Cellular Respiration In Plants Diagram вђ Idalias Salon
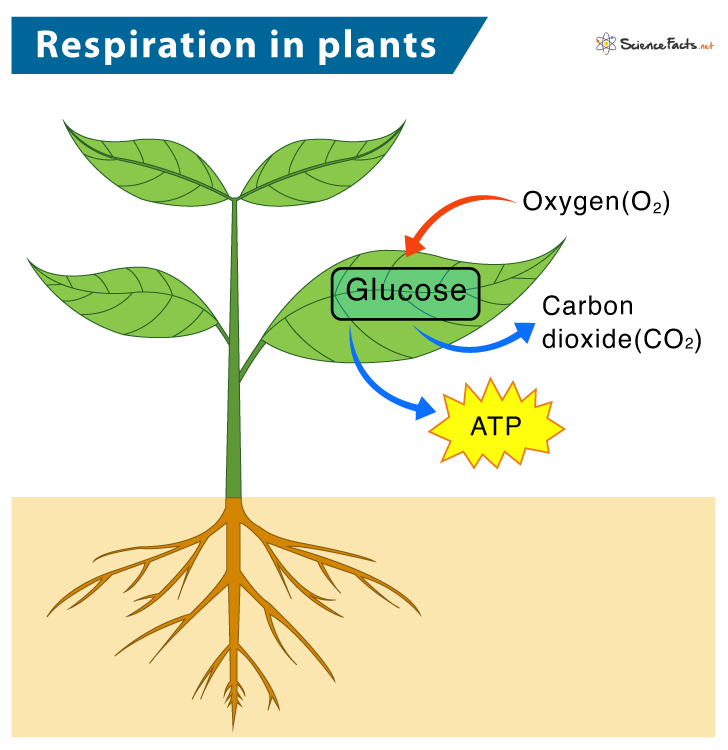
Cellular Respiration In Plants Diagram Steps of cellular respiration. cellular respiration is an oxidative process where glucose gets converted into carbon dioxide, yielding atp and nadh fadh 2. the process takes place in four stages. 1) glycolysis: also known as the embden meyerhof parnas pathway, it is the first step of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a process that happens inside an organism’s cells. this process releases energy that can be used by the organism to live and grow. many food molecules are broken down into glucose, a simple sugar. glucose is used in cellular respiration. glucose and oxygen are inputs of cellular respiration.
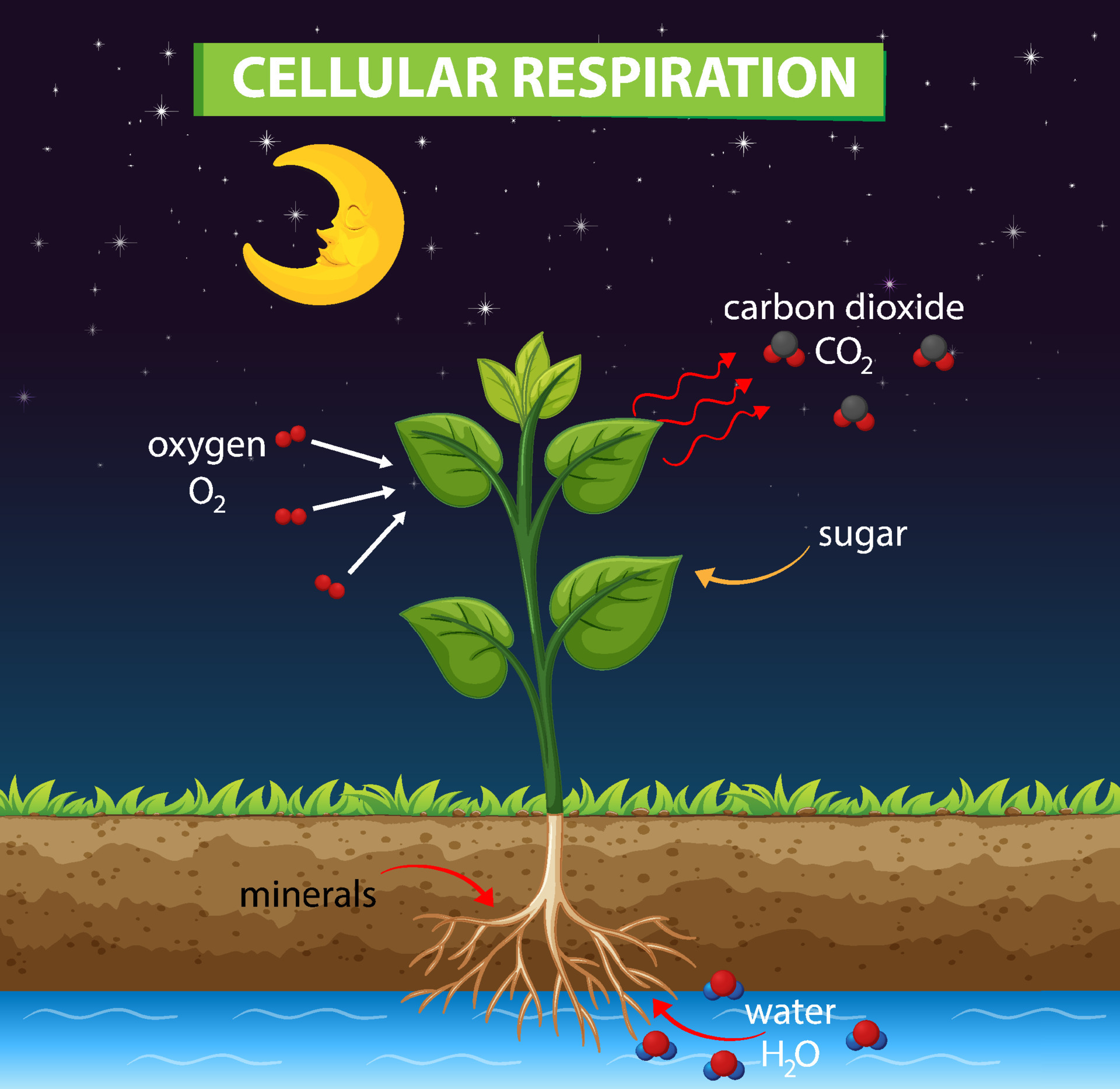
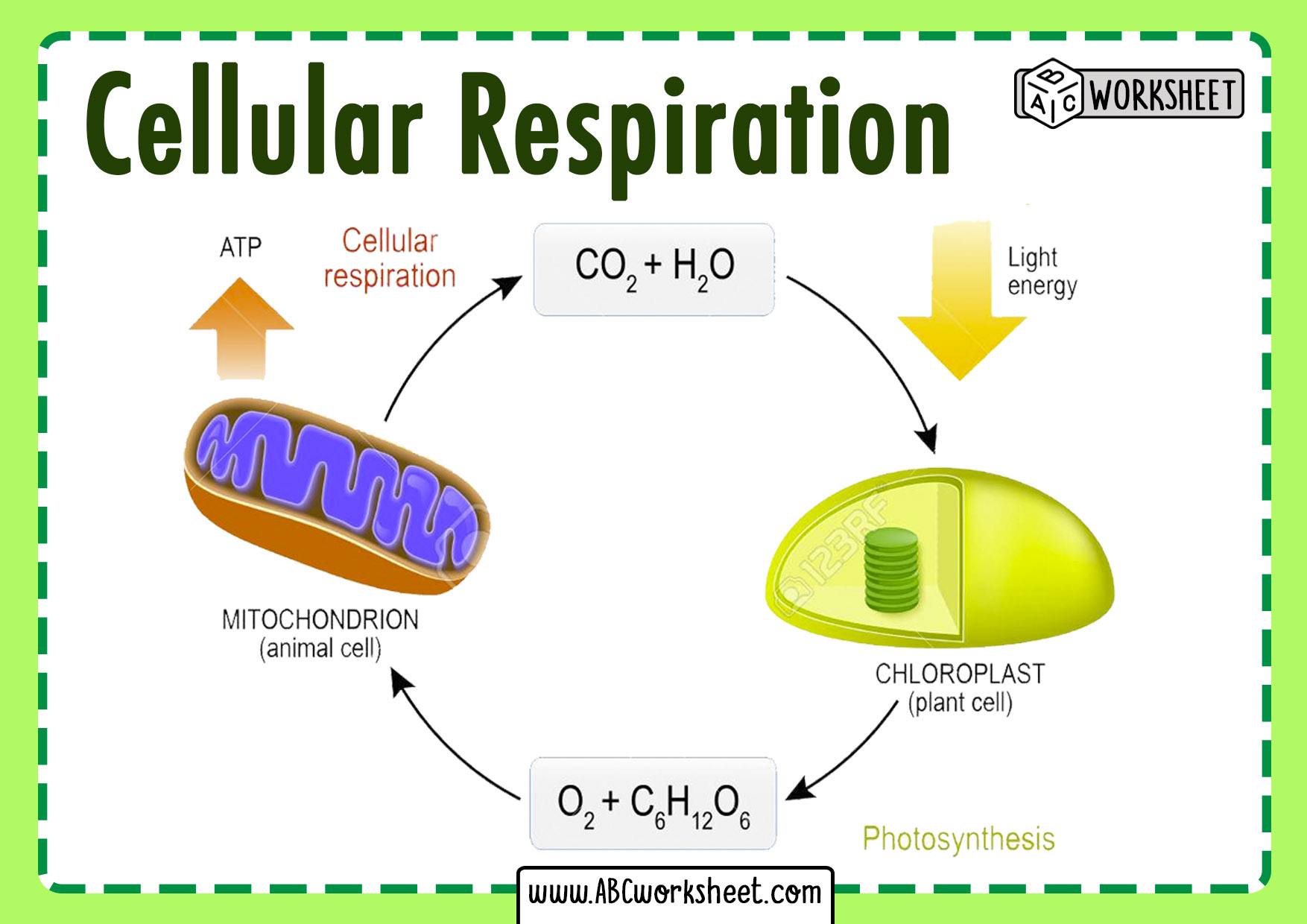
Diagram Showing Cellular Respiration In Plant 7106843 Vector Art At Respiration is a process in which oxidation breaks the carbon carbon (c c) bonds of complex molecules; this process is accompanied by the release of energy. the molecules which are oxidised are known as respiratory substrates. a glucose molecule is the primary respiratory substrate and yields carbon dioxide and water. Cellular respiration. cellular respiration is a biochemical process of breaking down food, usually glucose, into simpler substances. the energy released in this process is tapped by the cell to drive various energy requiring processes. cellular respiration can occur both aerobically (using oxygen), or anaerobically (without oxygen). The outcome of cellular respiration is that the plant takes in glucose and oxygen, gives out carbon dioxide and water and releases energy. plants respire at all times of the day and night because their cells need a constant energy source to stay alive. as well as being used by the plant to release energy via respiration, the glucose produced. The carbon dioxide is again utilized during photosynthesis to continue the cycle. the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration can be best understood using the chemical equations given below: equations. photosynthesis: 6co 2 12h 2 o sunlight → c 6 h 12 o 6 6o 2 6h 2 o. cellular respiration: c 6 h 12 o 6 6o 2 →.
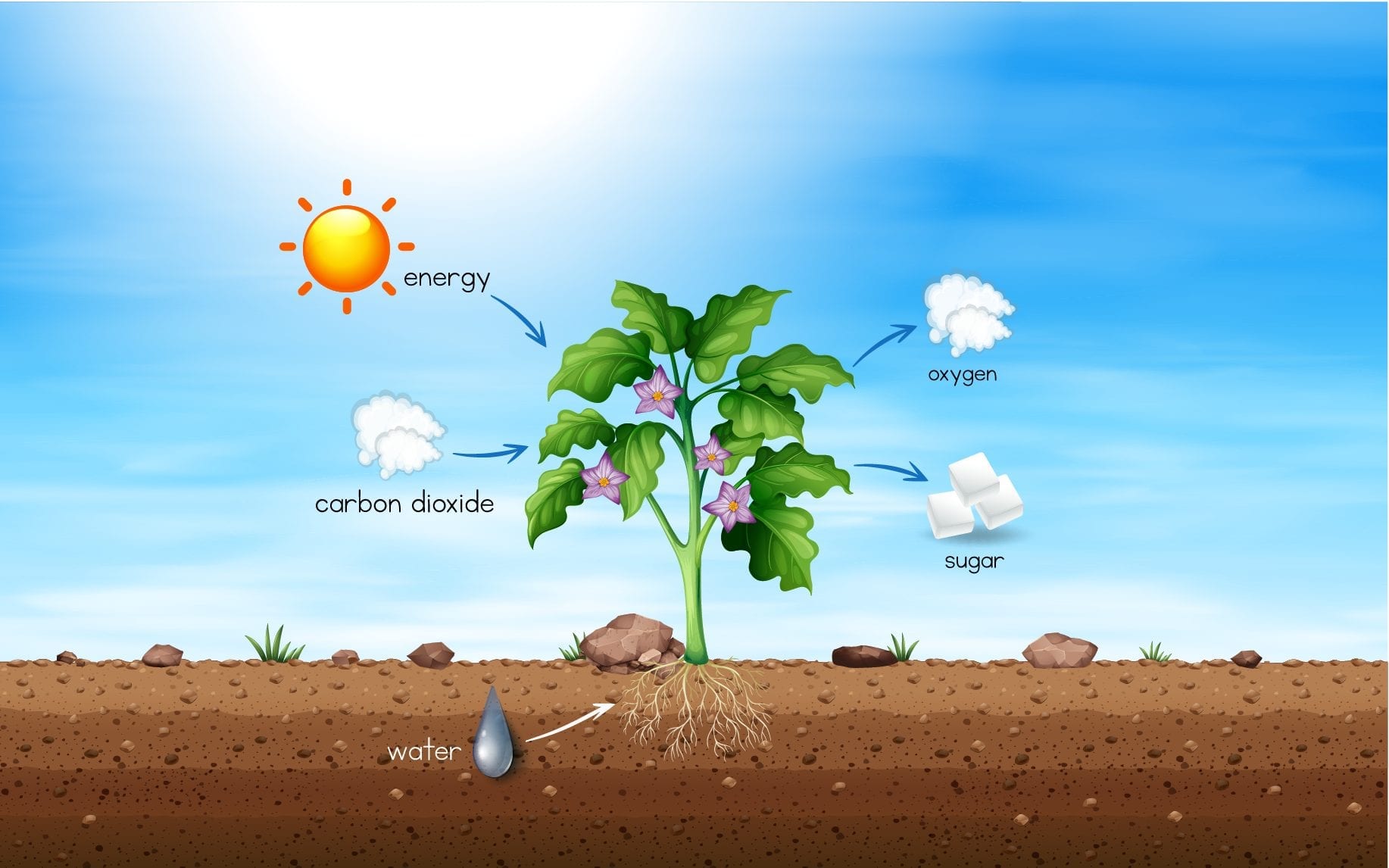
Cellular Respiration In Plants Diagram The outcome of cellular respiration is that the plant takes in glucose and oxygen, gives out carbon dioxide and water and releases energy. plants respire at all times of the day and night because their cells need a constant energy source to stay alive. as well as being used by the plant to release energy via respiration, the glucose produced. The carbon dioxide is again utilized during photosynthesis to continue the cycle. the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration can be best understood using the chemical equations given below: equations. photosynthesis: 6co 2 12h 2 o sunlight → c 6 h 12 o 6 6o 2 6h 2 o. cellular respiration: c 6 h 12 o 6 6o 2 →. The process of respiration in plants. during respiration, in different plant parts, significantly less exchange of gas takes place. hence, each part nourishes and fulfils its own energy requirements. consequently, leaves, stems and roots of plants separately exchange gases. leaves possess stomata – tiny pores, for gaseous exchange. Respiration in plants refers to a process in which a plant utilizes atmospheric oxygen to oxidize glucose and other respiratory substrates like fats or proteins. respiratory substrates are high energy biomolecules that produce energy, carbon dioxide, and water due to the c c bond breaks. plants undergo cellular respiration in the presence or.
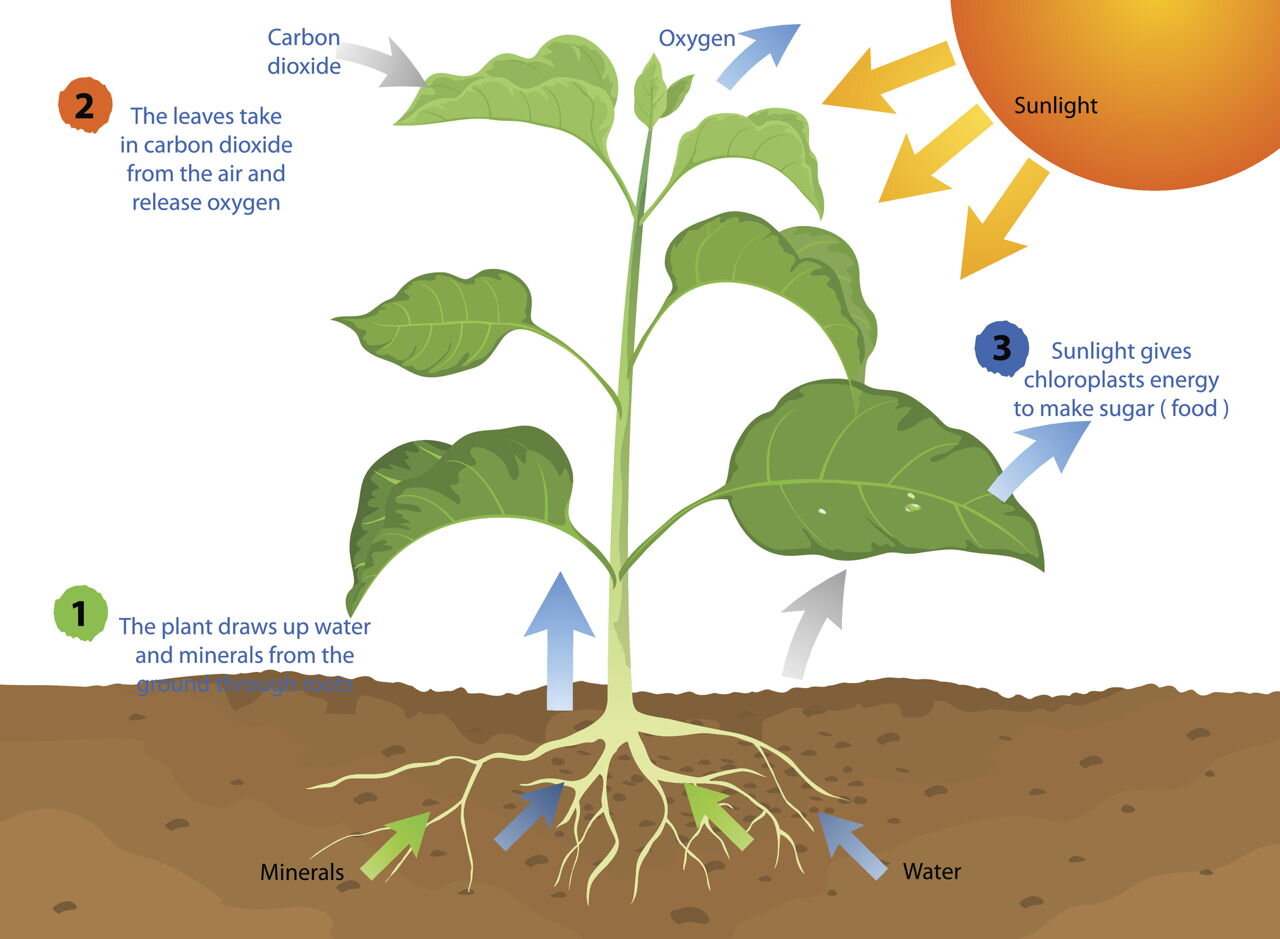
Cellular Respiration In Plants Diagram The process of respiration in plants. during respiration, in different plant parts, significantly less exchange of gas takes place. hence, each part nourishes and fulfils its own energy requirements. consequently, leaves, stems and roots of plants separately exchange gases. leaves possess stomata – tiny pores, for gaseous exchange. Respiration in plants refers to a process in which a plant utilizes atmospheric oxygen to oxidize glucose and other respiratory substrates like fats or proteins. respiratory substrates are high energy biomolecules that produce energy, carbon dioxide, and water due to the c c bond breaks. plants undergo cellular respiration in the presence or.
Cellular Respiration Drawing Animal Plants Vocabulary Activities

Comments are closed.