Chemistry Chemical Change Chemical Equilibrium Graphs Youtube
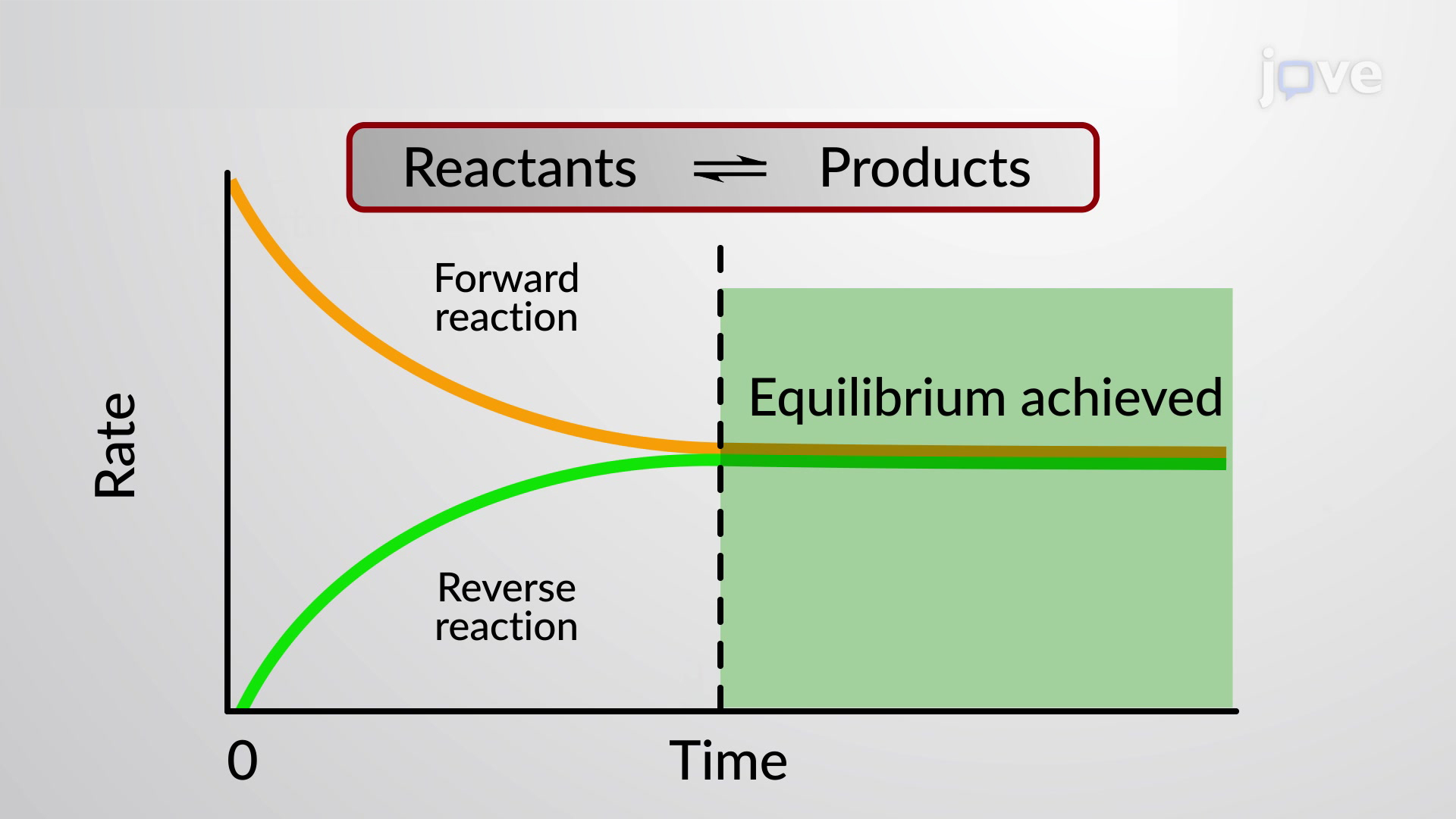
Chemistry A Level Revision Equilibrium This video covers the effect of concentration, temperature and pressure on equilibrium by applying le chartelie's principle. Grade 12 chemical change explanations on how to interpret equilibrium graphs. about.

Physical And Chemical Changes Chemistry Quizizz In this lesson we practice grade 12 equilibrium graphsdo you need more videos? i have a complete online course with way more content.click here: purc. About this unit. enter the dynamic world of chemical reactions! explore how factors like temperature and concentration shift reaction rates and witness the balancing act of reversible reactions. use le châtelier's principle to predict how changes impact chemical equilibrium, and discover how catalysts are a vital part of every living system!. A given chemical reaction system is defined by a balanced net chemical equation which is conventionally written as. reactants→ products (11.1.1) (11.1.1) reactants → products. the first thing we need to know about a chemical reaction represented by a balanced equation is whether it can actually take place. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic process consisting of forward and reverse reactions that proceed at equal rates. at equilibrium, the composition of the system no longer changes with time. the composition of an equilibrium mixture is independent of the direction from which equilibrium is approached. 4.2: the equilibrium constant.
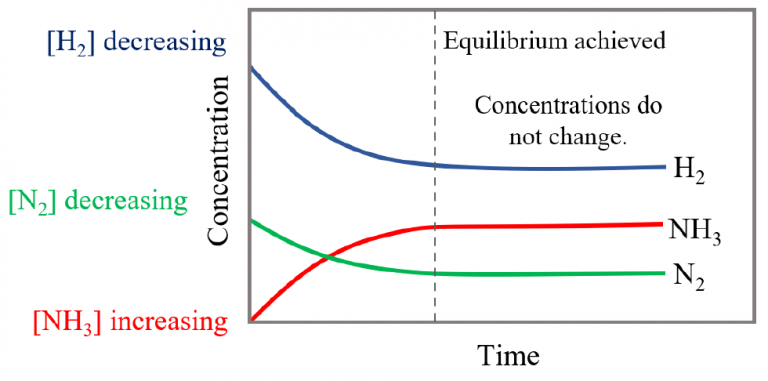
Chemical Equilibrium Chemistry Steps A given chemical reaction system is defined by a balanced net chemical equation which is conventionally written as. reactants→ products (11.1.1) (11.1.1) reactants → products. the first thing we need to know about a chemical reaction represented by a balanced equation is whether it can actually take place. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic process consisting of forward and reverse reactions that proceed at equal rates. at equilibrium, the composition of the system no longer changes with time. the composition of an equilibrium mixture is independent of the direction from which equilibrium is approached. 4.2: the equilibrium constant. When we wish to speak about one particular component of a reversible reaction, we use a single arrow. for example, in the equilibrium shown in figure 13.2.1 13.2. 1, the rate of the forward reaction. 2no2(g) → n2o4(g) (13.2.3) (13.2.3) 2 no 2 ( g) → n 2 o 4 ( g) is equal to the rate of the backward reaction. An equilibrium can be established for a physical change—like this liquid to gas transition—as well as for a chemical reaction. figure 4 shows an equilibrium is pictured between liquid bromine, br 2 (l), the dark liquid, and bromine vapor, br 2 (g), the orange gas. because the container is sealed, bromine vapor cannot escape and equilibrium.
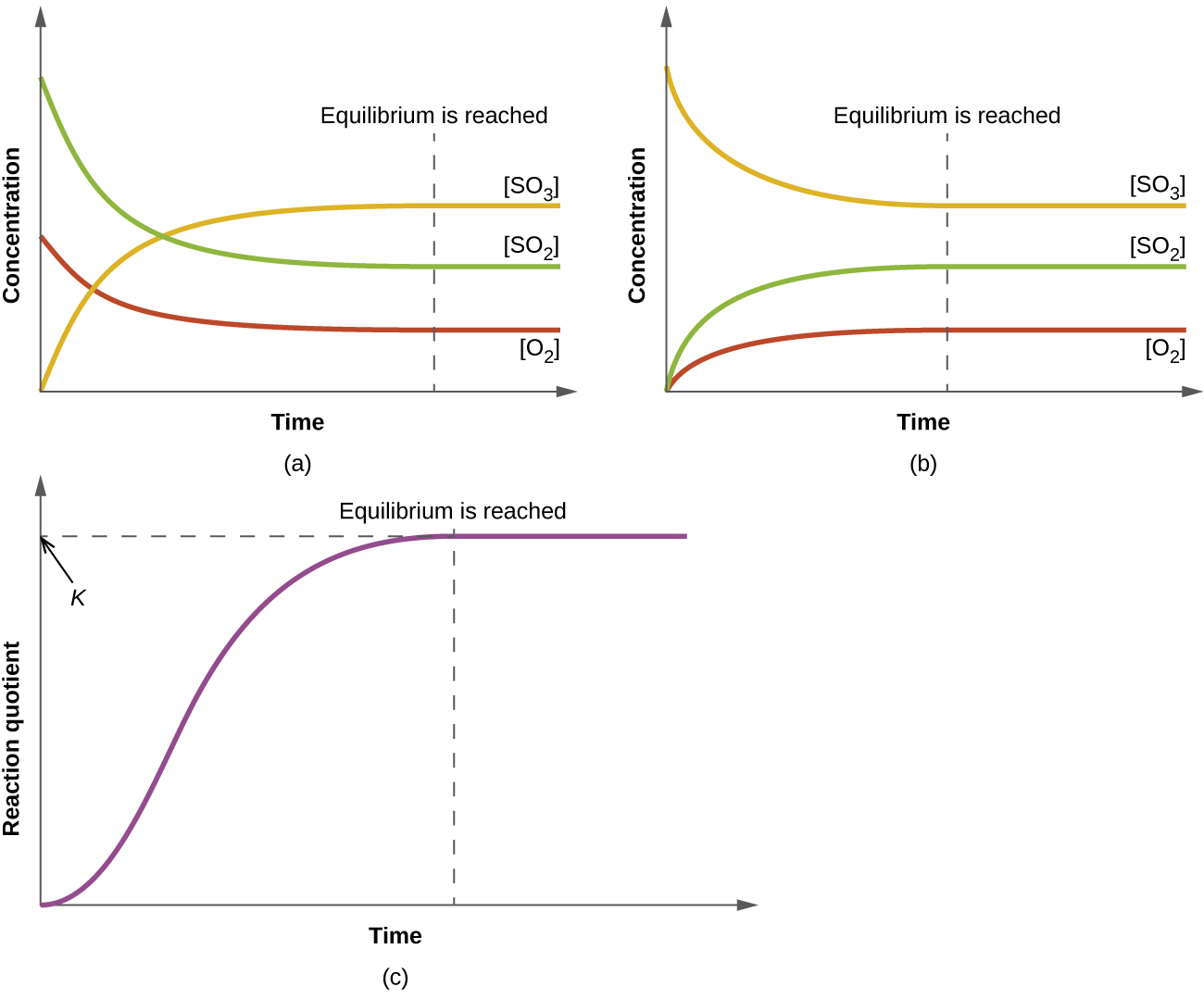
13 2 Equilibrium Constants Chemistry Libretexts When we wish to speak about one particular component of a reversible reaction, we use a single arrow. for example, in the equilibrium shown in figure 13.2.1 13.2. 1, the rate of the forward reaction. 2no2(g) → n2o4(g) (13.2.3) (13.2.3) 2 no 2 ( g) → n 2 o 4 ( g) is equal to the rate of the backward reaction. An equilibrium can be established for a physical change—like this liquid to gas transition—as well as for a chemical reaction. figure 4 shows an equilibrium is pictured between liquid bromine, br 2 (l), the dark liquid, and bromine vapor, br 2 (g), the orange gas. because the container is sealed, bromine vapor cannot escape and equilibrium.

Comments are closed.