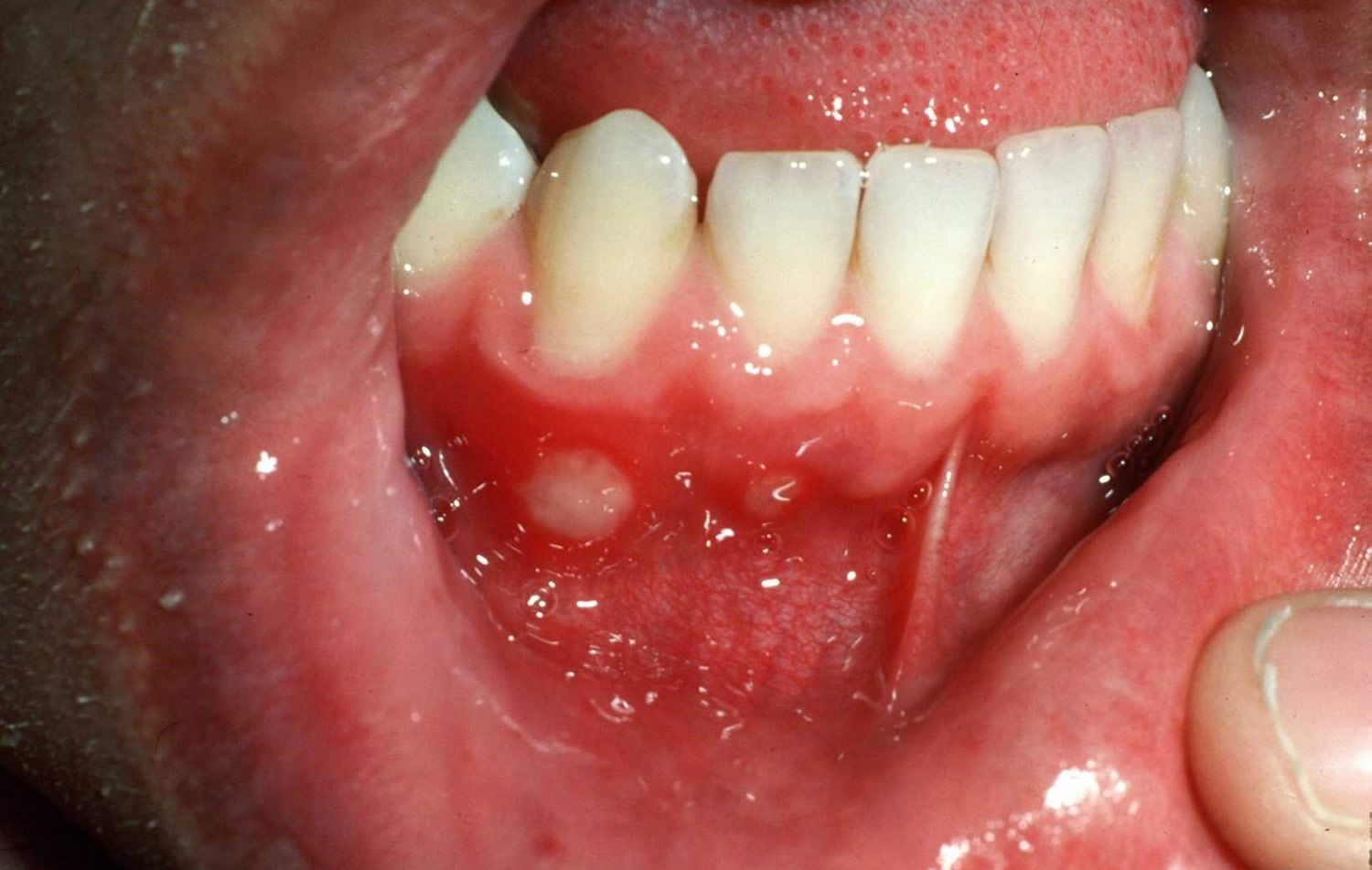
Aphthous Stomatitis Treatment Introduction. recurrent aphthous stomatitis (ras) is considered as the most common oral mucosal lesion. these present as recurrent, multiple, small, or ovoid ulcers, having yellow floors and are surrounded by erythematous haloes, present first in childhood or adolescence.1 aphthous ulcers affect up to 25% of the general population, and 3 month recurrence rates are as high as 50%.1 it is more. Recurrent aphthous stomatitis (ras), also known as "canker sores," is a common disease of unknown etiology that affects the oral mucosa and is characterized by the repeated development of one to many discrete, painful ulcers that usually heal within 7 to 14 days [ 1 6 ]. the lesions are typically 3 to 5 mm, round to oval ulcers with a. These ulcers usually occur on the lips, cheeks. tongue, palate, and pharynx. just like a minor aphthous ulcer, the sex ratio in men and women is equal. the age of onset for major aphthae is approximately between 10 19 years. the number of ulcers is usually 1 10 and the size is greater than 10 mm. Approximately 80 percent of patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis present with minor aphthous ulcers. these are 2 to 8 mm in diameter, affect nonkeratinized mucosae such as the labial and.

Comments are closed.