Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii 49 Off
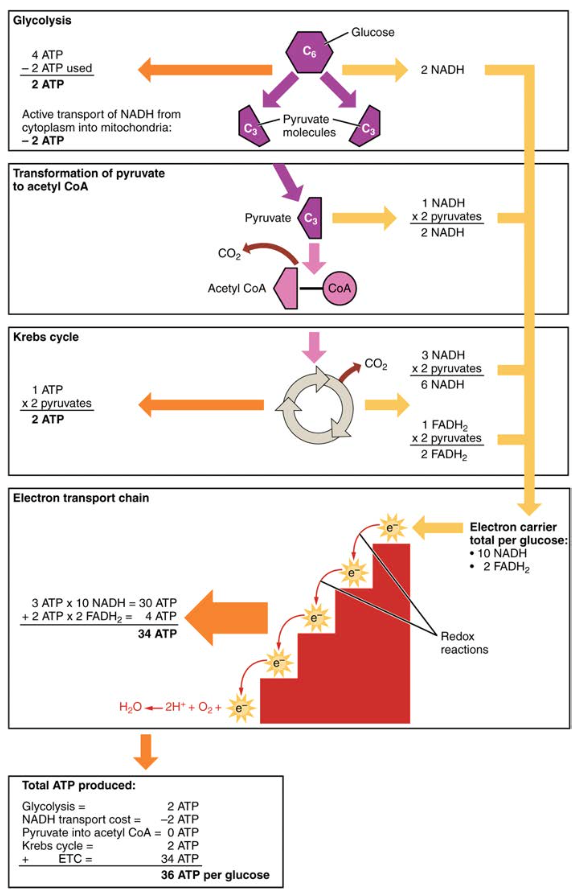
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. the family of carbohydrates includes both simple and complex sugars. glucose and fructose are examples of simple sugars, and starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all examples of complex sugars. Figure 24.9 carbohydrate metabolism carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. gluconeogenesis this process takes place primarily in the liver during periods of low glucose, that is, under conditions of fasting, starvation, and low carbohydrate diets.

Carbohydrate Metabolism Figure 24.2.6 – carbohydrate metabolism: carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. gluconeogenesis. gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. this process takes place primarily in the liver during. Excess or unutilized energy is stored as fat or glycogen for later use. carbohydrate metabolism begins in the mouth, where the enzyme salivary amylase begins to break down complex sugars into monosaccharides. these can then be transported across the intestinal membrane into the bloodstream and then to body tissues. Cell structures and functions. 41 terms. calhoyt20. preview. glucose metabolism pathways. 83 terms. annie maxfield. preview. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like metabolism, catabolism, anabolism and more. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine. once the absorbed monosaccharides are transported to the tissues, the process of cellular respiration begins (figure 24.3.1 ).
Carbohydrate Metabolism Cell structures and functions. 41 terms. calhoyt20. preview. glucose metabolism pathways. 83 terms. annie maxfield. preview. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like metabolism, catabolism, anabolism and more. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine. once the absorbed monosaccharides are transported to the tissues, the process of cellular respiration begins (figure 24.3.1 ). A hormone that regulates carbohydrate metabolism by making glucose leave the blood and enter the cells at a more rapid rate. secreted by beta cells of the pancreas to decrease the blood glucose level. glycogen synthesis. the preferred energy food of the body. energy is essential because it provides the body with to perform its task and to. Figure 24.9 carbohydrate metabolism carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. gluconeogenesis. gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. this process takes place primarily in the liver during periods.

Comments are closed.