Carbohydrate Metabolism Introduction
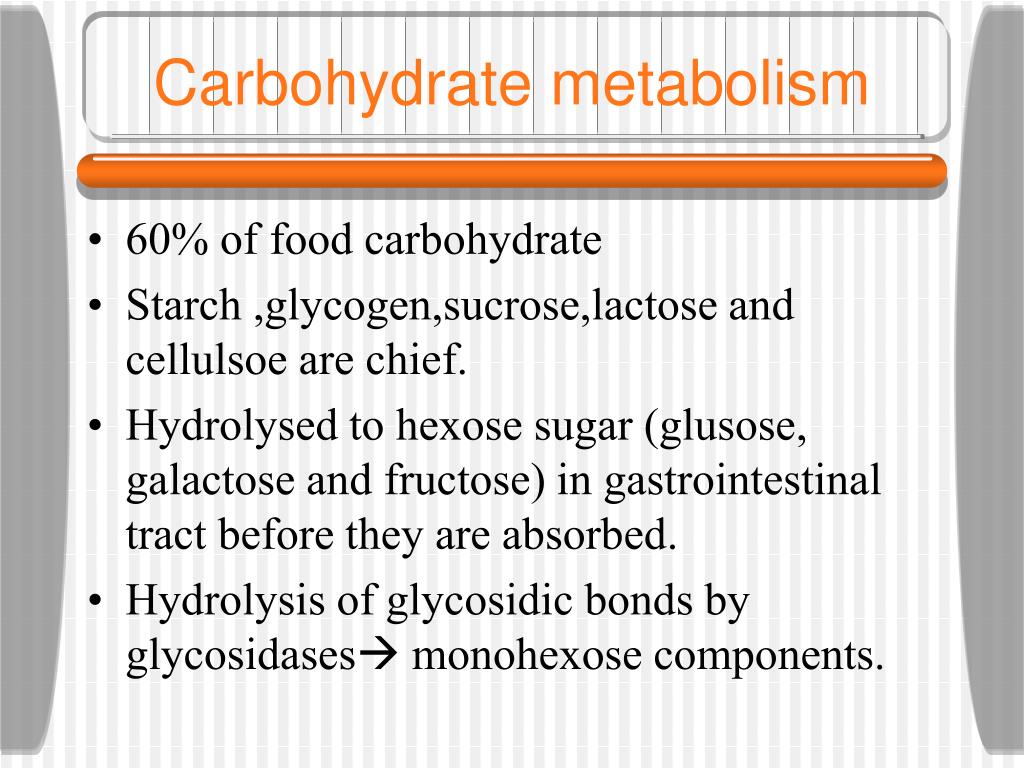
Ppt Carbohydrate Metabolism Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Carbohydrate metabolism is the whole of the biochemical processes responsible for the metabolic formation, breakdown, and interconversion of carbohydrates in living organisms . carbohydrates are central to many essential metabolic pathways. [ 1] plants synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water through photosynthesis, allowing them. Excess or unutilized energy is stored as fat or glycogen for later use. carbohydrate metabolism begins in the mouth, where the enzyme salivary amylase begins to break down complex sugars into monosaccharides. these can then be transported across the intestinal membrane into the bloodstream and then to body tissues.

Disorder Of Carbohydrate Metabolism Ppt Powerpoint Figure 24.2.6 – carbohydrate metabolism: carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. gluconeogenesis. gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. this process takes place primarily in the liver during. Carbohydrate metabolism. carbohydrates are the most abundant macromolecules on our planet, in part because of the plant carbohydrates cellulose and starch, both composed of multiple conjugated glucose molecules. cellulose is an important structural element of plant cell walls. animals lack enzymes that can break down the cellulose into smaller. Introduction. glucose is a universal fuel for every human cell type. in mammals, glucose is the only fuel that the brain uses under non starvation conditions and the only fuel that red blood cells can use under all conditions. although many carbohydrates exist in nature, glucose, instead of some other monosaccharide, is the prominent. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine. once the absorbed monosaccharides are transported to the tissues, the process of cellular respiration begins (figure 24.3.1 ).
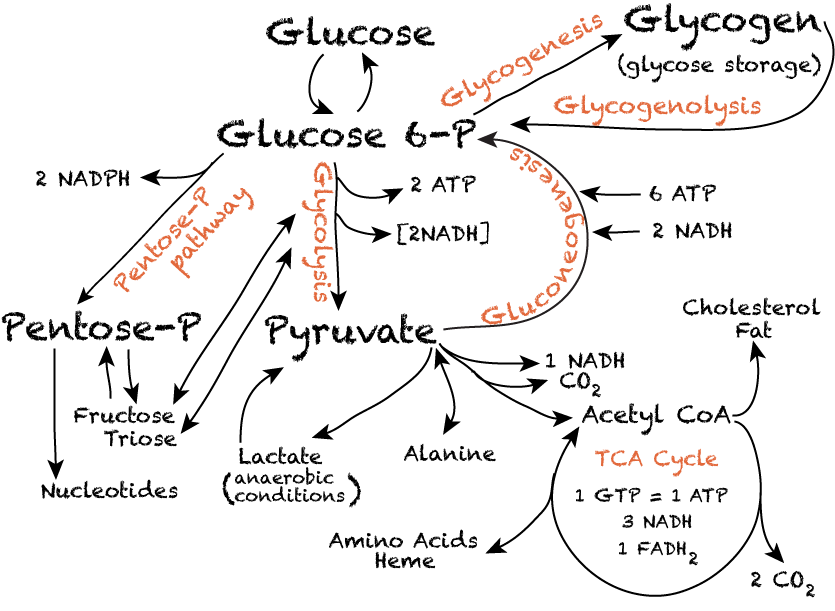
Pathway Of Carbohydrate Metabolism Introduction. glucose is a universal fuel for every human cell type. in mammals, glucose is the only fuel that the brain uses under non starvation conditions and the only fuel that red blood cells can use under all conditions. although many carbohydrates exist in nature, glucose, instead of some other monosaccharide, is the prominent. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine. once the absorbed monosaccharides are transported to the tissues, the process of cellular respiration begins (figure 24.3.1 ). Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. the family of carbohydrates includes both simple and complex sugars. glucose and fructose are examples of simple sugars, and starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all examples of complex sugars. Principles of biochemistry. 65935. 8.1: carbohydrates overview. 8.2: glycolysis. glycolysis, which literally means “breakdown of sugar," is a catabolic process in which six carbon sugars (hexoses) are oxidized and broken down into pyruvate molecules. the corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized is termed gluconeogenesis.
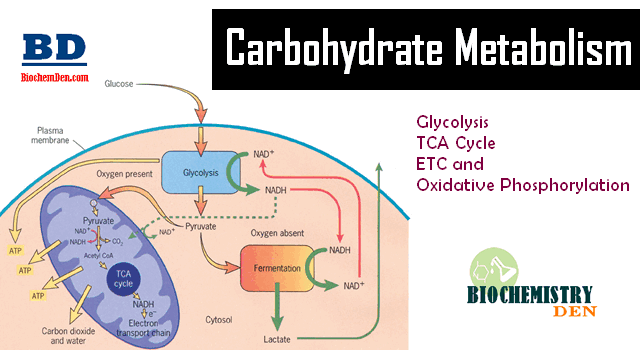
Basic Overview Of Carbohydrate Metabolism Learning objectives. by the end of this section, you will be able to: carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. the family of carbohydrates includes both simple and complex sugars. glucose and fructose are examples of simple sugars, and starch, glycogen, and cellulose are all examples of complex sugars. Principles of biochemistry. 65935. 8.1: carbohydrates overview. 8.2: glycolysis. glycolysis, which literally means “breakdown of sugar," is a catabolic process in which six carbon sugars (hexoses) are oxidized and broken down into pyruvate molecules. the corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized is termed gluconeogenesis.

Comments are closed.