Carbohydrate Metabolism в Anatomy And Physiology
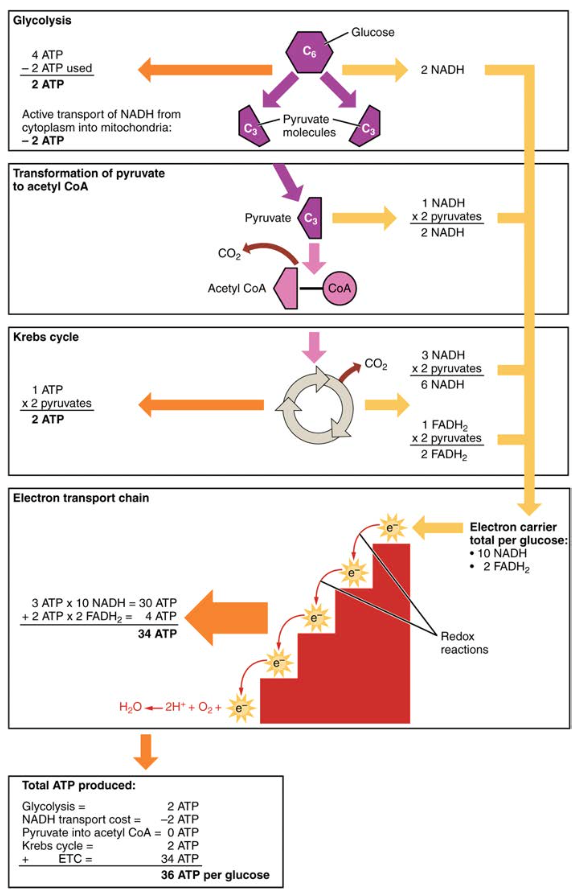
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii Figure 24.2.6 – carbohydrate metabolism: carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. gluconeogenesis. gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. this process takes place primarily in the liver during. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine. once the absorbed monosaccharides are transported to the tissues, the process of cellular respiration begins ( figure 24.4 ).
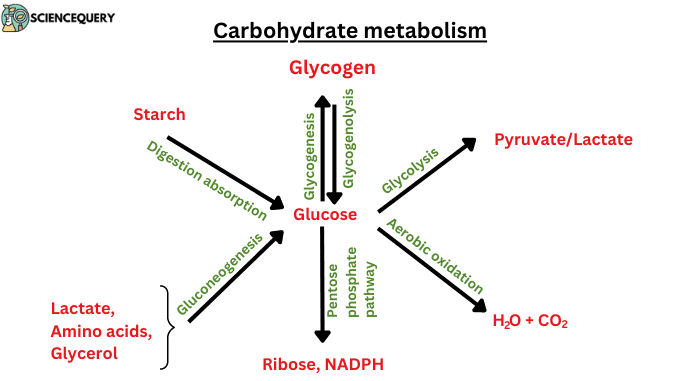
Define Carbohydrate Metabolism Sciencequery Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine. once the absorbed monosaccharides are transported to the tissues, the process of cellular respiration begins (figure 24.3.1 ). Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. the family of carbohydrates includes both simple and complex sugars. glucose and fructose are examples of simple sugars, and starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all examples of complex sugars. Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients in the human diet, along with protein and fat. these molecules contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. they act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism, and help with fermentation. the digestive. Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. the normal range of glucose in the blood is 70 99 mg dl. any deviation in this level is a sign of poor metabolism and a weak regulatory system. for example, dysfunction of insulin production and secretion, as well as the target cells' responsiveness to insulin, can lead to a condition termed diabetes mellitus.

Carbohydrates Metabolism Pharmaceutical Biochemistry Important Notes Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients in the human diet, along with protein and fat. these molecules contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. carbohydrates play an important role in the human body. they act as an energy source, help control blood glucose and insulin metabolism, participate in cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism, and help with fermentation. the digestive. Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. the normal range of glucose in the blood is 70 99 mg dl. any deviation in this level is a sign of poor metabolism and a weak regulatory system. for example, dysfunction of insulin production and secretion, as well as the target cells' responsiveness to insulin, can lead to a condition termed diabetes mellitus. Figure 24.1 metabolism metabolism is the sum of all energy requiring and energy consuming processes of the body. many factors contribute to overall metabolism, including lean muscle mass, the amount and quality of food consumed, and the physical demands placed on the human body. Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. the normal range of glucose in the blood is 70 99 mg dl. any deviation in this level is a sign of poor metabolism and a weak regulatory system. for example, dysfunction of insulin production and secretion, as well as the target cells' responsiveness to insulin, can lead to a condition termed diabetes mellitus.

Solution 24 2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Studypool Figure 24.1 metabolism metabolism is the sum of all energy requiring and energy consuming processes of the body. many factors contribute to overall metabolism, including lean muscle mass, the amount and quality of food consumed, and the physical demands placed on the human body. Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. the normal range of glucose in the blood is 70 99 mg dl. any deviation in this level is a sign of poor metabolism and a weak regulatory system. for example, dysfunction of insulin production and secretion, as well as the target cells' responsiveness to insulin, can lead to a condition termed diabetes mellitus.

1 Overview Carbohydrate Metabolism Carbohydrate Metabolism 1

Comments are closed.