Carbohydrate Structure And Metabolism An Overview Animation
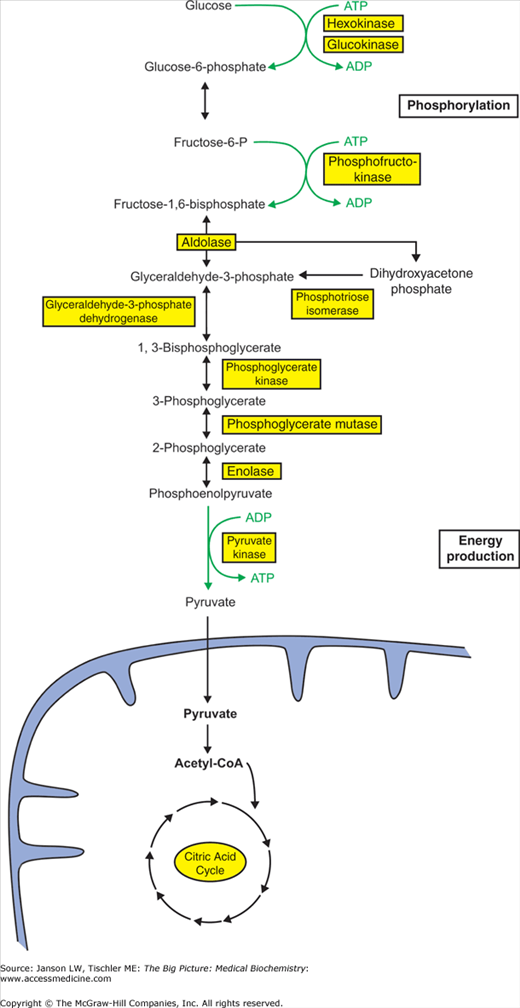
Chapter 6 Carbohydrate Metabolism Basicmedical Key (usmle topics) structure of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. digestion of carbs. glucose metabolic pathways. this video also answers commo. Watch on. carbohydrates are biomolecules that consist of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. carbohydrates play crucial roles in living organisms. among other functions, they serve as major sources of energy, and structural components. carbohydrates are made of base units called monosaccharides.
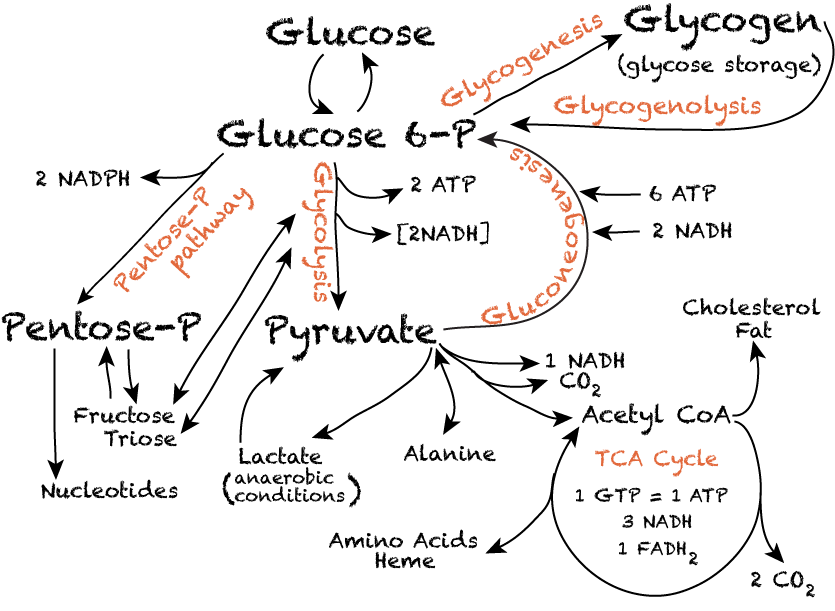
Pathway Of Carbohydrate Metabolism Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like carbohydrates, 1. they serve as major sources of energy 2. structural components 3. role in cell identification, signaling, monosaccharides and more. Carbohydrate structure and metabolism, an overview, narrated animation. 2020 07 20t08:28:37z structure of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. digestion of carbs. A carbohydrate is a type of molecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. carbohydrates can be simple sugars (monosaccharides) like glucose, or they can be made up of multiple sugar units (polysaccharides) like glycogen. they are important in biology as a source of energy and as structural components in plants. questions. Figure 24.2.6 – carbohydrate metabolism: carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. gluconeogenesis. gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. this process takes place primarily in the liver during.
Carbohydrate Metabolism Disorders Medlineplus A carbohydrate is a type of molecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. carbohydrates can be simple sugars (monosaccharides) like glucose, or they can be made up of multiple sugar units (polysaccharides) like glycogen. they are important in biology as a source of energy and as structural components in plants. questions. Figure 24.2.6 – carbohydrate metabolism: carbohydrate metabolism involves glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. gluconeogenesis. gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate, lactate, glycerol, or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. this process takes place primarily in the liver during. Start typing, then use the up and down arrows to select an option from the list.?. Principles of biochemistry. 65935. 8.1: carbohydrates overview. 8.2: glycolysis. glycolysis, which literally means “breakdown of sugar," is a catabolic process in which six carbon sugars (hexoses) are oxidized and broken down into pyruvate molecules. the corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized is termed gluconeogenesis.

Comments are closed.