Characteristics Of Cardiac Muscle

Cardiac Muscle Definition Function Structure Britannica Learn about the characteristics of cardiac muscle, the specialized tissue that forms the heart. find out how cardiac muscle cells are connected, how they contract, and how they differ from skeletal muscle. Learn about the role of cardiac muscle tissue in the heart, its structure and function, and the types of conditions that affect it. find out how to keep your heart's muscle tissue healthy and prevent cardiomyopathy.

Ppt Muscle Structure And Function Powerpoint Presentation Id 2195047 Cardiac muscle differs from skeletal muscle in that it exhibits rhythmic contractions and is not under voluntary control. the rhythmic contraction of cardiac muscle is regulated by the sinoatrial node of the heart, which serves as the heart’s pacemaker. the heart consists mostly of cardiac muscle cells (or myocardium). Introduction. cardiac muscle also called the myocardium, is one of three major categories of muscles found within the human body, along with smooth muscle and skeletal muscle. cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, is made up of sarcomeres that allow for contractility. however, unlike skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is under involuntary control. Learn how cardiac muscle tissue differs from skeletal and smooth muscle tissue, and how it works to pump blood through your body. find out about cardiomyopathy, a disease that affects cardiac muscle tissue, and how exercise can help prevent it. Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. it is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. the cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the.

Cardiac Muscle Structure Learn how cardiac muscle tissue differs from skeletal and smooth muscle tissue, and how it works to pump blood through your body. find out about cardiomyopathy, a disease that affects cardiac muscle tissue, and how exercise can help prevent it. Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, the others being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. it is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. the cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the. Learn about the characteristics of cardiac muscle tissue, which forms the heart and contracts involuntarily. find out how cardiac muscle tissue works, what conditions can affect it, and how to keep it healthy. Cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. it is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle. the myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. coronary arteries supply to the cardiac muscle, and cardiac veins drain this blood. cardiomyocytes are the.
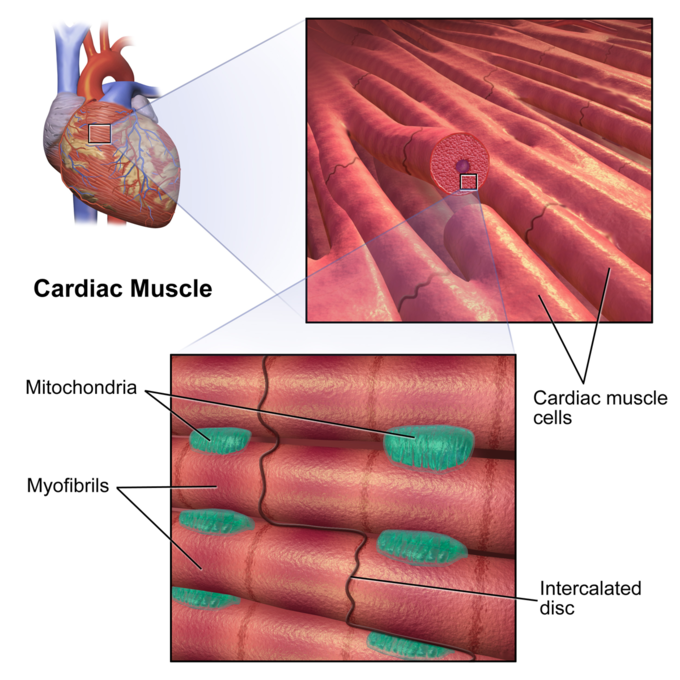
The Heart Boundless Anatomy And Physiology Learn about the characteristics of cardiac muscle tissue, which forms the heart and contracts involuntarily. find out how cardiac muscle tissue works, what conditions can affect it, and how to keep it healthy. Cardiac muscle (or myocardium) makes up the thick middle layer of the heart. it is one of three types of muscle in the body, along with skeletal and smooth muscle. the myocardium is surrounded by a thin outer layer called the epicardium (aka visceral pericardium) and an inner endocardium. coronary arteries supply to the cardiac muscle, and cardiac veins drain this blood. cardiomyocytes are the.

Comments are closed.