Chapter 9 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Bio201 Youtube

Chapter 9 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Bio201 Youtube About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright.
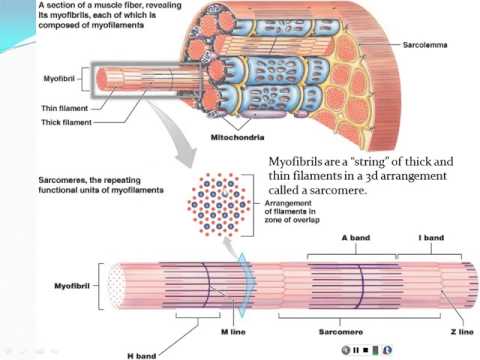
Chapter 9 Skeletal Muscle Part 1 Youtube Skeletal muscle tissue is one of three types of muscle tissue in the human body. the other two types of muscle tissue include cardiac and smooth muscle tissu. In skeletal muscle, this sequence begins with signals from the somatic motor division of the nervous system. in other words, the “excitation” step in skeletal muscles is always triggered by signalling from the nervous system (figure 9.2.4). figure 9.2.4. motor end plate and innervation. at the nmj, the axon terminal releases ach. 4 steps of muscle contraction. 1. nerve stimulation. 2. action potential. 3. action potential reproduces. 4. intracellula calcium level rise. responsiveness. chemical signals stretch and electrical changes across the plasma membrance. conductivity. electrical change triggers a wave of excitement along muscle fiber. Endomysium: around a single muscle fiber (contains capillaries, nerve fibers and satelllite cells) perimysium: around a fascicle (bundle) of fibers (contains blood vessels) epimysium: surrounds all fascicles (exterior collagen layers, connected to deep fascia, seperates muscle from surrounding tissues).
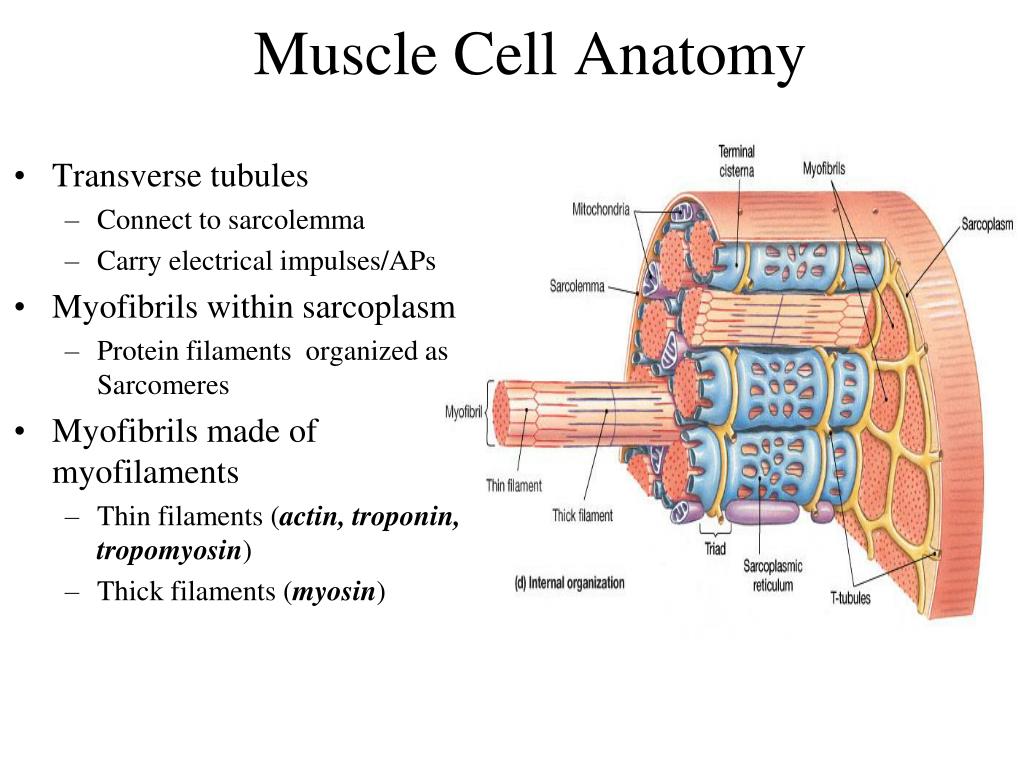
Skeletal Muscle Cell Anatomy 4 steps of muscle contraction. 1. nerve stimulation. 2. action potential. 3. action potential reproduces. 4. intracellula calcium level rise. responsiveness. chemical signals stretch and electrical changes across the plasma membrance. conductivity. electrical change triggers a wave of excitement along muscle fiber. Endomysium: around a single muscle fiber (contains capillaries, nerve fibers and satelllite cells) perimysium: around a fascicle (bundle) of fibers (contains blood vessels) epimysium: surrounds all fascicles (exterior collagen layers, connected to deep fascia, seperates muscle from surrounding tissues). Contraction of the muscle steps. 1. an electrical impulse travels down a nerve fiber. 2. the nerve impulse reaches the end of the nerve and causes it to release acetylcholine. 3. ach binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane and causes the electrical impulse to be transmitted to the muscle cell. 65. 9.2 skeletal muscle. the best known feature of skeletal muscle is its ability to contract and cause movement. skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting gravity to maintain posture. small, constant adjustments of the skeletal muscles are needed to hold a body upright or balanced in any.

Chapter 9 Skeletal Muscle Tissue Diagram Quizlet Contraction of the muscle steps. 1. an electrical impulse travels down a nerve fiber. 2. the nerve impulse reaches the end of the nerve and causes it to release acetylcholine. 3. ach binds to receptors on the muscle cell membrane and causes the electrical impulse to be transmitted to the muscle cell. 65. 9.2 skeletal muscle. the best known feature of skeletal muscle is its ability to contract and cause movement. skeletal muscles act not only to produce movement but also to stop movement, such as resisting gravity to maintain posture. small, constant adjustments of the skeletal muscles are needed to hold a body upright or balanced in any.

Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Youtube

Comments are closed.