Carbohydrate Metabolism
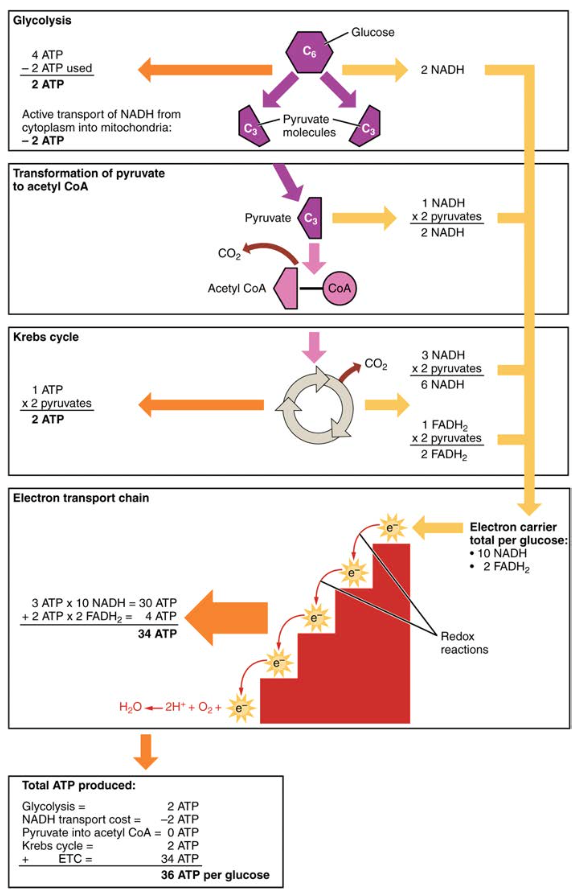
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii Learn about the biochemical processes of carbohydrate formation, breakdown, and interconversion in living organisms. explore the metabolic pathways of glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, and glycogenesis, and their regulation and applications. Learn how glucose is broken down into pyruvate through glycolysis, and how pyruvate enters the krebs cycle and the electron transport chain to produce atp. also, understand gluconeogenesis, the reverse process of carbohydrate metabolism.

Carbohydrates Metabolism Pharmaceutical Biochemistry Important Notes Overview of carbohydrate metabolism. simple sugars, such as glucose, fructose, or galactose, have different points of entry into glycolysis. a process referred to as gluconeogenesis can also generate glucose. complex carbohydrates such as glycogen can also enter glycolysis. Learn how the body digests and metabolizes carbohydrates to produce atp through glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. explore the processes of gluconeogenesis, the transport of electrons, and the role of coenzymes in cellular respiration. Learn how glucose is broken down into pyruvate through glycolysis, and how pyruvate enters the krebs cycle and the electron transport chain to produce atp. this section also covers gluconeogenesis, the reverse process of carbohydrate metabolism. Openstax. this free textbook is an openstax resource written to increase student access to high quality, peer reviewed learning materials.
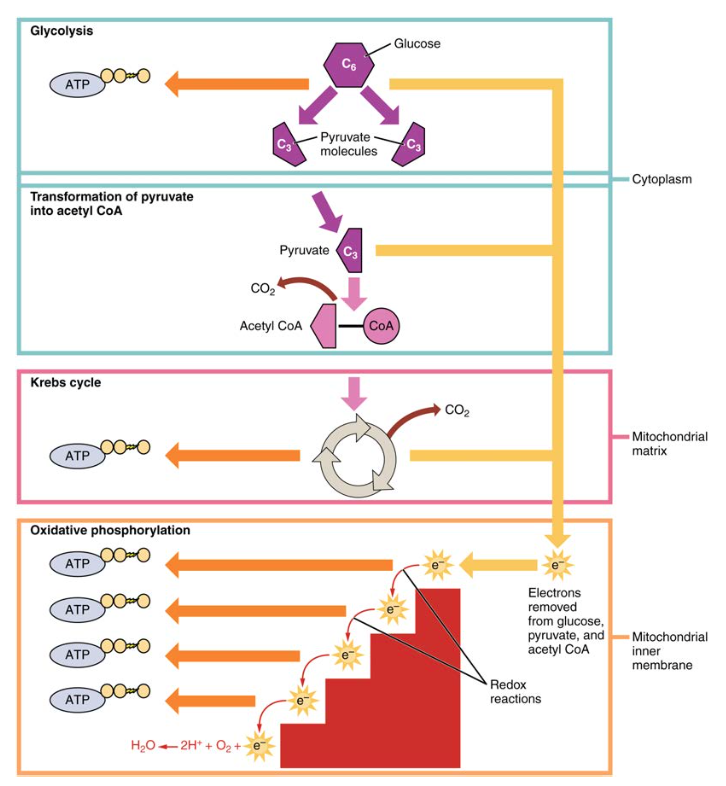
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii Learn how glucose is broken down into pyruvate through glycolysis, and how pyruvate enters the krebs cycle and the electron transport chain to produce atp. this section also covers gluconeogenesis, the reverse process of carbohydrate metabolism. Openstax. this free textbook is an openstax resource written to increase student access to high quality, peer reviewed learning materials. Learn how carbohydrates are broken down and synthesized by living organisms to produce energy and atp. explore the equations and processes of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, and the role of glucose and starch. Learn how glucose is oxidized to produce atp through glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. explore the processes, enzymes, and equations involved in carbohydrate metabolism.

Comments are closed.