Cardiac Muscle Function Rajus Biology
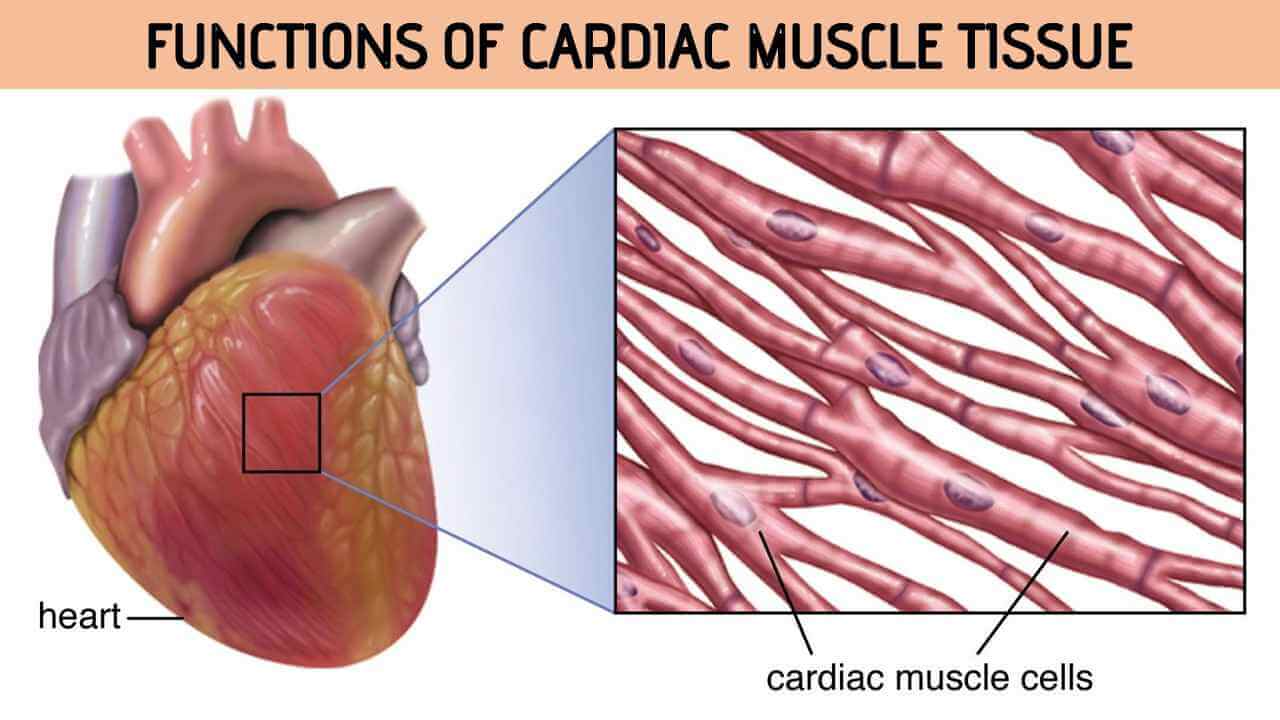
Cardiac Muscle Function Rajus Biology Cardiac muscle function. cardiac muscle tissue helps to keep your heart pumping through involuntary movements. it also helps in the flow of blood. they regulate the contraction and relaxation of the heart, which helps in pumping blood through the circulatory system. the cardiac muscle tissue works without stopping, day and night. Cardiac muscle definition. cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. these inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs. cardiac muscle is made from sheets of cardiac muscle.

Ppt Cardiac Muscle And Heart Function Powerpoint Presentation Free Skeletal muscle function. skeletal muscle is responsible for all voluntary actions of the body. by pulling on tendons, they then produce movement of the skeleton. maintaining posture and body position. support soft tissues and store nutrient reserves. skeletal muscles protect the internal organs from injury. There are three types of muscle tissues in animal. skeletal muscle. cardiac muscle. smooth muscle. 3 types of muscle tissue. 1. skeletal muscle. skeletal muscles are attached to the skeleton. they are also known as striated muscles because of the presence of alternate patterns of light and dark bands. Introduction. cardiac muscle also called the myocardium, is one of three major categories of muscles found within the human body, along with smooth muscle and skeletal muscle. cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, is made up of sarcomeres that allow for contractility. however, unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is under involuntary control. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle (figure 10.21). however, cardiac muscle.
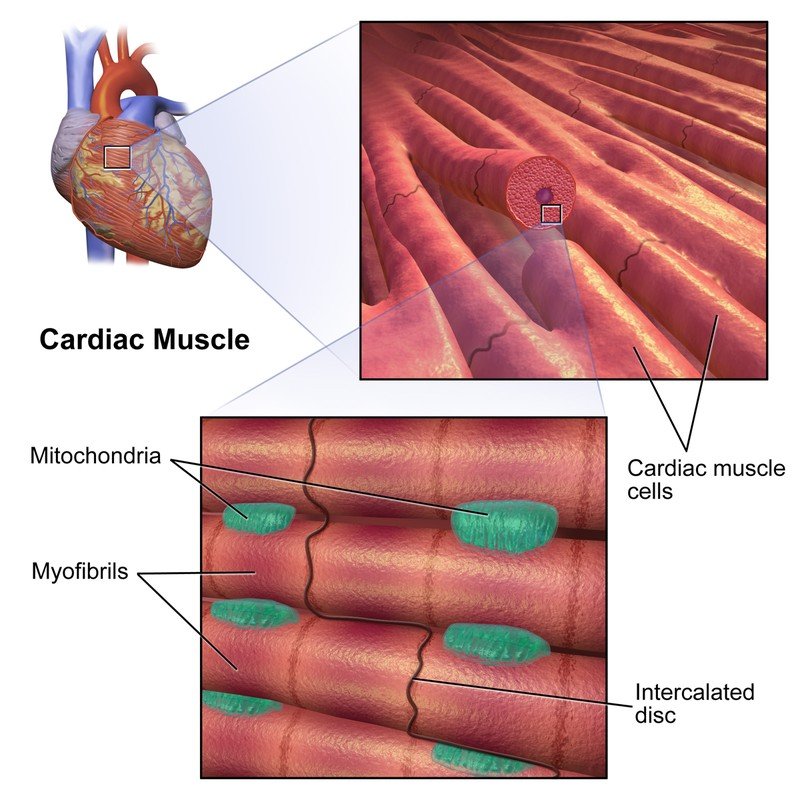
Human Body Muscles Functions Classification And Significance Introduction. cardiac muscle also called the myocardium, is one of three major categories of muscles found within the human body, along with smooth muscle and skeletal muscle. cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, is made up of sarcomeres that allow for contractility. however, unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is under involuntary control. Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal muscle (figure 10.21). however, cardiac muscle. Another feature that is unique to cardiac muscle tissue is autorhythmicity. cardiac muscle tissue is able to set its own contraction rhythm due to the presence of pacemaker cells that stimulate the other cardiac muscle cells. the pacemaker cells normally receive inputs from the nervous system to increase or decrease the heart rate depending on. Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. an intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. cardiac muscle tissue. cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.
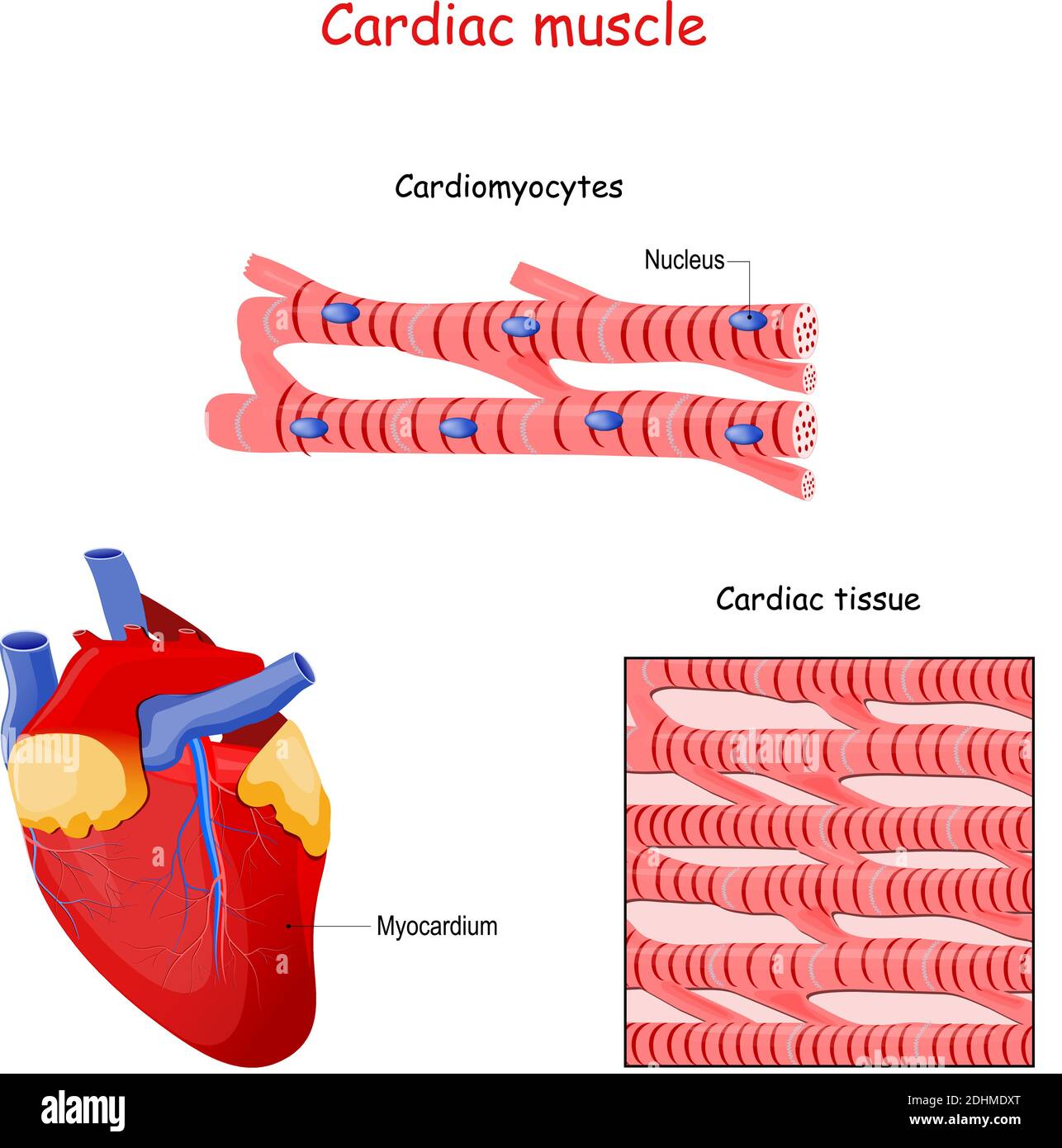
Cardiac Muscle Tissue Anatomy Another feature that is unique to cardiac muscle tissue is autorhythmicity. cardiac muscle tissue is able to set its own contraction rhythm due to the presence of pacemaker cells that stimulate the other cardiac muscle cells. the pacemaker cells normally receive inputs from the nervous system to increase or decrease the heart rate depending on. Cardiac muscle fibers cells also are extensively branched and are connected to one another at their ends by intercalated discs. an intercalated disc allows the cardiac muscle cells to contract in a wave like pattern so that the heart can work as a pump. cardiac muscle tissue. cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart.

Cardiac Muscle Definition Function Structure Britannica

Comments are closed.