Bio201 Muscle Fiber Human Anatomy And Physiology Muscle Anatomy
Muscular System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs Macroscopic anatomy visible structures surface anatomy exterior features regional anatomy body regions systematic anatomy groups of organs functioning as a system developmental anatomy embryology to maturity clinical anatomy medical specialties microscopic anatomy cells and molecules histology tissues & their structures cytology cells and their structures; cyt = cell. 4 steps of muscle contraction. 1. nerve stimulation. 2. action potential. 3. action potential reproduces. 4. intracellula calcium level rise. responsiveness. chemical signals stretch and electrical changes across the plasma membrance. conductivity. electrical change triggers a wave of excitement along muscle fiber.

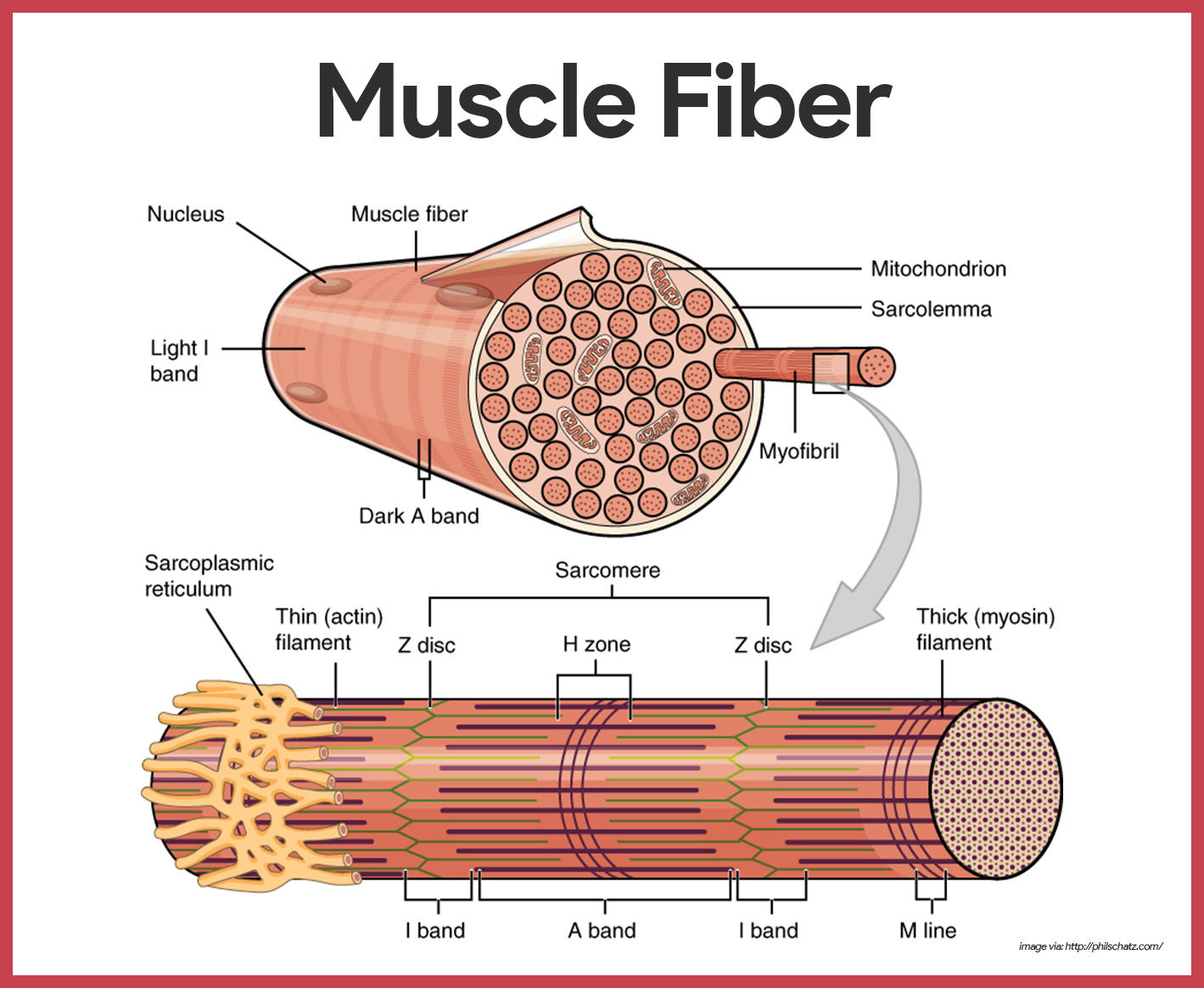
Bio201 Muscle Fiber Human Anatomy And Physiology Muscle Anatomy Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Studocu is not affiliated to or endorsed by any school, college or university. studeersnel b.v., keizersgracht 424 sous, 1016 gc amsterdam, kvk: 56829787, btw: nl852321363b01. studying bio 201 human anatomy and physiology i at grand canyon university? on studocu you will find 173 lecture notes, 80 practice materials, 67 coursework and much. Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers recognized (table 10.5.1). slow oxidative (also called slow twitch or type i) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce atp. fast oxidative (also called fast twitch or type iia) fibers have relatively fast contractions. Relaxation of a skeletal muscle. relaxing skeletal muscle fibers, and ultimately, the skeletal muscle, begins with the motor neuron, which stops releasing its chemical signal, ach, into the synapse at the nmj. the muscle fiber will repolarize, which closes the gates in the sr where ca was being released. atp driven pumps will move ca out.

Skeletal Muscle Anatomy And Physiology I Using these criteria, there are three main types of skeletal muscle fibers recognized (table 10.5.1). slow oxidative (also called slow twitch or type i) fibers contract relatively slowly and use aerobic respiration (oxygen and glucose) to produce atp. fast oxidative (also called fast twitch or type iia) fibers have relatively fast contractions. Relaxation of a skeletal muscle. relaxing skeletal muscle fibers, and ultimately, the skeletal muscle, begins with the motor neuron, which stops releasing its chemical signal, ach, into the synapse at the nmj. the muscle fiber will repolarize, which closes the gates in the sr where ca was being released. atp driven pumps will move ca out. Divides the abdomin with nine regions, 1 & 2 right and left hypochondriac regions, 3 & 4 right and left lumbar regions, 5 & 6 right and left inguinal regions, 7. epigastric region, 8. umilical region, 9. hypogastric region. organ systems. 11 organ systems of the body. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like anatomy. Muscle is one of the four primary tissue types of the body (along with epithelial, nervous, and connective tissues), and the body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle (figure 33.1). all three muscle tissues have some properties in common; they all exhibit a quality called excitability as.

Comments are closed.