C 1 Introduction To The Respiratory System

C 1 Introduction To The Respiratory System A simple introduction: 1. 2. the task of the respiratory system is to get fresh air, especially oxygen (o2), into the lungs and to get rid of the gaseous waste, carbon dioxide (co2), that we are constantly producing (with our metabolism). 3. the upper airway transports the air between the outside world and the lungs. The circulatory system transports gases from the lungs to tissues throughout the body and vice versa. a variety of diseases can affect the respiratory system, such as asthma, emphysema, chronic obstruction pulmonary disorder (copd), and lung cancer. all of these conditions affect the gas exchange process and result in labored breathing and.
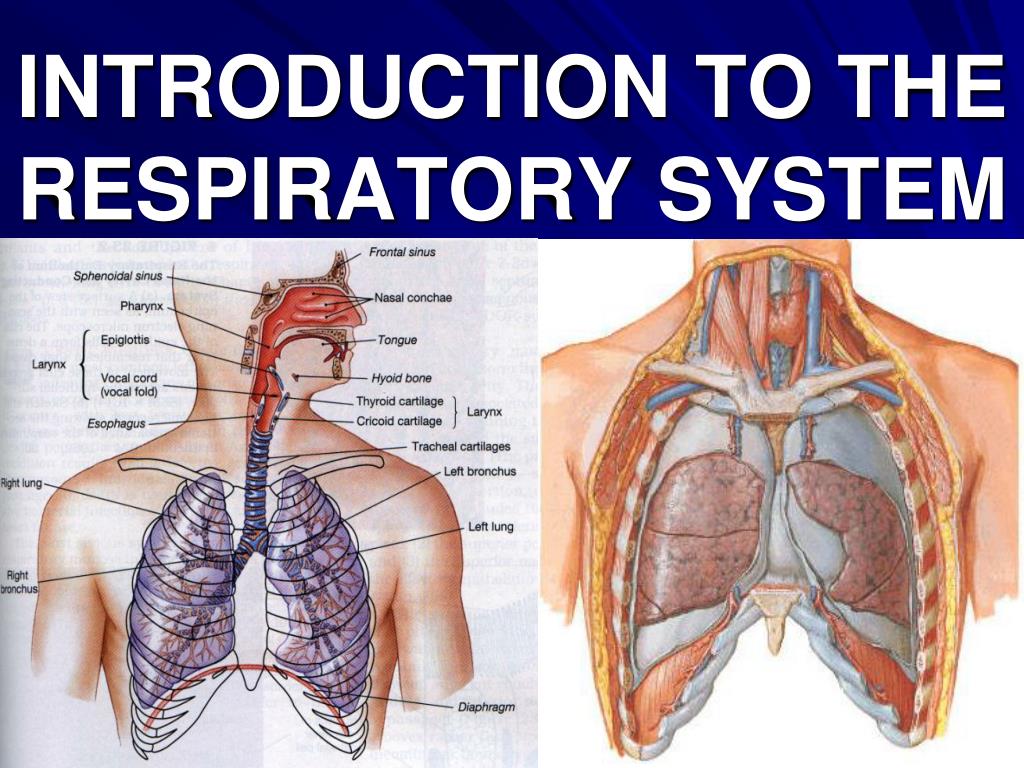
Ppt Introduction To The Respiratory System Powerpoint Presentation The circulatory system transports gases from the lungs to tissues throughout the body and vice versa. a variety of diseases can affect the respiratory system, such as asthma, emphysema, chronic obstruction pulmonary disorder (copd), and lung cancer. all of these conditions affect the gas exchange process and result in labored breathing and. View the structures which allow the respiratory system to take in oxygen and have a close up look at the respiratory system divisions.explore more in complet. About two dozen olfactory nerves convey the sensation of smell from the olfactory cells through the bony roof of the nasal cavity to the central nervous system. human respiratory system, the system in humans that takes up oxygen and expels carbon dioxide. the major organs of the respiratory system include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea. This is because every cell in the body needs to run the oxidative stages of cellular respiration, the process by which energy is produced in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp). for oxidative phosphorylation to occur, oxygen is used as a reactant and carbon dioxide is released as a waste product. figure 20.1.1 20.1. 1: mountain climbers.
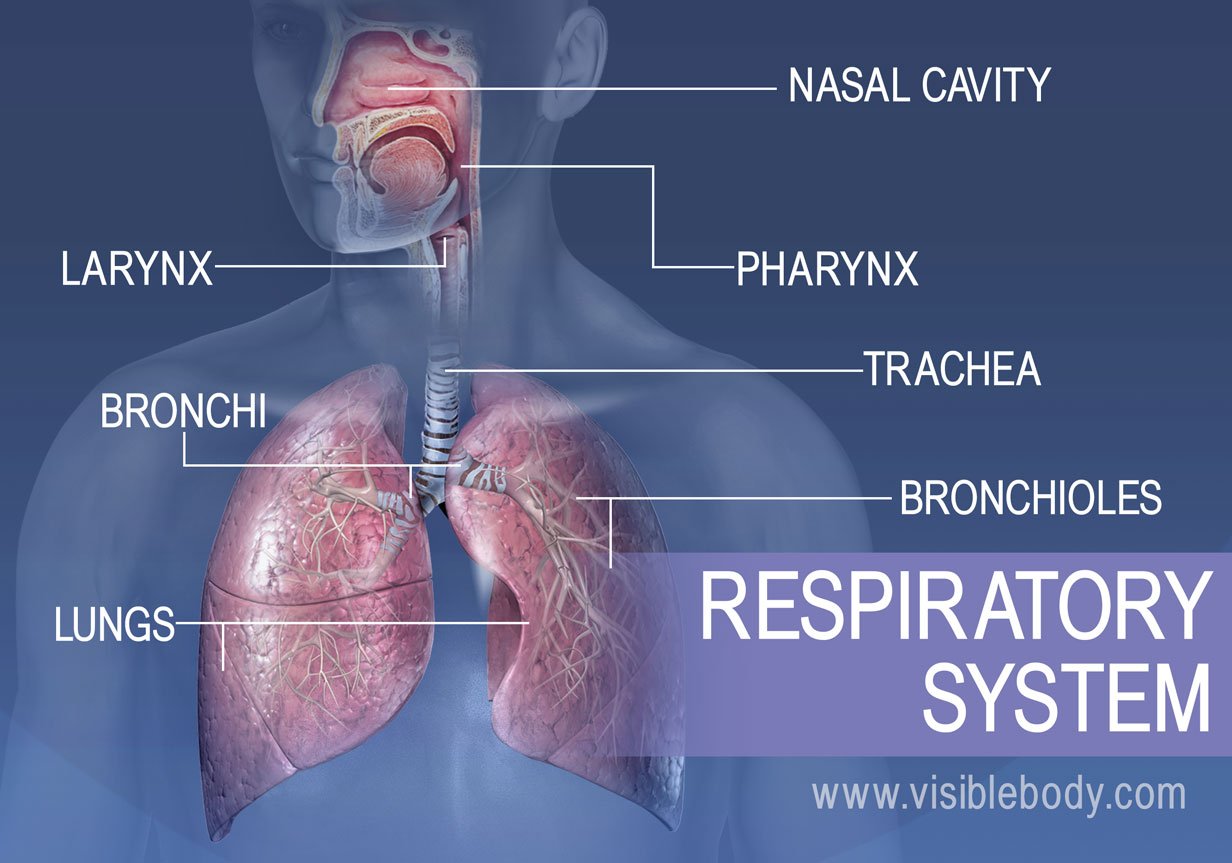
Respiratory System Learn Respiratory Anatomy About two dozen olfactory nerves convey the sensation of smell from the olfactory cells through the bony roof of the nasal cavity to the central nervous system. human respiratory system, the system in humans that takes up oxygen and expels carbon dioxide. the major organs of the respiratory system include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea. This is because every cell in the body needs to run the oxidative stages of cellular respiration, the process by which energy is produced in the form of adenosine triphosphate (atp). for oxidative phosphorylation to occur, oxygen is used as a reactant and carbon dioxide is released as a waste product. figure 20.1.1 20.1. 1: mountain climbers. Respiratory system. your respiratory system is made up of your lungs, airways (trachea, bronchi and bronchioles), diaphragm, voice box, throat, nose and mouth. its main function is to breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. it also helps protect you from harmful particles and germs and allows you to smell and speak. 59. introduction to the respiratory system. the major function of the respiratory system is to obtain oxygen and remove carbon dioxide for metabolic processes in the body. the aerobic metabolic pathway of conversion of nutrients to energy requires oxygen, for example: c 6 h 12 o 6 o 2 → co 2 6 h 2 o energy as atp.

Introduction To Respiratory System вђ Nursing Lecture Respiratory system. your respiratory system is made up of your lungs, airways (trachea, bronchi and bronchioles), diaphragm, voice box, throat, nose and mouth. its main function is to breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. it also helps protect you from harmful particles and germs and allows you to smell and speak. 59. introduction to the respiratory system. the major function of the respiratory system is to obtain oxygen and remove carbon dioxide for metabolic processes in the body. the aerobic metabolic pathway of conversion of nutrients to energy requires oxygen, for example: c 6 h 12 o 6 o 2 → co 2 6 h 2 o energy as atp.

Introduction To The Respiratory System Pediagenosis

Comments are closed.