Cardiac Muscle Cell Structure

Cardiac Muscle Cell Cardiac Muscle Cell Cardiac Online Sci Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. these inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle cells. The heart consists mostly of cardiac muscle cells (or myocardium). the outstanding characteristics of the action of the heart are its contractility, which is the basis for its pumping action, and the rhythmicity of the contraction.
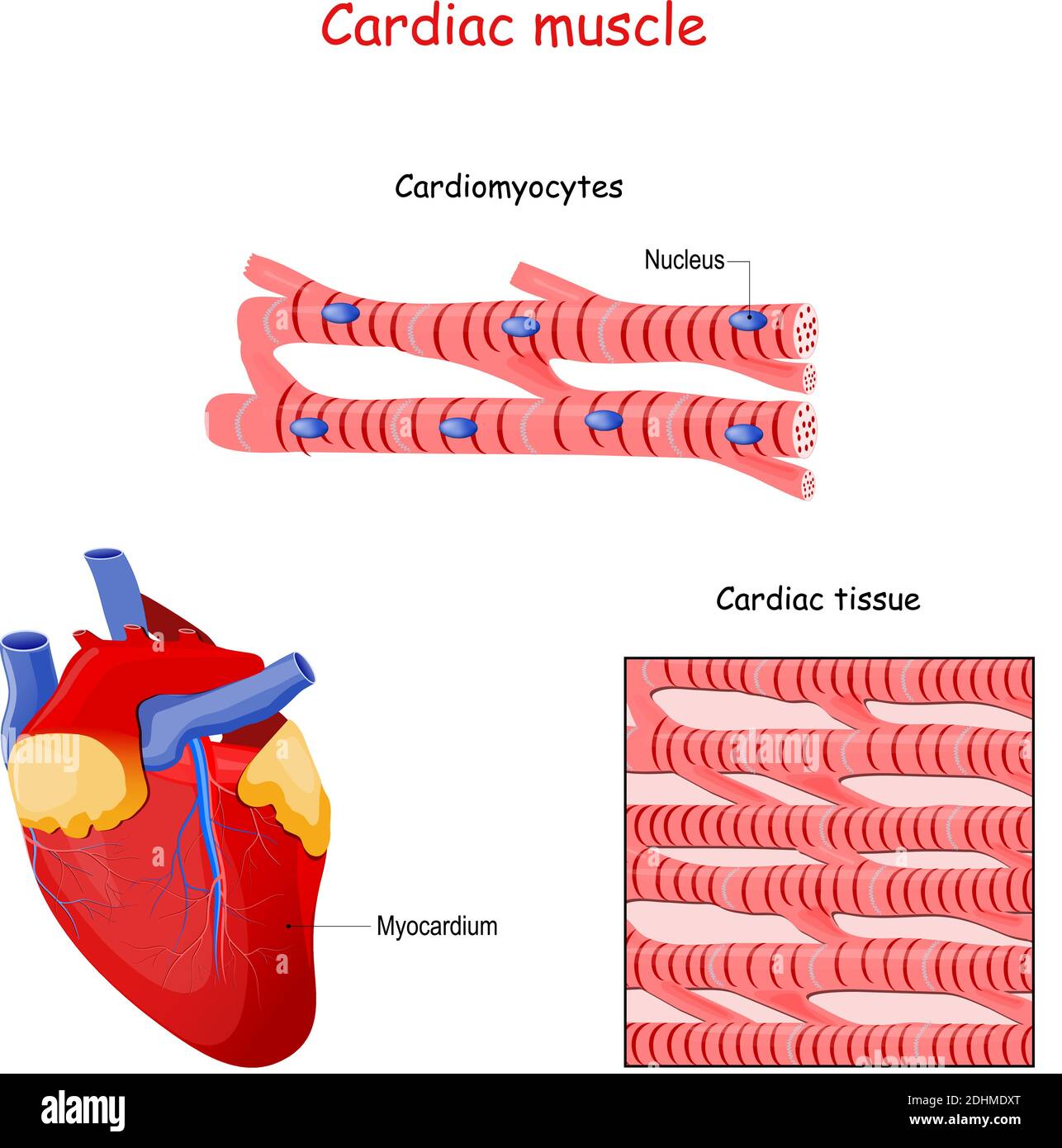
Cell Ultrastructure Medical Human Muscle Tissue Cardiac Muscle The individual cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte) is a tubular structure composed of chains of myofibrils, which are rod like units within the cell. the myofibrils consist of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which are the fundamental contractile units of the muscle cells. Cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) are striated, branched, contain many mitochondria, and are under involuntary control. each myocyte contains a single, centrally located nucleus surrounded by a cell membrane known as the sarcolemma. Intercalated discs are part of the sarcolemma and contain two structures important in cardiac muscle contraction: gap junctions and desmosomes. a gap junction forms channels between adjacent cardiac muscle fibers that allow the depolarizing current produced by cations to flow from one cardiac muscle cell to the next. The distributions of these main cell types, estimated from nuclei data, differ between atrial and ventricular tissues. atrial tissues contain 30.1% cardiomyocytes, 24.3% fbs, 17.1% mural cells.
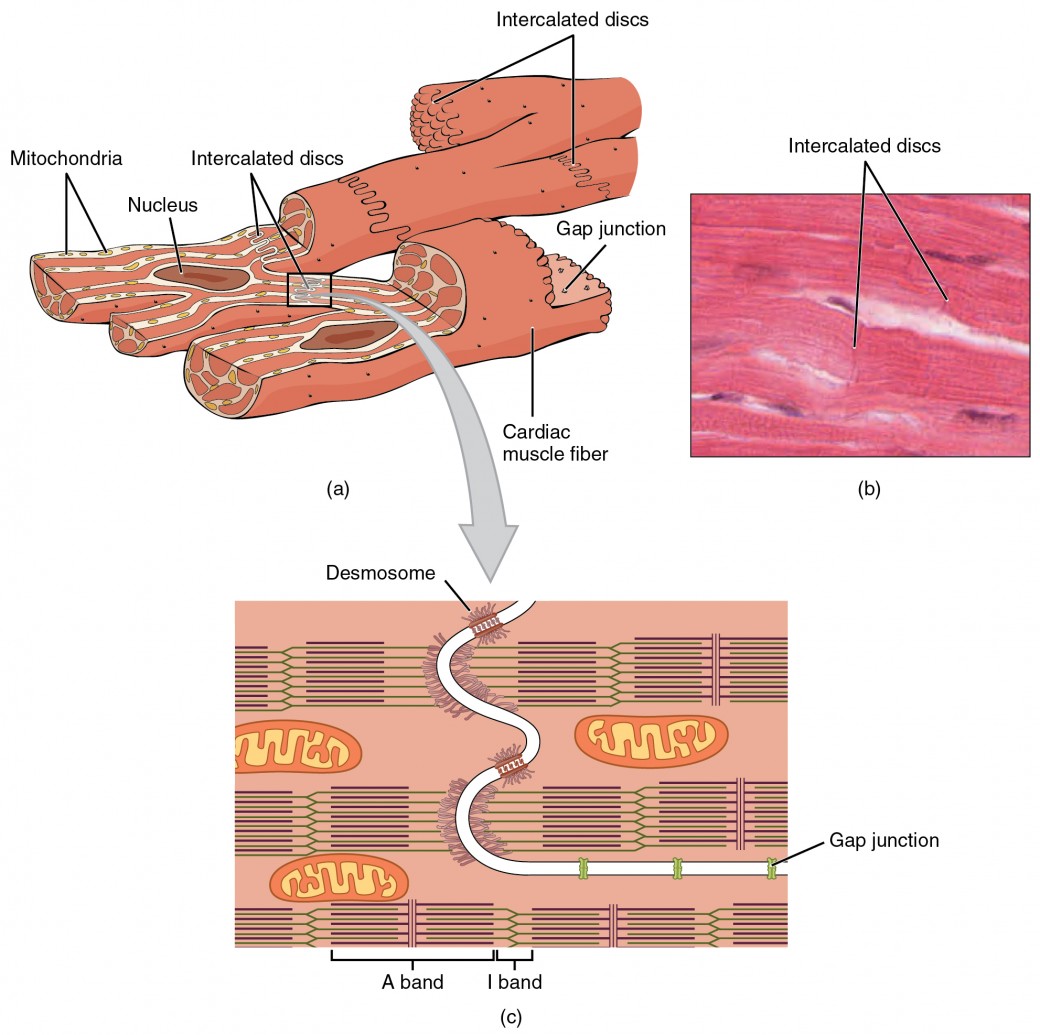
Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology Ii Intercalated discs are part of the sarcolemma and contain two structures important in cardiac muscle contraction: gap junctions and desmosomes. a gap junction forms channels between adjacent cardiac muscle fibers that allow the depolarizing current produced by cations to flow from one cardiac muscle cell to the next. The distributions of these main cell types, estimated from nuclei data, differ between atrial and ventricular tissues. atrial tissues contain 30.1% cardiomyocytes, 24.3% fbs, 17.1% mural cells. Learn how cardiac muscle tissue differs from skeletal and smooth muscle tissue, and how it works to pump blood through your body. find out what cardiomyopathy is, how it affects your heart, and how exercise can help prevent it. A desmosome is a cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers together so the cells do not pull apart during the stress of individual fibers contracting (figure 2). figure 2. cardiac muscle. intercalated discs are part of the cardiac muscle sarcolemma and they contain gap junctions and desmosomes. contractions of the heart.
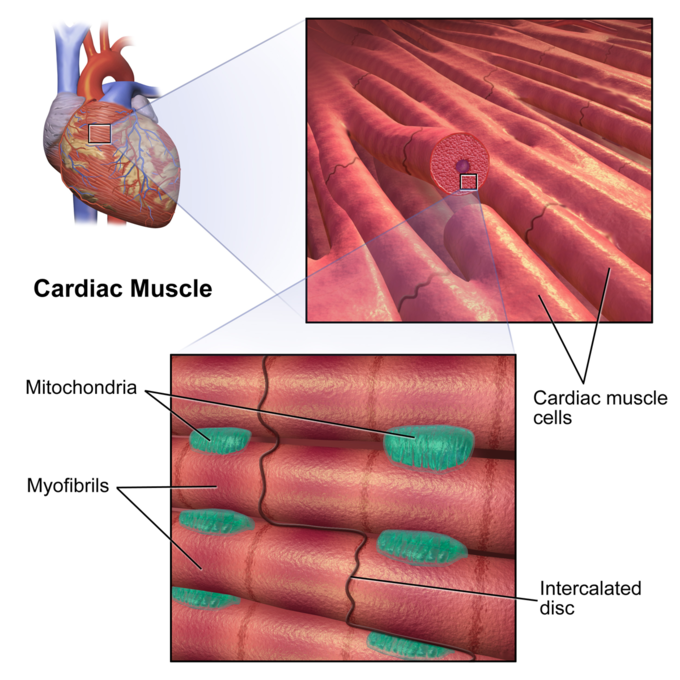
17 1f Myocardial Thickness And Function Medicine Libretexts Learn how cardiac muscle tissue differs from skeletal and smooth muscle tissue, and how it works to pump blood through your body. find out what cardiomyopathy is, how it affects your heart, and how exercise can help prevent it. A desmosome is a cell structure that anchors the ends of cardiac muscle fibers together so the cells do not pull apart during the stress of individual fibers contracting (figure 2). figure 2. cardiac muscle. intercalated discs are part of the cardiac muscle sarcolemma and they contain gap junctions and desmosomes. contractions of the heart.

Comments are closed.