Character Encoding Ascii Unicode Utf 8 Kidchen
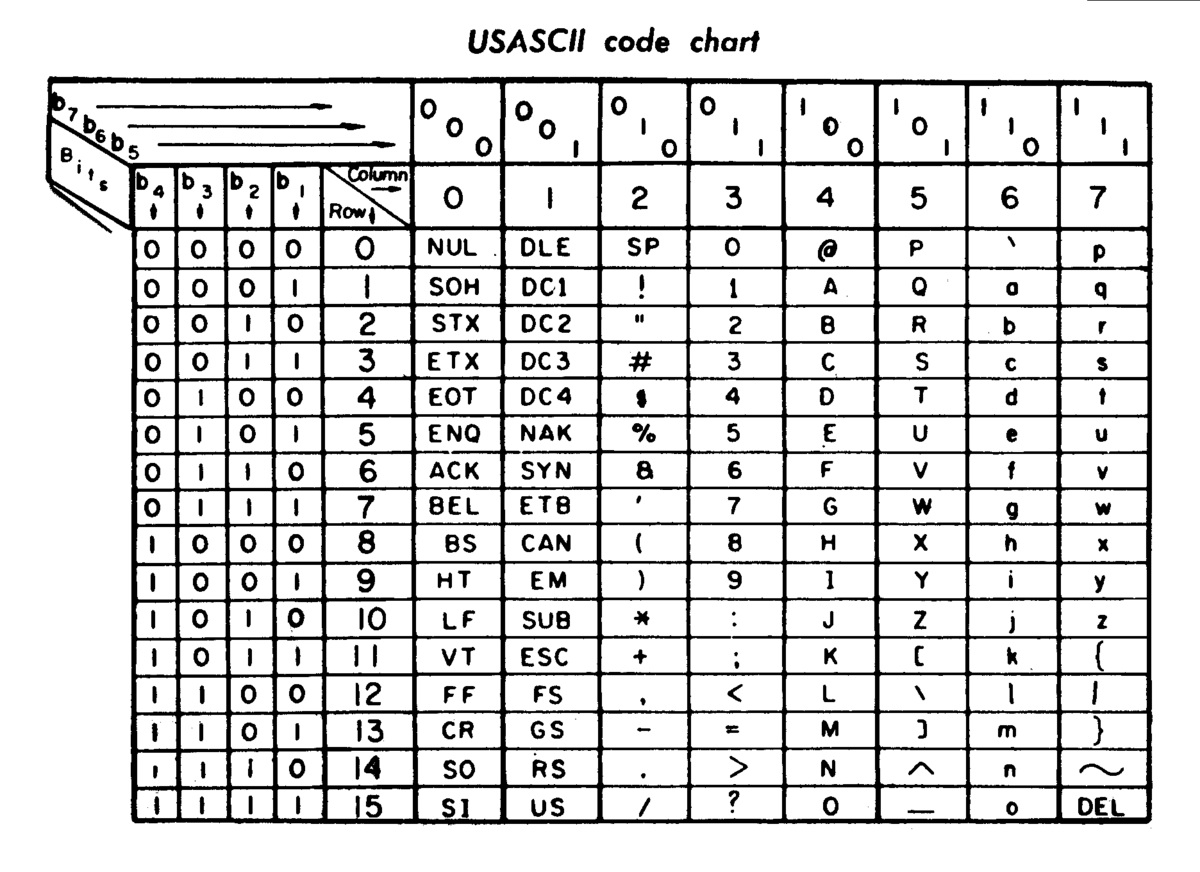
Character Encoding Ascii Unicode Utf 8 Kidchen Utf 8 has become the dominant character encoding for the world wide web. the rule of utf 8 is: (1) if this is in ascii, utf 8 is the same with ascii. (2) for n utf bytes (n > 1), the first n bits in the first byte set as 1, the n 1 bit sets as 0, all the first two bits in the following bytes are all 10. the rest of the bits are represented as. Values outside the basic multilingual plane (bmp) are encoded as surrogate pairs. these used to be relatively rarely used, but now many consumer applications will need to be aware of non bmp characters in order to support emojis. utf 8: variable length encoding, 1 4 bytes per code point. ascii values are encoded as ascii using 1 byte.
Character Encoding Ascii Unicode Utf 8 Kidchen 45 Off Utf 8 is named for how it uses a minimum of 8 bits (or 1 byte) to store the unicode code points. remember that it can still use more bits, but does so only if it needs to. utf 16, in the other. Utf 8 attempts to allow for maximum compatibility with ascii. it's 8 bit, but allows for all of the characters via a substitution mechanism and multiple pairs of values per character. utf 16 ditches perfect ascii compatibility for a more complete 16 bit compatibility with the standard. iso 10646 this isn't an actual encoding, just a character. The encoding of a character in utf 8 starts with a leading byte, which indicates the number of bytes used for that character. the number of high order bits set to 1 in the leading byte tells us. Add to that the figure for ascii only web pages (since ascii is a subset of utf 8), and the figure rises to around 80%. there are three different unicode character encodings: utf 8, utf 16 and utf 32. of these three, only utf 8 should be used for web content. the html5 specification says "authors are encouraged to use utf 8.

Character Encoding Ascii Unicode Utf 8 Kidchen Images The encoding of a character in utf 8 starts with a leading byte, which indicates the number of bytes used for that character. the number of high order bits set to 1 in the leading byte tells us. Add to that the figure for ascii only web pages (since ascii is a subset of utf 8), and the figure rises to around 80%. there are three different unicode character encodings: utf 8, utf 16 and utf 32. of these three, only utf 8 should be used for web content. the html5 specification says "authors are encouraged to use utf 8. Utf 8 encoding: hex. · decimal · hex. (0x) · octal · binary · for perl string literals · one latin 1 char per byte · no display: unicode character names: not displayed · displayed · also display deprecated unicode 1.0 names: links for adding char to text: displayed · not displayed: numerical html encoding of the unicode character. Utf 8, utf 16 and utf 32 are encodings that apply the unicode character table. but they each have a slightly different way on how to encode them. utf 8 will only use 1 byte when encoding an ascii character, giving the same output as any other ascii encoding. but for other characters, it will use the first bit to indicate that a 2nd byte will.

Character Encoding Ascii Unicode Utf 8 Kidchen Images Vrogue Co Utf 8 encoding: hex. · decimal · hex. (0x) · octal · binary · for perl string literals · one latin 1 char per byte · no display: unicode character names: not displayed · displayed · also display deprecated unicode 1.0 names: links for adding char to text: displayed · not displayed: numerical html encoding of the unicode character. Utf 8, utf 16 and utf 32 are encodings that apply the unicode character table. but they each have a slightly different way on how to encode them. utf 8 will only use 1 byte when encoding an ascii character, giving the same output as any other ascii encoding. but for other characters, it will use the first bit to indicate that a 2nd byte will.

Character Encoding Ascii Unicode Utf 8 Kidchen Images Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.