Cartesian Product Of Sets Relations In Discrete Mathematics Xii Nd A
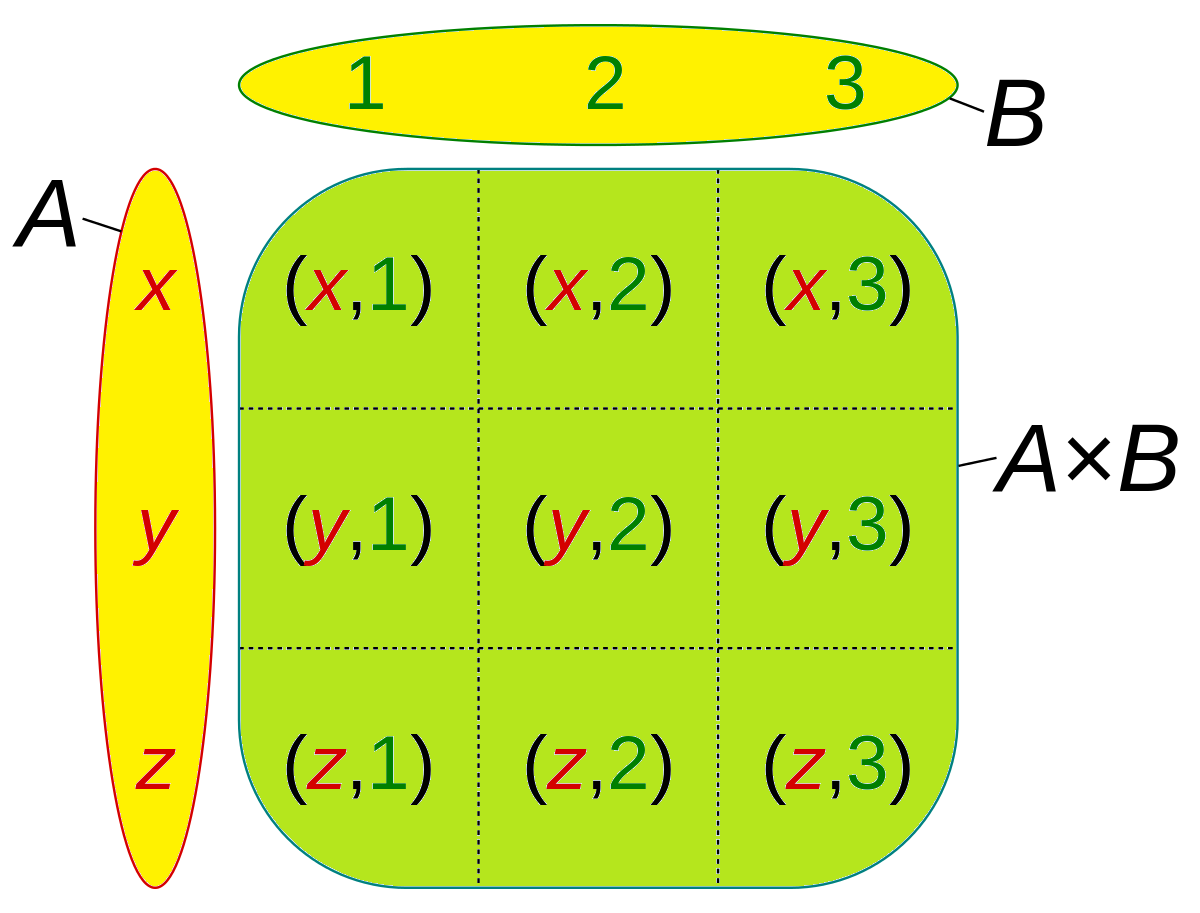
Cartesian Product Of Two Sets Cartesian products. definition 1.3.1: cartesian product. let a and b be sets. the cartesian product of a and b, denoted by a × b, is defined as follows: a × b = {(a, b) ∣ a ∈ a and b ∈ b}, that is, a × b is the set of all possible ordered pairs whose first component comes from a and whose second component comes from b. Cartesian products can be extended to more than two sets. instead of ordered pairs, we need ordered \(n\) tuples . the \(n\) fold cartesian product of \(n\) sets \(a 1, a 2, \ldots, a n\) is the set.

Cartesian Product Of Sets Relations In Discrete Mathematics Xii Nd A We can define the cartesian product of three (or more) sets similarly. for example, \ (a \times b \times c = \ { (a, b, c):a \in a, b \in b, c \in c\}\text {.}\) it is common to use exponents if the sets in a cartesian product are the same: \begin {equation*} a^2= a \times a \end {equation*} \begin {equation*} a^3=a \times a \times a \end. There is one more way to combine sets which will be useful for us: the cartesian product, \(a \times b\text{.}\) this sounds fancy but is nothing you haven't seen before. when you graph a function in calculus, you graph it in the cartesian plane. this is the set of all ordered pairs of real numbers \((x,y)\text{.}\). Definition: cartesian product. if a and b are sets, then the cartesian product, a × b, of a and b is the set of all ordered pairs ( x, y) where x ∈ a and y ∈ b. we use the notation a × b for the cartesian product of a and b, and using set builder notation, we can write. a × b = {(x, y) | x ∈ a and y ∈ b}. Cartesian product. the cartesian product of two or more sets is the set of all ordered pairs n tuples of the sets. it is most commonly implemented in set theory. in addition to this, many real life objects can be represented by using cartesian products such as a deck of cards, chess boards, computer images, etc.

Discrete Mathematics Cartesian Product And Sets 26 Youtube Definition: cartesian product. if a and b are sets, then the cartesian product, a × b, of a and b is the set of all ordered pairs ( x, y) where x ∈ a and y ∈ b. we use the notation a × b for the cartesian product of a and b, and using set builder notation, we can write. a × b = {(x, y) | x ∈ a and y ∈ b}. Cartesian product. the cartesian product of two or more sets is the set of all ordered pairs n tuples of the sets. it is most commonly implemented in set theory. in addition to this, many real life objects can be represented by using cartesian products such as a deck of cards, chess boards, computer images, etc. Basic building block for types of objects in discrete mathematics. set operations in programming languages: issues about data structures used to represent sets and the computational cost of set operations. set theory is the foundation of mathematics. many different systems of axioms have been proposed. zermelo fraenkel set theory (zf) is standard. The idea of a cartesian product of two sets introduced in chapter 3 is a very powerful one, and will enable us to considerably extend the range of applications we can model. example 4.1 in a modula 2 program, several procedures proc 1, proc 2, proc 3, …, are defined.

Cartesian Product Definition Properties Examples Cartesian Basic building block for types of objects in discrete mathematics. set operations in programming languages: issues about data structures used to represent sets and the computational cost of set operations. set theory is the foundation of mathematics. many different systems of axioms have been proposed. zermelo fraenkel set theory (zf) is standard. The idea of a cartesian product of two sets introduced in chapter 3 is a very powerful one, and will enable us to considerably extend the range of applications we can model. example 4.1 in a modula 2 program, several procedures proc 1, proc 2, proc 3, …, are defined.

Comments are closed.