Beta Blockers By Camille Pharmacology Nursing Nursing School

Nursing Pharmacology Beta Blockers Youtube Understanding beta blockers, their uses, mechanisms, and potential side effects is crucial for success in nursing exams and clinical practice. familiarize yourself with commonly prescribed beta blockers such as metoprolol, atenolol, propranolol, carvedilol, and labetalol to ensure you are well prepared for both the nclex and ati exams. So beta blockers are classified into two main groups; nonselective and selective. nonselective beta blockers can block both beta 1 and beta 2 receptors, and include nadolol, propranolol, pindolol, and sotalol. on the other hand, selective beta blockers only block beta 1 receptors, and include atenolol, metoprolol, carvedilol, and nebivolol.

What Are Beta Blockers Uses Types Examples Side Effects Study Beta blockers: episode 78. one of the most common medication classes you’ll see in the clinical setting is the beta blocker. in this episode we’ll talk about what they are, how they work, what they do, what conditions they’re used for and how you’re going to monitor your patient. some key information you’ll learn is: how beta blockers. Common meds are atenolol, propranolol and metoprolol. dysrhythmias: beta blockers are often used to control the rate in atrial fibrillation. expect to see esmolol, propranolol and maybe metroprolol used in this way. myocardial infarction: when given within 24 hours of onset, beta blockers reduce cardiac workload and improve likelihood of survival. Beta adrenergic blocking agents, commonly known as beta blockers, are medications used to reduce blood pressure and are often prescribed to treat cardiac problems. they work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, also called epinephrine, which is “the fight or flight” hormone. beta blockers may affect the heart and blood vessels. More. beta blockers are medications that help decrease blood pressure, slow down the heart rate, and treat dysrhythmias. this review will discuss the mechanism of action of beta blockers, what conditions they treat, nursing implications, side effects, and patient education. don't forget to take the beta blockers quiz after reviewing this material.
Beta Blockers Nursing Considerations Pharmacology Beta adrenergic blocking agents, commonly known as beta blockers, are medications used to reduce blood pressure and are often prescribed to treat cardiac problems. they work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, also called epinephrine, which is “the fight or flight” hormone. beta blockers may affect the heart and blood vessels. More. beta blockers are medications that help decrease blood pressure, slow down the heart rate, and treat dysrhythmias. this review will discuss the mechanism of action of beta blockers, what conditions they treat, nursing implications, side effects, and patient education. don't forget to take the beta blockers quiz after reviewing this material. Related documents. anticoagulants heparin nursing pharmacology osmosis 1; 897099988gbjknhh; exam review; blood sugar racial pharmacology and food justice in black america by anthony ryan hatch. Beta blockers are negative, chronotropic drugs that block that sa node from contracting excessively. beta blockers block the beta adrenergic receptor also known beta 1 and beta 2. beta 1 are receptors in the heart stimulates increased heart contraction. if stimulated, these beta receptors can cause contraction at higher rates.
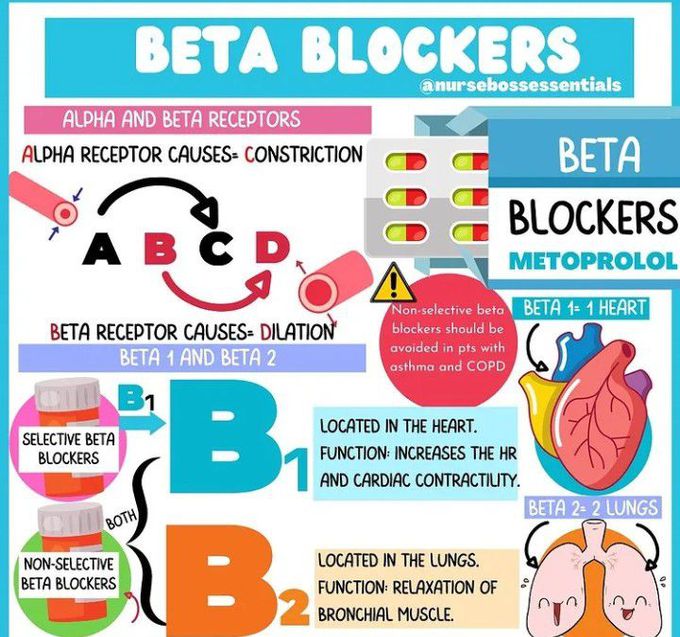
Beta Blockers Medizzy Related documents. anticoagulants heparin nursing pharmacology osmosis 1; 897099988gbjknhh; exam review; blood sugar racial pharmacology and food justice in black america by anthony ryan hatch. Beta blockers are negative, chronotropic drugs that block that sa node from contracting excessively. beta blockers block the beta adrenergic receptor also known beta 1 and beta 2. beta 1 are receptors in the heart stimulates increased heart contraction. if stimulated, these beta receptors can cause contraction at higher rates.
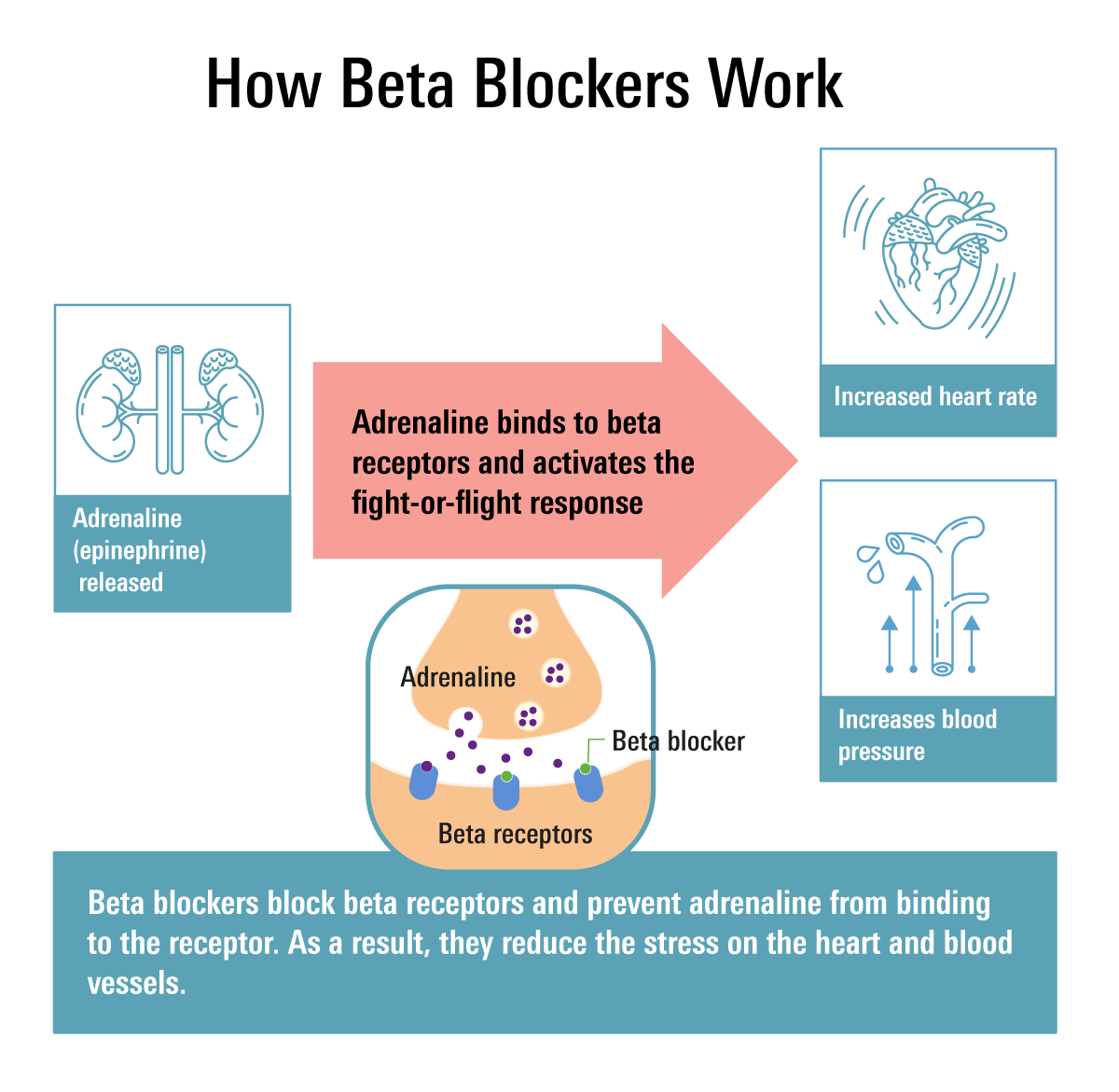
What Are Beta Blockers

Comments are closed.