Approach To Non Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers
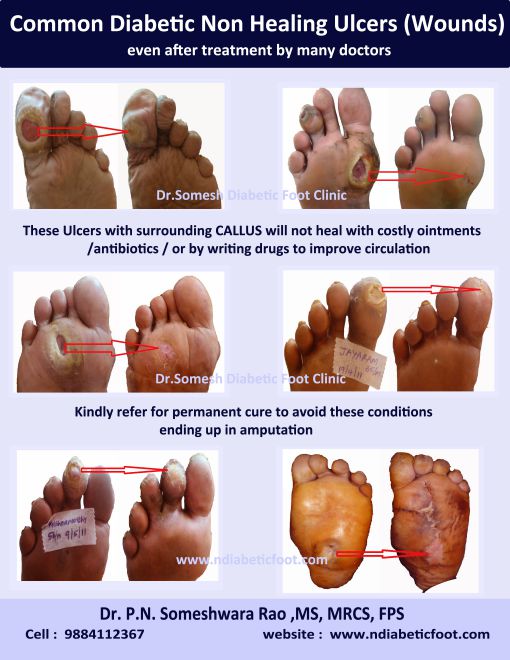
Non Healing Diabetic Ulcer Locations Podiatry Doctor Approach to non healing diabetic foot ulcers. gary m. rothenberg, dpm, cde, cws the university of michigan medical school clinical assistant professor department of internal medicine metabolism, endocrinology and diabetes division. no relevant financial relationships related to this presentation. The first step in managing diabetic foot ulcers is assessing, grading, and classifying the ulcer. classification is based upon clinical evaluation of the extent and depth of the ulcer and the presence of infection or ischemia, which determine the nature and intensity of treatment. to assess for ischemia, all patients with diabetic foot ulcers.

Osteomyelitis In Non Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers In diabetic foot clinics, there has been a paradigm shift away from a focus on ulcers in neuropathic feet and toward ulcers in neuroischemic feet, which occur more frequently. there is now good evidence to support the successful treatment of neuroischemic ulcers with sucrose octasulfate in addition to best practice standard care ( 59 ). Abstract. diabetic foot ulcers are the consequence of multiple factors including peripheral neuropathy, decreased blood supply, high plantar pressures, etc ., and pose a significant risk for morbidity, limb loss and mortality. the critical aspects of the wound healing mechanism and host physiological status in patients with diabetes necessitate. At least half of all amputations occur in people with diabetes, most commonly because of an infected diabetic foot ulcer. a thorough understanding of the causes and management of diabetic foot ulceration is essential to reducing lower extremity amputation risk. this compendium elucidates the pathways leading to foot ulcers and enumerates multiple contributory risk factors. the authors. Abstract. diabetic foot ulcers (dfus) are a serious complication of diabetes that results in significant morbidity and mortality. mortality rates associated with development of a dfu are estimated to be 5% in the first 12 months, and 5 year morality rates have been estimated at 42%. the standard practices in dfu management include surgical.
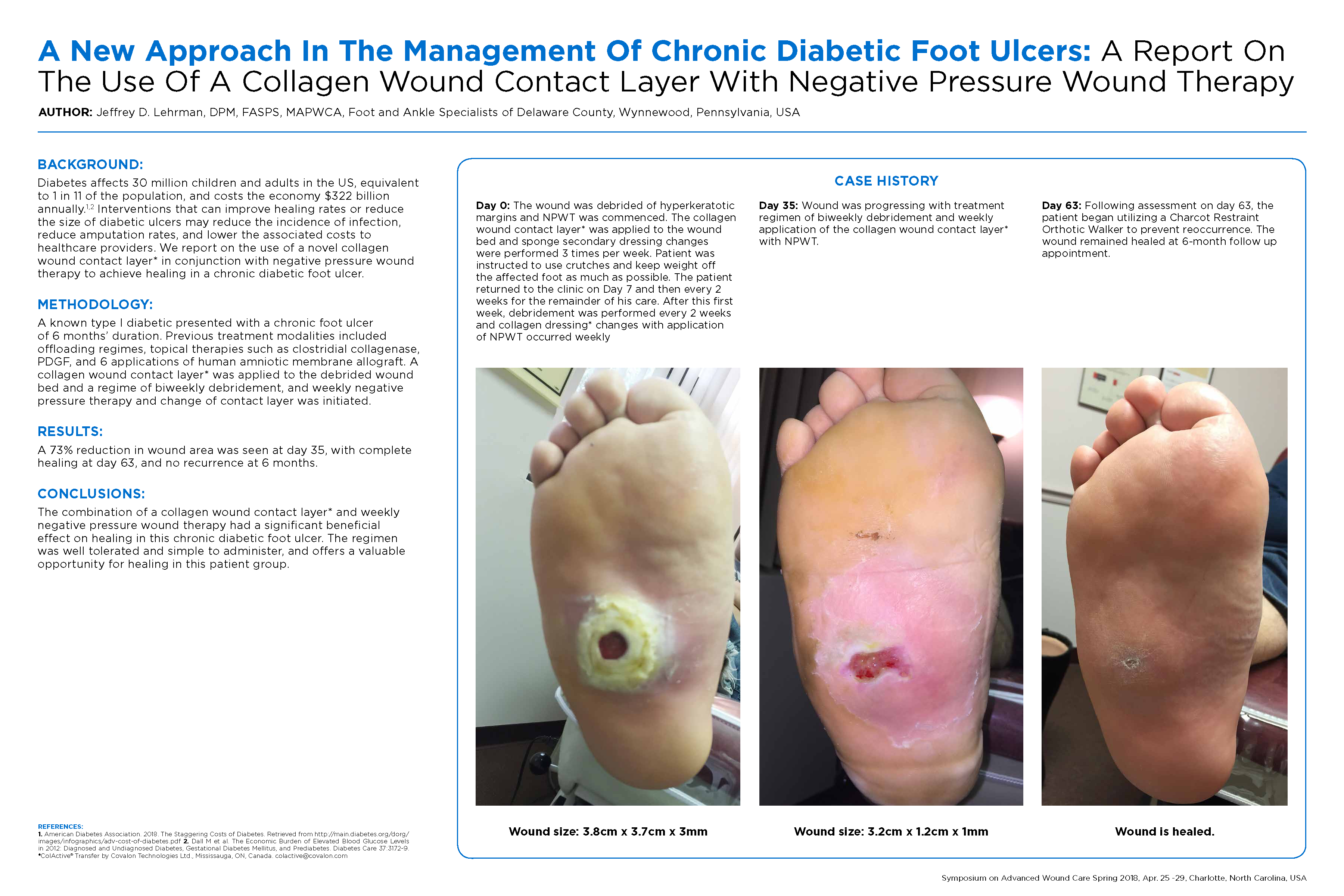
Diabetic Foot Ulcer At least half of all amputations occur in people with diabetes, most commonly because of an infected diabetic foot ulcer. a thorough understanding of the causes and management of diabetic foot ulceration is essential to reducing lower extremity amputation risk. this compendium elucidates the pathways leading to foot ulcers and enumerates multiple contributory risk factors. the authors. Abstract. diabetic foot ulcers (dfus) are a serious complication of diabetes that results in significant morbidity and mortality. mortality rates associated with development of a dfu are estimated to be 5% in the first 12 months, and 5 year morality rates have been estimated at 42%. the standard practices in dfu management include surgical. The management of diabetic foot ulcers requires offloading the wound, [6, 7] daily saline or similar dressings to provide a moist wound environment, [] débridement when necessary, antibiotic therapy with or without surgical intervention if osteomyelitis or soft tissue infection is present, [9, 10] optimal control of blood glucose, and evaluation and correction of peripheral arterial. Diabetic foot ulcers (dfus) are one of the most serious and devastating complication of diabetes mellitus, affecting about 15% of diabetic patients. this review describes the innovative treatment options currently available in the treatment of non healing dfus. the use of platelet rich plasma (prp) is a safe and valid approach in the treatment.

Approach To Non Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Doovi The management of diabetic foot ulcers requires offloading the wound, [6, 7] daily saline or similar dressings to provide a moist wound environment, [] débridement when necessary, antibiotic therapy with or without surgical intervention if osteomyelitis or soft tissue infection is present, [9, 10] optimal control of blood glucose, and evaluation and correction of peripheral arterial. Diabetic foot ulcers (dfus) are one of the most serious and devastating complication of diabetes mellitus, affecting about 15% of diabetic patients. this review describes the innovative treatment options currently available in the treatment of non healing dfus. the use of platelet rich plasma (prp) is a safe and valid approach in the treatment.

Comments are closed.