Attachment For Skeletal Muscle

Muscle Attachments And Actions Learn Muscle Anatomy Learn the terms and concepts of muscle attachments, origins, insertions, and actions. see 3d models and animations of common muscle movements and joints. Skeletal muscle: skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles, meaning you control how and when they move and work. nerves in your somatic nervous system send signals to make them function. if you reach for a book on a shelf, you’re using skeletal muscles in your neck, arm and shoulder. cardiac muscle: cardiac muscles are only in your heart.
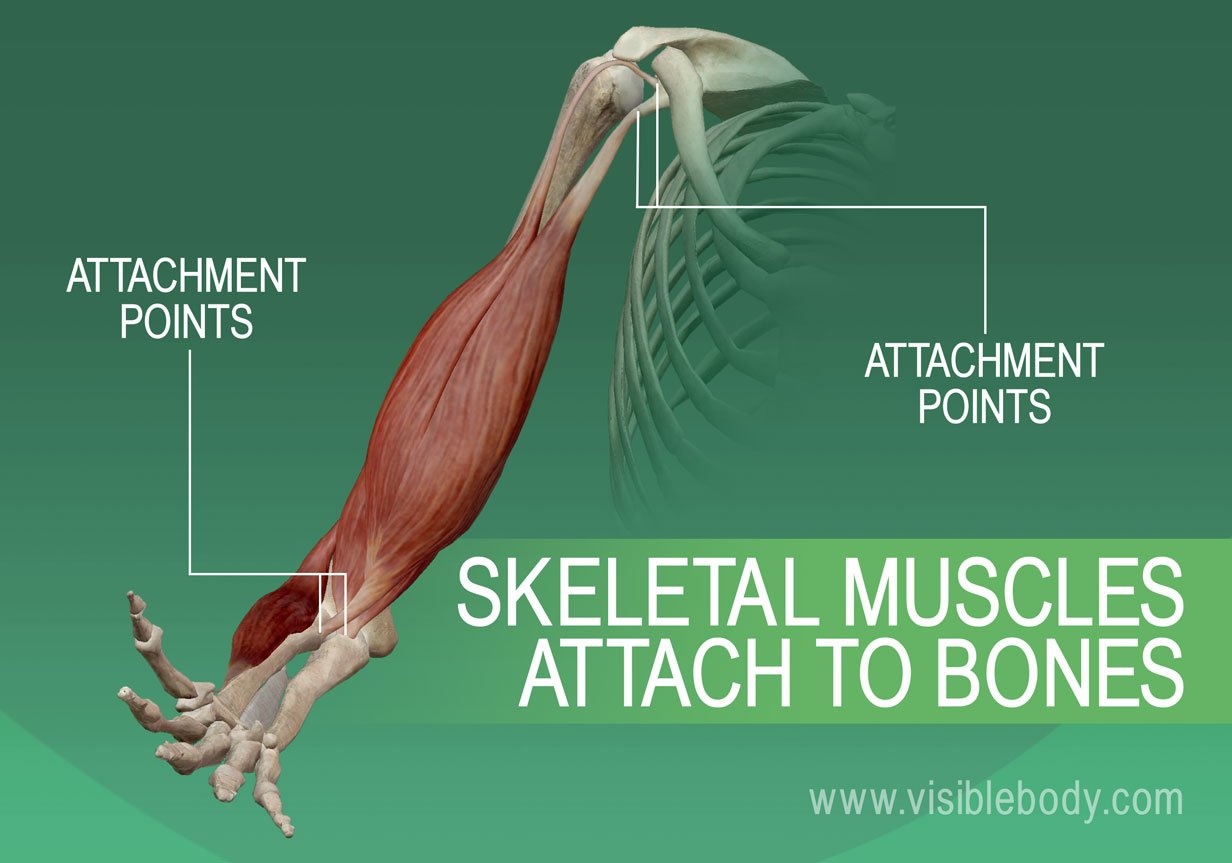
Muscular System Overview 5 Facts About Muscles Learn Muscle Anatomy Musculoskeletal system. the musculoskeletal system (locomotor system) is a human body system that provides our body with movement, stability, shape, and support. it is subdivided into two broad systems: muscular system, which includes all types of muscles in the body. skeletal muscles, in particular, are the ones that act on the body joints to. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. The musculoskeletal system comprises one of the body's major tissue organ systems. the three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle groups.[1][2][3] skeletal muscle attaches to the bone by tendons, and together they produce all body movements. the skeletal muscle fibers are crossed with a regular pattern of fine red and white lines, giving the muscle a distinctive. Based on the patterns of fascicle arrangement, skeletal muscles can be classified in several ways. what follows are the most common fascicle arrangements. parallel muscles have fascicles that are arranged in the same direction as the long axis of the muscle (figure 11.3). the majority of skeletal muscles in the body have this type of organization.

Comments are closed.