Cardiac Muscle Characteristics Functions And Location Preview

Cardiac Muscle Characteristics Functions And Location Preview Cardiac muscle is the main type of tissue found in the human heart. watch the full video here to learn everything about histology of cardiac muscle:. Cardiac muscle is found in the walls of the heart. it helps the heart perform its function of pumping blood throughout the body. cardiac muscle tissue is located in the middle of three layers of the heart, called the myocardium. problems in the myocardium can cause heart failure and arrhythmias or contribute to sudden cardiac death.

Labeled Diagram Of Cardiac Muscle These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle cells. these cells, unlike skeletal muscle cells, are typically unicellular and connect to one another through special intercalated discs. Introduction. cardiac muscle also called the myocardium, is one of three major categories of muscles found within the human body, along with smooth muscle and skeletal muscle. cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, is made up of sarcomeres that allow for contractility. however, unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is under involuntary control. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in your heart. it performs involuntary, coordinated contractions that allow your heart to pump blood through your circulatory system. cardiac muscle tissue is. Cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. it is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle. the myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. coronary arteries supply to the cardiac muscle, and cardiac veins drain this blood. cardiomyocytes are the.

Cardiac Muscle Definition Function Structure Britannica Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in your heart. it performs involuntary, coordinated contractions that allow your heart to pump blood through your circulatory system. cardiac muscle tissue is. Cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. it is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle. the myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. coronary arteries supply to the cardiac muscle, and cardiac veins drain this blood. cardiomyocytes are the. Cardiac muscle also demonstrates striations, the alternating pattern of dark a bands and light i bands attributed to the precise arrangement of the myofilaments and fibrils that are organized in sarcomeres along the length of the cell (figure 17.3.1 17.3. 1 .a). these contractile elements are virtually identical to skeletal muscle. Characteristics. cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues. it is capable of strong, continuous, and rhythmic contractions that are automatically generated.
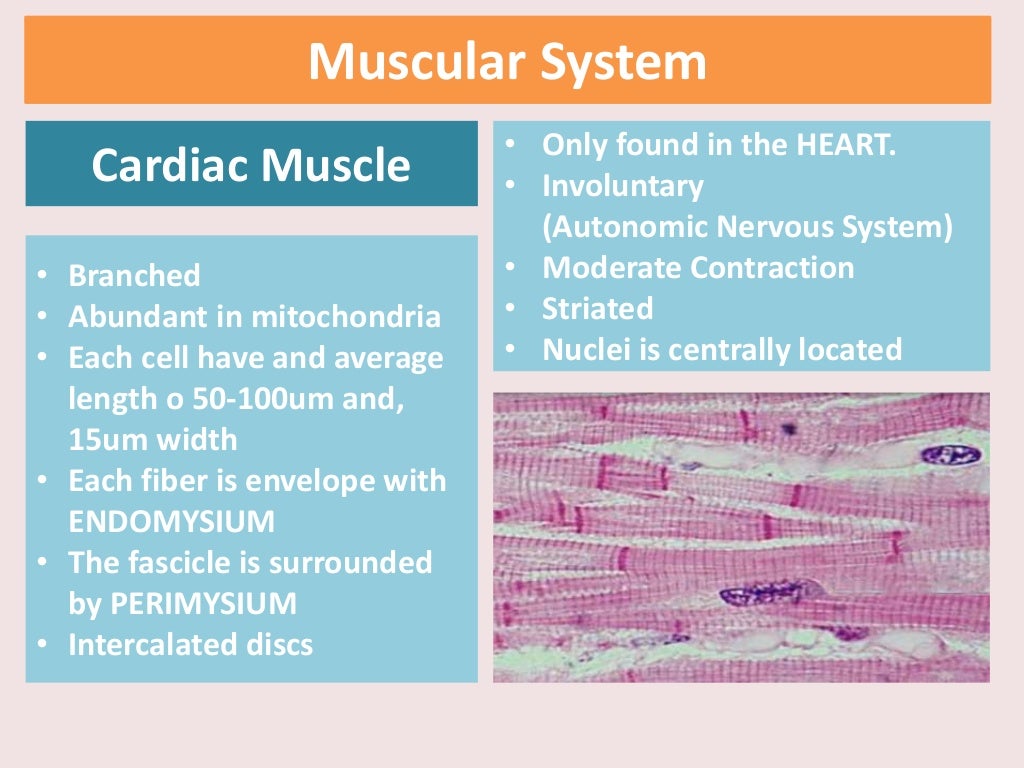
Muscular System The Cardiac Muscle Heart Cardiac muscle also demonstrates striations, the alternating pattern of dark a bands and light i bands attributed to the precise arrangement of the myofilaments and fibrils that are organized in sarcomeres along the length of the cell (figure 17.3.1 17.3. 1 .a). these contractile elements are virtually identical to skeletal muscle. Characteristics. cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues. it is capable of strong, continuous, and rhythmic contractions that are automatically generated.

Comments are closed.