Cellular Respiration In Plants Definition Steps Equation
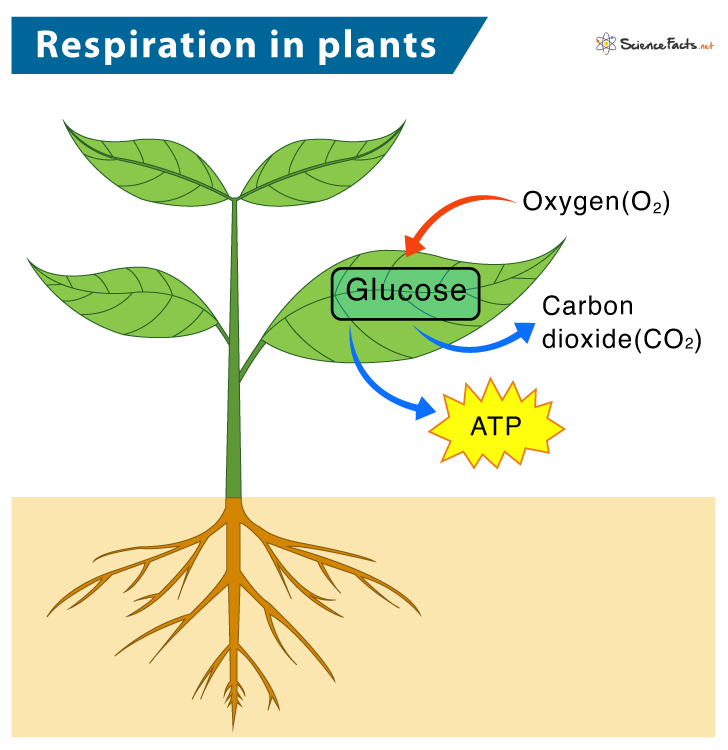
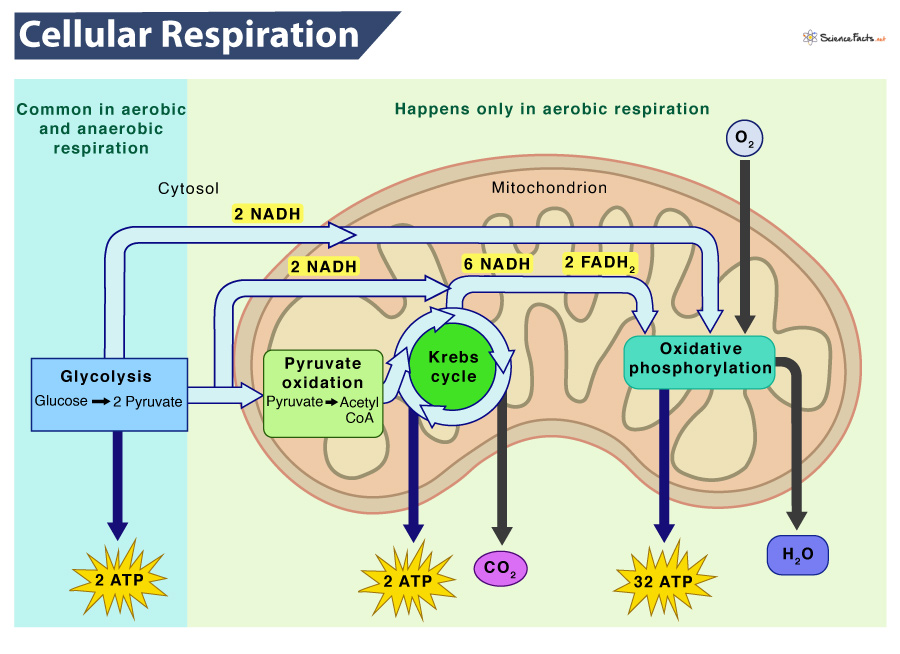
Cellular Respiration In Plants Definition Steps Equation Steps of cellular respiration. cellular respiration is an oxidative process where glucose gets converted into carbon dioxide, yielding atp and nadh fadh 2. the process takes place in four stages. 1) glycolysis: also known as the embden meyerhof parnas pathway, it is the first step of cellular respiration. The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and adp to produce carbon dioxide, water, and atp: c6h12o6 (glucose) 6o2 36 adp (depleted atp) 36 pi (phosphate groups)→ 6co2 6h2o 36 atp. you can see that once it is completely broken down, the carbon molecules of glucose are exhaled as six molecules of.
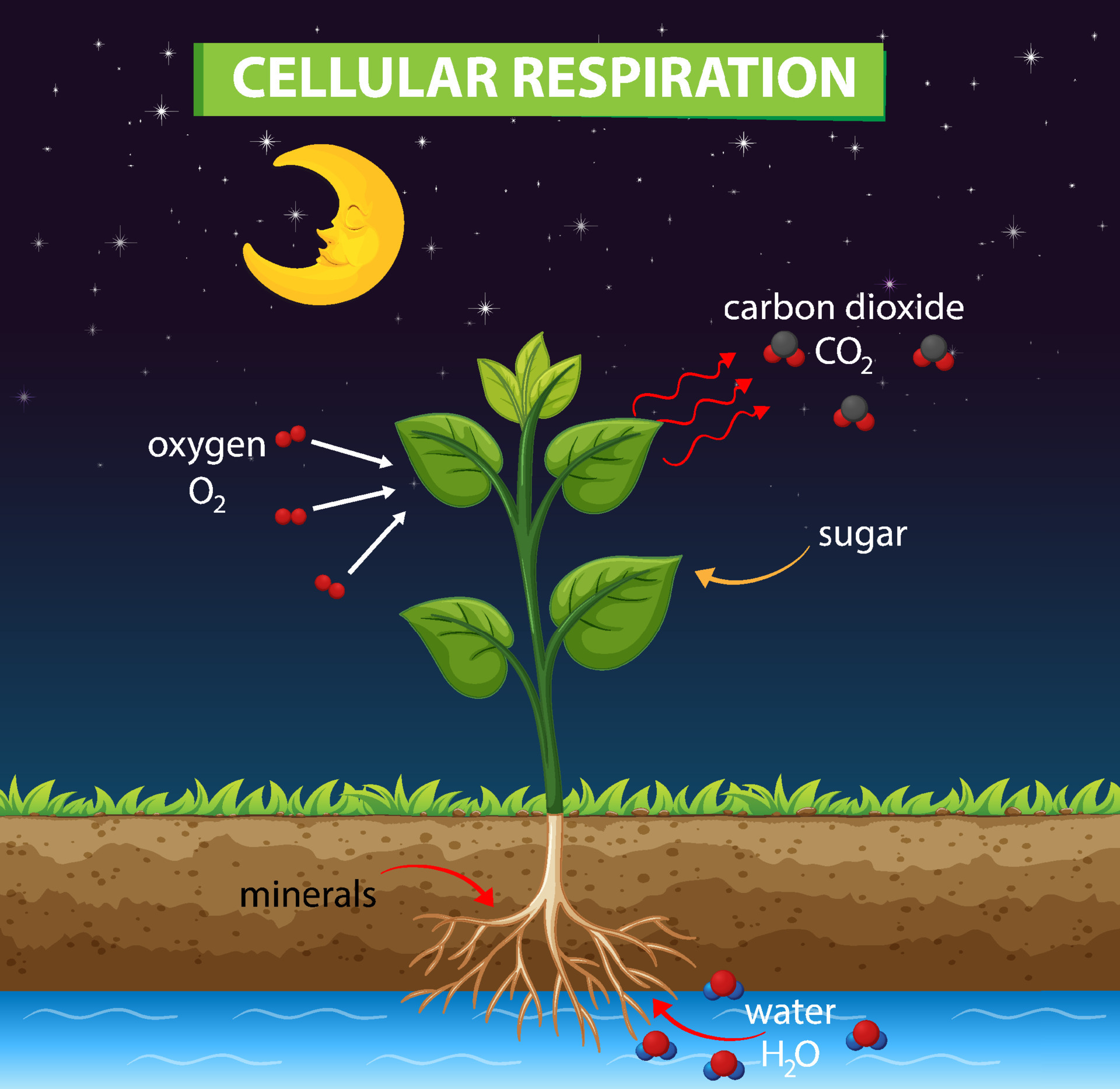
Cellular Respiration In Plants Definition Steps Equat Vrogue Co Cellular respiration, or aerobic respiration, is used by animals and plants to generate energy in the form of atp, with 38 atp molecules released per molecule of glucose metabolized. the successive steps include glycolysis, the krebs cycle and the electron transport chain, in that order. Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. this process releases energy that can be used by the organism to live and grow. many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. glucose is used in cellular respiration. glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration. Steps of cellular respiration. during cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. along the way, some atp is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. much more atp, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. oxidative phosphorylation is powered. Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation.

Bkeyword 0 3 Steps of cellular respiration. during cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water. along the way, some atp is produced directly in the reactions that transform glucose. much more atp, however, is produced later in a process called oxidative phosphorylation. oxidative phosphorylation is powered. Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. Cellular respiration. cellular respiration is a biochemical process of breaking down food, usually glucose, into simpler substances. the energy released in this process is tapped by the cell to drive various energy requiring processes. cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen). Figure 4.1.2.1 4.1.2. 1: the mitochondria are the energy conversion factories of the cell. a mitochondrion is composed of two separate lipid bilayer membranes. the folds of the inner membrane are called cristae, and the space between membranes is the intermembrane space. the matrix is in the center.
Cellular Respiration In Plants Definition Steps Equation Cellular respiration. cellular respiration is a biochemical process of breaking down food, usually glucose, into simpler substances. the energy released in this process is tapped by the cell to drive various energy requiring processes. cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen). Figure 4.1.2.1 4.1.2. 1: the mitochondria are the energy conversion factories of the cell. a mitochondrion is composed of two separate lipid bilayer membranes. the folds of the inner membrane are called cristae, and the space between membranes is the intermembrane space. the matrix is in the center.

The Word Component For The Waste Product Of Respiration Is

Comments are closed.