Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant
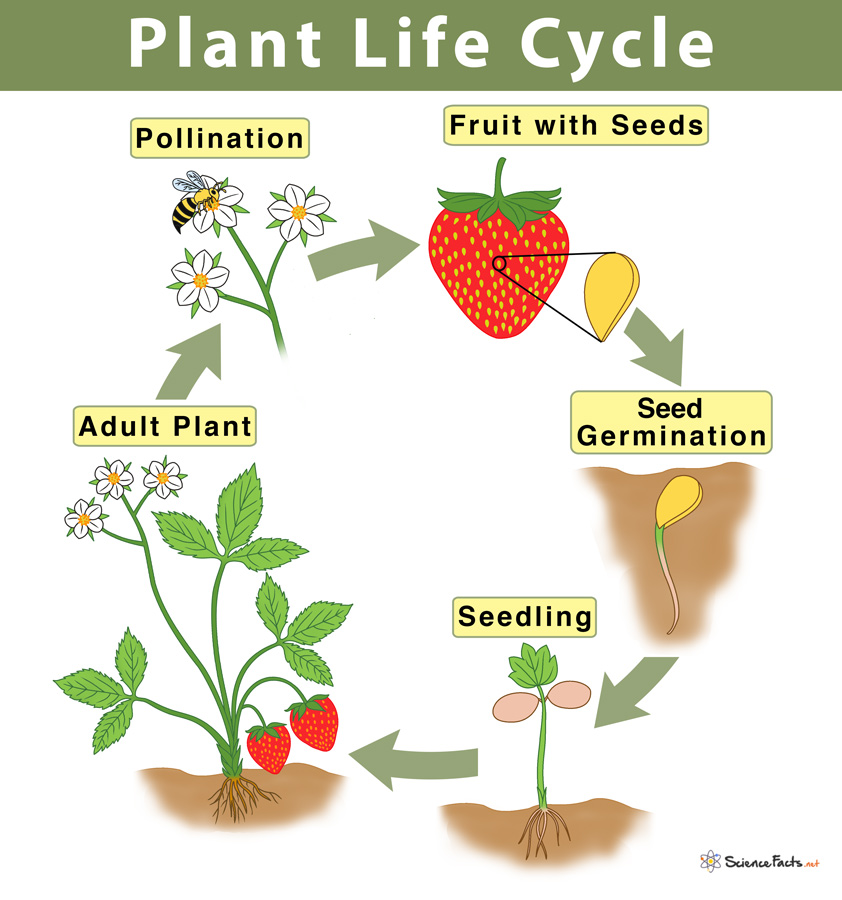
Plant Life Cycle Stages And Diagram A basic plant life cycle goes through five stages: 1) seed, 2) seed germination, 3) seedling, 4) adult plant, and 5) pollination and fertilization. they are discussed below in detail. 1) seed. the life cycle of a flowering plant begins with a seed. it has a protective outer covering called the shell. The flowers and fruit of flowering plants come and go as part of their life cycle. some flowering plants don’t even have stems and leaves all the time. the fruit and vegetables we eat come from different parts of the life cycle of various plants, such as roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruit and seeds. there is a good botany lesson to be found in food on our plate, which may include a few.
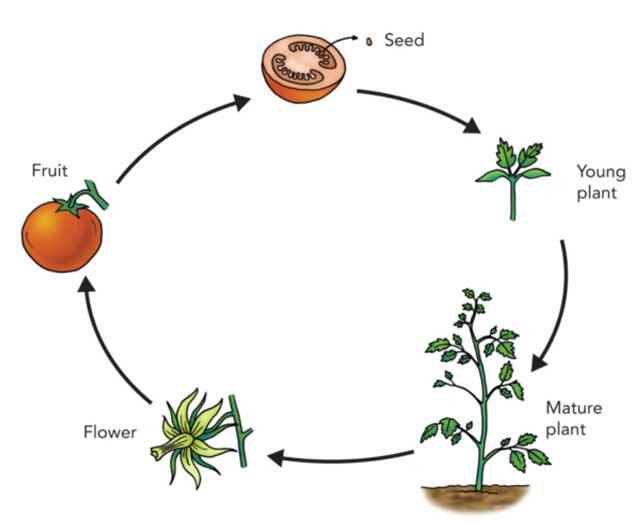
Life Cycle Of Plants Stages Types And Facts The life cycle of the flowering plant begins with the seed. a seed is an embryonic plant inside a protective coating. the life cycle of angiosperms can be described in four parts. Filament: supports the anther. pistil: the female part of the plant, sometimes called the ‘carpel’. stigma: collects pollen grains. style: allows pollen to pass to the ovary. ovary: produces seeds inside tiny ‘ovules’. sepal: found outside the petals, the sepal protects the flower when it’s unopened. General life cycle of a plant. learning about the life cycle of a flowering plant can be fascinating, especially for kids. start by explaining what a seed is. all seeds contain new plants, called embryos. most seeds have an outer cover, or seed coat, which protects and nourishes the embryo. show them examples of the various types of seeds. A general plant life cycle is represented by the diagram in figure below. from the figure, you can see that the diploid sporophyte has a structure called a sporangium (plural, sporangia) that undergoes meiosis to form haploid spores. a spore develops into a haploid gametophyte. the gametophyte has male or female reproductive organs that undergo.

Comments are closed.