Cell Structure And Function Biology
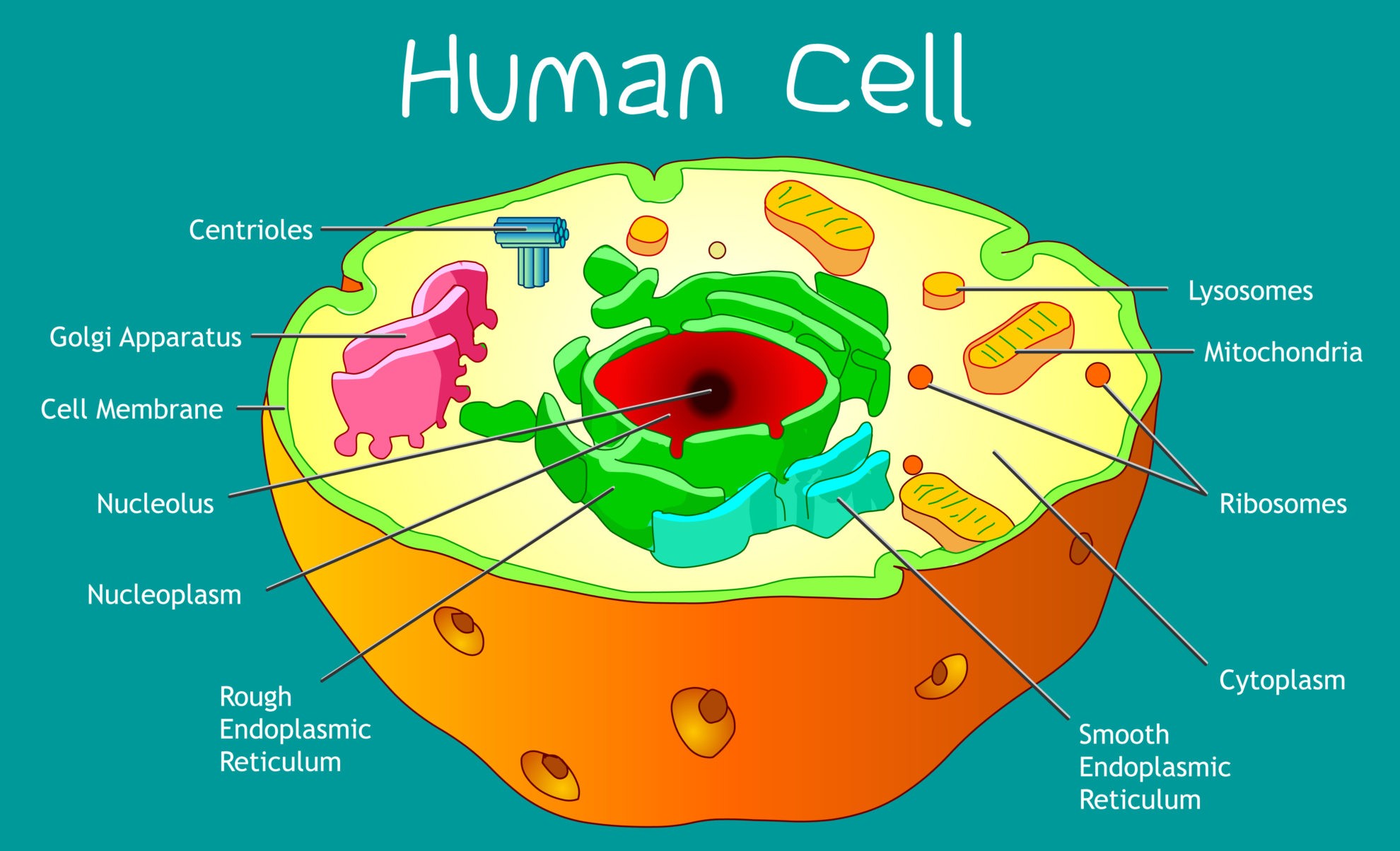
Cell Structure Biology Online Tutorial Cell structures and their functions. a cell is like a whole city. it has a power plant, a post office, and even public transportation. learn. introduction to the cell. organelles in eukaryotic cells. intro to eukaryotic cells. endoplasmic reticulum and golgi bodies. endomembrane system. Cell, in biology, the basic membrane bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. a single cell may be a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium, or it may acquire a specialized function, becoming a building block of a multicellular organism.

Cell Biology в Resources в Surfnetkids 1. description of cell structure and function. cells are fundamental to the study of biology. every living thing is composed of cells, they are the building blocks of life. all cells share similar characteristics and can be defined by the cell theory. cell theory . 1. all living things are composed of cells. 2. all cells arise from preexisting. A cell has three main parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. the cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls the substances that go into and out of the cell. the nucleus is a structure inside the cell that contains the nucleolus and most of the cell's dna. it is also where most rna is made. Cell biology. cell biology is the study of cell structure and function, and it revolves around the concept that the cell is the fundamental unit of life. focusing on the cell permits a detailed. Organelle. function. flagella. whip tail like structure that helps propel the cell forward. cilia. short, hair like structure that surround the cell and help it move. pseudopodia. extension of cytoplasm into the cell membrane that allows the cell to “crawl”. image modified from openstax college, biology, cc by 4.0.

Simple Eukaryotic Cell Structure Cell biology. cell biology is the study of cell structure and function, and it revolves around the concept that the cell is the fundamental unit of life. focusing on the cell permits a detailed. Organelle. function. flagella. whip tail like structure that helps propel the cell forward. cilia. short, hair like structure that surround the cell and help it move. pseudopodia. extension of cytoplasm into the cell membrane that allows the cell to “crawl”. image modified from openstax college, biology, cc by 4.0. Bone cells help to support and protect the body. cells of the immune system fight invading bacteria. additionally, red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body. each of these cell types plays a vital role during the growth, development, and day to day maintenance of the body. in spite of their enormous variety, however, all cells share. 3.3: eukaryotic cells. at this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time. before discussing the functions of organelles within a eukaryotic cell, let us first examine two important components of the cell.
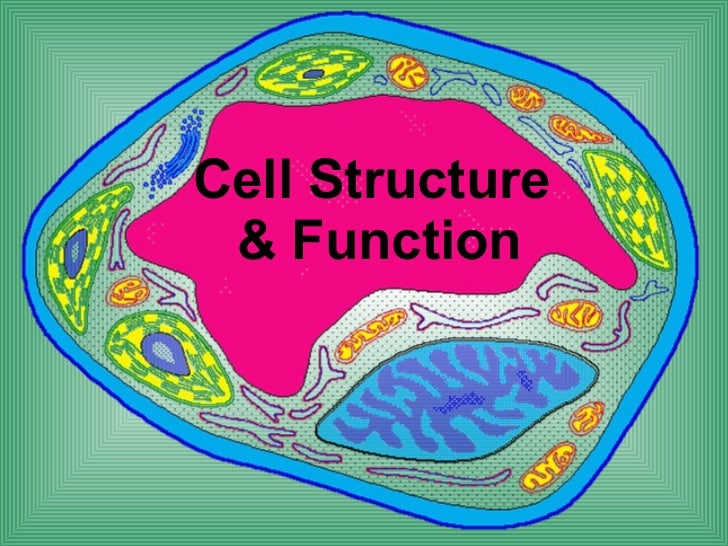
Biology Cell Structure Function Bone cells help to support and protect the body. cells of the immune system fight invading bacteria. additionally, red blood cells carry oxygen throughout the body. each of these cell types plays a vital role during the growth, development, and day to day maintenance of the body. in spite of their enormous variety, however, all cells share. 3.3: eukaryotic cells. at this point, it should be clear that eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than do prokaryotic cells. organelles allow for various functions to occur in the cell at the same time. before discussing the functions of organelles within a eukaryotic cell, let us first examine two important components of the cell.

Comments are closed.