Cell Biology вђ Cells Tissues Organs Systems Cell Biology Cells
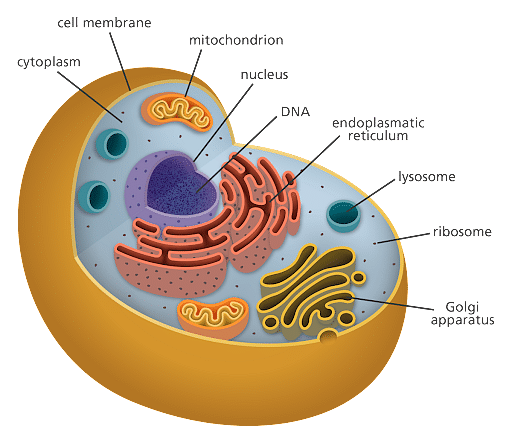
Major Differences Between Plant Animal And Bacterial Cells Humans and other complex multicellular organisms are made up of nested, interacting systems: specialized cells make up tissues. tissues make up organs. organs make up organ systems. because of the way these different levels build on each other, we say that multicellular organisms have a hierarchical organization. The body has levels of organization that build on each other. cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, and organs make up organ systems. the function of an organ system depends on the integrated activity of its organs. for instance, digestive system organs cooperate to process food. the survival of the organism depends on the integrated.

Cell Biology Mit Department Of Biology There are four basic types of tissue in the human body: epithelial, muscle, nerve and connective. epithelial tissue covers the exterior of the body as well as the linings of the organs and cavities of the body. muscle tissue contains cells that are sometimes called “excitable” because they are able to contract and enable movement. A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones. involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body. a muscle that is not under conscious control. a muscle that is under conscious control. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like cell, tissue, organ and more. The first person to observe cells as microscopic structures was the british scientist robert hooke. in fact, he was the person who gave cells their name. in his book micrographia, he used the term cell to refer to the box like structures he saw when he looked at dead cork tissue through a simple microscope 1 . Muscle tissue is made up of cells that have the unique ability to contract or become shorter. there are three major types of muscle tissue, as pictured in figure 10.3.14 10.3. 14: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissues. skeletal muscles are striated, or striped in appearance, because of their internal structure.

Cell Tissue Organ System Chart The first person to observe cells as microscopic structures was the british scientist robert hooke. in fact, he was the person who gave cells their name. in his book micrographia, he used the term cell to refer to the box like structures he saw when he looked at dead cork tissue through a simple microscope 1 . Muscle tissue is made up of cells that have the unique ability to contract or become shorter. there are three major types of muscle tissue, as pictured in figure 10.3.14 10.3. 14: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissues. skeletal muscles are striated, or striped in appearance, because of their internal structure. Cell, in biology, the basic membrane bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. a single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. these cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become. An organ is a group of tissues that has a specific function or group of functions. organs can be as primitive as the brain of a flatworm (a group of nerve cells), as large as the stem of a sequoia (up to 90 meters, or 300 feet, in height), or as complex as a human liver. the most complex organisms (such as mammals, trees, and flowers) have.

Comments are closed.