Chapter 5 Direct Variation

Ppt Chapter 5 Direct Variation Powerpoint Presentation Free Variation – direct variation, inverse variation and joint variation chapter 5.1 sometimes the equation that relates two or more variables can be described in words by the idea of “variation”. there are three types. direct variation; how are distance and rate related?. In your equation, "y = 4x 3 6", for x = 1, 2, and 3, you get y = 4 2 3, 3 1 3, and 2. for x = 1, 2, and 3, y is 7 1 3, 8 2 3, and 10. notice that as x doubles and triples, y does not do the same, because of the constant 6. to quote zblakley from his answer here 5 years ago: "the difference between the values of x and y is not what.
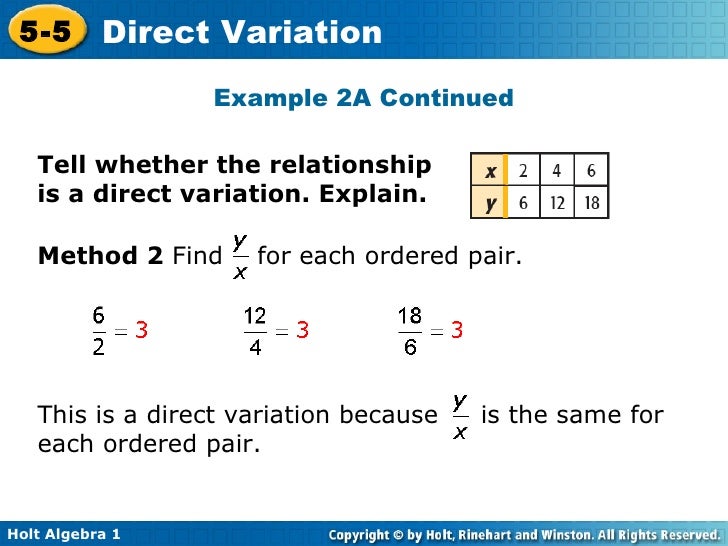
What Is An Example Of Direct Variation Slidesharetrick This is direct variation because one variable, y, varies directly with the other variable, x, which is scaled by a constant, k. y=k*1 x is the only form of inverse variation, although it can look quite different when you apply some algebraic manipulation. for instance, y=k*1 x is the exact same thing as y=k x, or xy=k. For example, if y represents the total cost of buying x items that cost $7 each, then the direct variation equation would be. y = 7x. in this direct variation equation, 7 is the constant of proportionality, which represents the cost per item. and, for example: when x=2, y=14. when x=3, y=21. when x=10, y=70. Chapter 5 direct variation. this document discusses direct variation and how to identify, write equations for, solve, and graph direct variations. it provides examples of identifying direct variations from equations and ordered pairs by checking if the equations are in the form y=kx or if the ratio k is the same for each pair. it also gives. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like is the equation which goes through the points (5, 4) and (5, 4) a direct variation equation, is the equation which goes through the points ( 6,7) and ( 6,7) a direct variation equation, is the equation which goes through the points ( 3, 6) and (3,6) a direct variation equation and more.
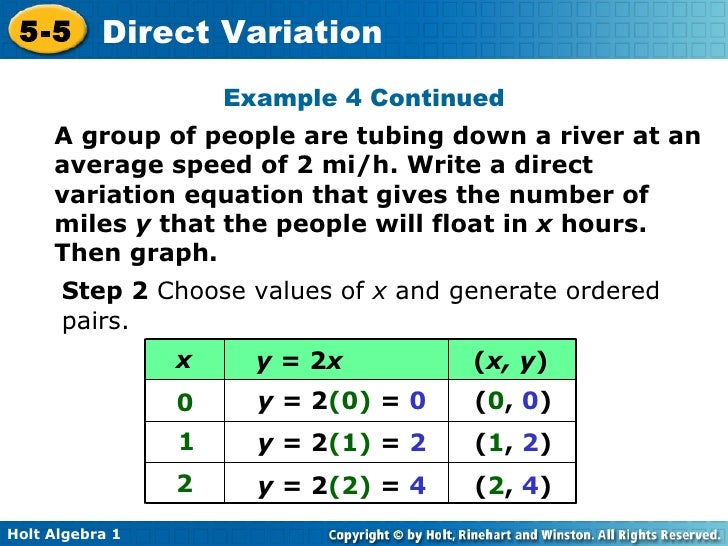
Chapter 5 Direct Variation Chapter 5 direct variation. this document discusses direct variation and how to identify, write equations for, solve, and graph direct variations. it provides examples of identifying direct variations from equations and ordered pairs by checking if the equations are in the form y=kx or if the ratio k is the same for each pair. it also gives. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like is the equation which goes through the points (5, 4) and (5, 4) a direct variation equation, is the equation which goes through the points ( 6,7) and ( 6,7) a direct variation equation, is the equation which goes through the points ( 3, 6) and (3,6) a direct variation equation and more. Definition: inverse variation. for any two variables x and y, y varies inversely with x if. y= k x k x ,where k ≠ 0 k ≠ 0. the word ‘inverse’ in inverse variation refers to the multiplicative inverse. the multiplicative inverse of x is 1 x 1 x. we solve inverse variation problems in the same way we solved direct variation problems. This page titled 7.5: direct and inverse variation is shared under a cc by nc nd 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by david arnold via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform.

Comments are closed.