Chemical Bonds Flow Chart
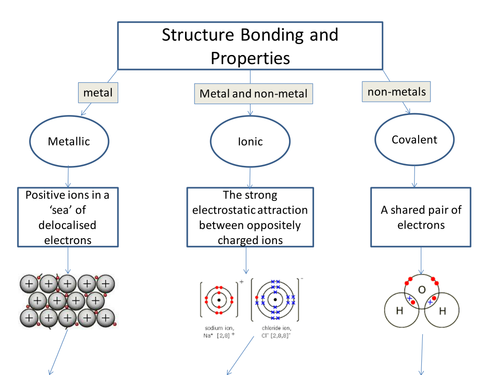
Aqa C2 Structure Bonding And Properties Flowchart By Azdzylowski An ionic bond is the electrostatic attraction formed between ( ) cations and ( ) anions. the cations and anions are formed when a non metal (high en) steals an electron from a metal (low ie). this transfer of electrons gives each atom a filled valence shell (stable octet) of electrons. ionic bonding. Chapter 9 chemical bondingchapter 9 chemical bonding (. h 9 chang, ch 8 jespersen)lewis in 1916 stated that atoms combine to achieve a more sta. le electron configuration.this is achieved “usin. ” the valence electrons.lewis dot structures have one dot. for each valence electron.below are lewis dot symbols for the representative el.

Naming Compounds Flowchart Chemistry Guide A molecule with strong bonds generally has less tendency to undergo chemical change than does one with weak bonds. bond energies and the enthalpy of reactions. Δh = Σ (bond energies of bonds broken) – Σ (bond energies of bonds formed) if Δh > 0, the reaction is endothermic. if Δh < 0, the reaction is exothermic. Chemical bonding is one of the most basic fundamentals of chemistry that explains other concepts such as molecules and reactions. without it, scientists wouldn't be able to explain why atoms are attracted to each other or how products are formed after a chemical reaction has taken place. to understand the concept of bonding, one must first know. Summary. chemical bonding is the general term used to describe the forces that hold atoms together in molecules and ions. three idealized types of bonding are ionic bonding, in which positively and negatively charged ions are held together by electrostatic forces, covalent bonding, in which electron pairs are shared between atoms and metallic bonding where electrons are shared across large. • in chemical bonds, electrons are shared or transferred between atoms. • types of chemical bonds include: • ionic bonds (electrostatic forces that hold ions together, e.g., nacl); • covalent bonds (result from sharing electrons between atoms, e.g., cl2); • metallic bonds (refers to metal nuclei floating in a sea of electrons, e.g.

Chemical Bonding Flow Diagram Teaching Resources Summary. chemical bonding is the general term used to describe the forces that hold atoms together in molecules and ions. three idealized types of bonding are ionic bonding, in which positively and negatively charged ions are held together by electrostatic forces, covalent bonding, in which electron pairs are shared between atoms and metallic bonding where electrons are shared across large. • in chemical bonds, electrons are shared or transferred between atoms. • types of chemical bonds include: • ionic bonds (electrostatic forces that hold ions together, e.g., nacl); • covalent bonds (result from sharing electrons between atoms, e.g., cl2); • metallic bonds (refers to metal nuclei floating in a sea of electrons, e.g. Bond strength is a measure of the energy required to break a bond. covalent bonds can be single (meaning 2 electrons are shared), double (meaning 4 electrons are shared), or triple (meaning 6 electrons are shared). single bonds are the longest and the weakest. triple bonds are the shortest and the strongest. The millions of different chemical compounds that make up everything on earth are composed of 118 elements that bond together in different ways. this module explores two common types of chemical bonds: covalent and ionic. the module presents chemical bonding on a sliding scale from pure covalent to pure ionic, depending on differences in the electronegativity of the bonding atoms. highlights.

Comments are closed.