Basic Guide To Quantum Computing And Superposition By Mark Rethana

Basic Guide To Quantum Computing And Superposition By Mark Rethana Superposition. one of the main differences between classical computers and quantum computers is the use of the qubit. the computers we are accustomed to use bits, which is a binary digit that can. Read writing from mark rethana on medium. data scientist with a passion and curiosity for solving problems through analytics. every day, mark rethana and thousands of other voices read, write, and.
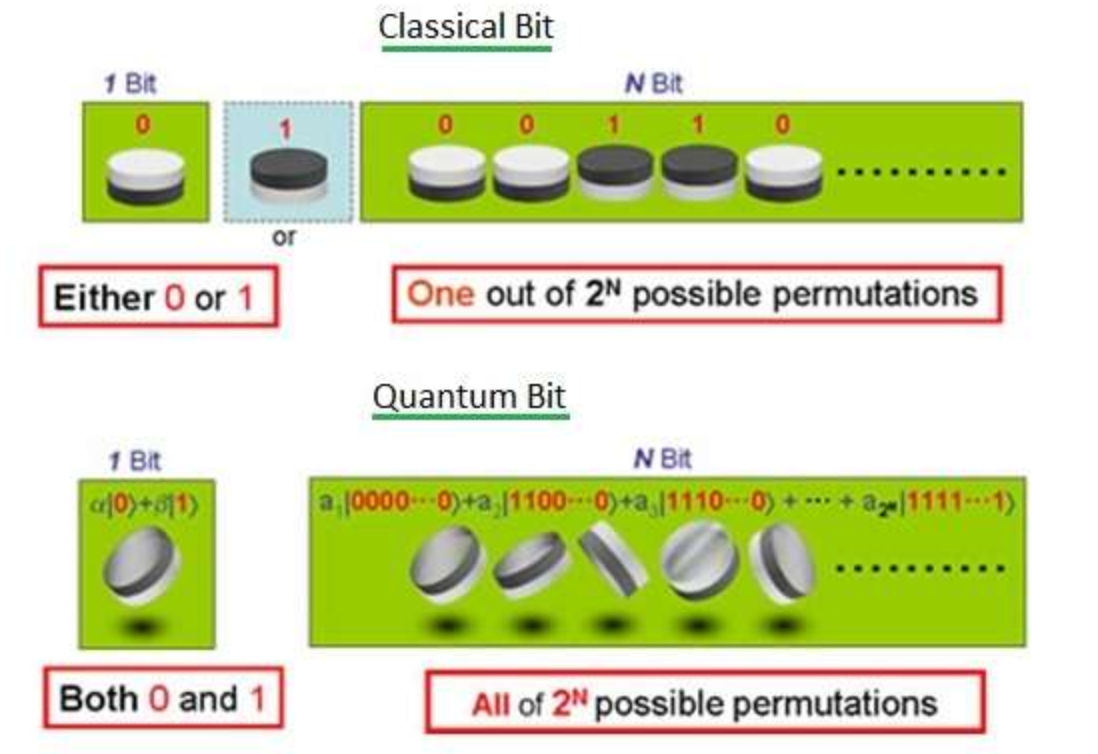
Basic Guide To Quantum Computing And Superposition By Mark Rethana And quantum computing is about chasing perhaps the biggest performance boost in the history of technology. the basic idea is to smash some barriers that limit the speed of existing computers by. To summarize this section, we have broken down the fundamentals of quantum computing to its most basic operators. we have analyzed the two most essential aspects of quantum computing: superposition and entanglement. we have also covered qubits, quantum gates, registers, etc. modern quantum computing and its applications. inside a quantum computer. A quantum computer isn't just a more powerful version of the computers we use today; it's something else entirely, based on emerging scientific understanding. In essence, the law of superposition definition asserts that if any two (or more) quantum states can be added together or "superposed," the result will be another valid quantum state. when we solve schrödinger's equation for a system, we get a set of solutions, each corresponding to a different system state. any physical state of the system.
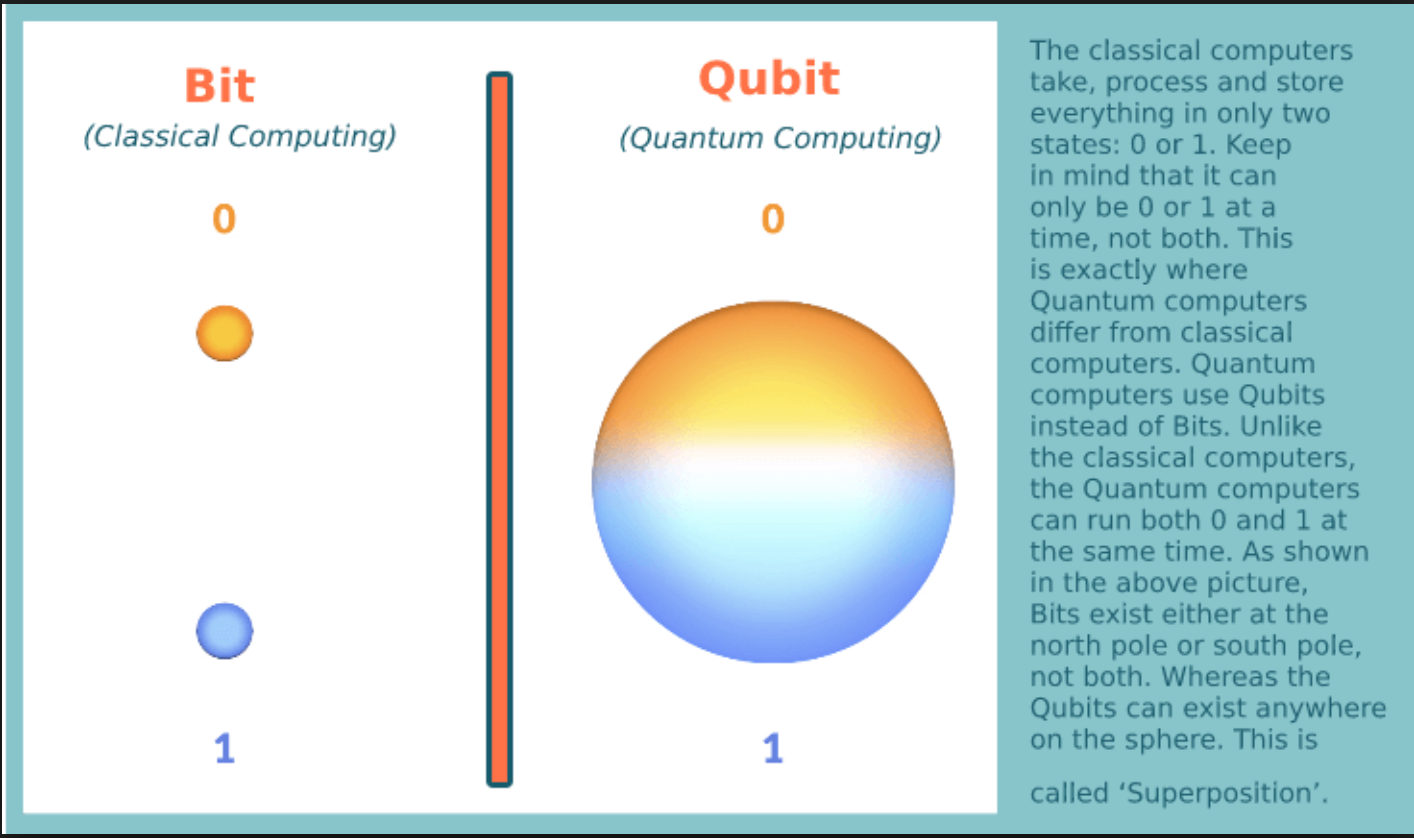
Basic Guide To Quantum Computing And Superposition By Mark Rethana A quantum computer isn't just a more powerful version of the computers we use today; it's something else entirely, based on emerging scientific understanding. In essence, the law of superposition definition asserts that if any two (or more) quantum states can be added together or "superposed," the result will be another valid quantum state. when we solve schrödinger's equation for a system, we get a set of solutions, each corresponding to a different system state. any physical state of the system. The basic properties of quantum computing are superposition, entanglement, and interference. superposition. superposition is the ability of a quantum system to be in multiple states simultaneously. the go to example of superposition is the flip of a coin, which consistently lands as heads or tails—a very binary concept. Mathematically, a qubit’s state in superposition can be represented as: ∣ ψ = α ∣0 β ∣1 . here, ∣ ψ denotes the state of the qubit, and α and β are complex numbers determining the probability of the qubit collapsing to either the 0 or 1 state upon measurement. the probabilities can be computed as ∣ α ∣2 for 0 and ∣ β.

Comments are closed.