Chapter 9 Skeletal Muscle Part 1 Youtube
Chapter 9 Skeletal Muscle Part 1 Youtube About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. We're kicking off our exploration of muscles with a look at the complex and important relationship between actin and myosin. your smooth, cardiac, and skelet.

Chapter 9 Skeletal Muscle Youtube Today hank explains the skeletal system and why astronauts scott kelly and mikhail kornienko are out in space studying it. he talks about the anatomy of the. Chapter 9: muscular system introduction. a body in motion the muscular system allows us to move, flex and manipulate our bodies in space. think about the things that you do each day—talking, walking, sitting, standing, and running—all of these activities require movement of particular skeletal muscles. [goodfon ]. 11.1 interactions of skeletal muscles, their fascicle arrangement, and their lever systems ; 11.2 naming skeletal muscles ; 11.3 axial muscles of the head, neck, and back ; 11.4 axial muscles of the abdominal wall, and thorax ; 11.5 muscles of the pectoral girdle and upper limbs ; 11.6 appendicular muscles of the pelvic girdle and lower limbs. Smooth muscle functions in various involuntary movements, such as having one’s hair stand on end when cold or frightened, or moving food through the digestive system. this chapter will focus on the structure and function of skeletal muscles. figure 9.1.1 9.1. 1: tennis player. athletes rely on toned skeletal muscles to supply the force.

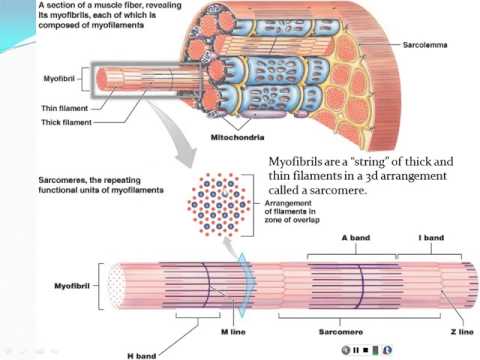
Chapter 9 Structure Of Skeletal Muscles Youtube 11.1 interactions of skeletal muscles, their fascicle arrangement, and their lever systems ; 11.2 naming skeletal muscles ; 11.3 axial muscles of the head, neck, and back ; 11.4 axial muscles of the abdominal wall, and thorax ; 11.5 muscles of the pectoral girdle and upper limbs ; 11.6 appendicular muscles of the pelvic girdle and lower limbs. Smooth muscle functions in various involuntary movements, such as having one’s hair stand on end when cold or frightened, or moving food through the digestive system. this chapter will focus on the structure and function of skeletal muscles. figure 9.1.1 9.1. 1: tennis player. athletes rely on toned skeletal muscles to supply the force. Chapter 9 muscle tissue part 1. get a hint. voluntary muscle tissue. click the card to flip 👆. muscle tissue, usually striated, can be controlled (contracted) consciously by motor commands from cerebral cortex, though some control is maintained by lower centers in cns. click the card to flip 👆. Because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical, they are commonly referred to as muscle fibers. skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large for human cells, with diameters up to 100 μm and lengths up to 30 cm (11.8 in) in the sartorius of the upper leg. during early development, embryonic myoblasts, each with its own nucleus, fuse with.

Chapter 9 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Bio201 Youtube Chapter 9 muscle tissue part 1. get a hint. voluntary muscle tissue. click the card to flip 👆. muscle tissue, usually striated, can be controlled (contracted) consciously by motor commands from cerebral cortex, though some control is maintained by lower centers in cns. click the card to flip 👆. Because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical, they are commonly referred to as muscle fibers. skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large for human cells, with diameters up to 100 μm and lengths up to 30 cm (11.8 in) in the sartorius of the upper leg. during early development, embryonic myoblasts, each with its own nucleus, fuse with.

Comments are closed.