Chemistry Practical Class 12 Salt Analysis Basics And Theory

Salt Analysis Practical File Handwritten Pdf Notes Class 12 Salt analysis is an integral part of the cbse class 12 chemistry practical examinations and is a topic that several students struggle with. therefore, we at byju’s have channelled our efforts into explaining this topic in a manner that is easy to understand and remember. In this video, i explain chemistry practical class 12 salt analysis theory for basic radicals. this also includes the format for writing it in your practical.
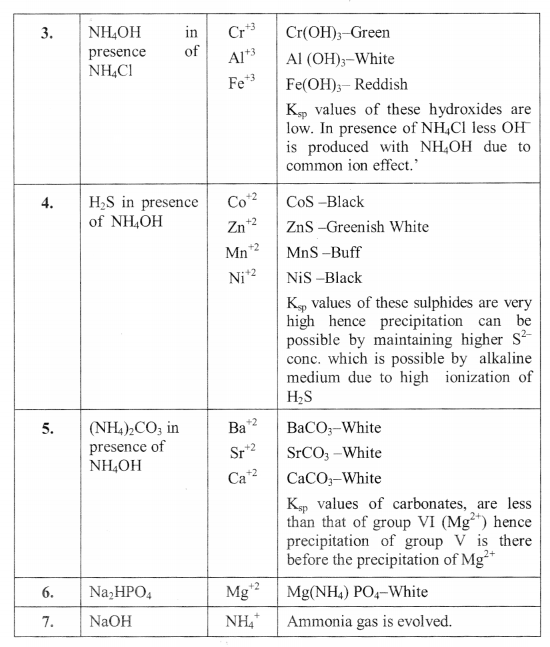
Salt Analysis Formulas Complete List Formulae Sheet For Salt Analysis The salt analysis is a very integral part of the cbse chemistry syllabus for class 12. to learn more about the preliminary tests for cations, basic radicals and inorganic salts, check out our range of engaging study material and content available on the site. download our vedantu app and register yourself for our free live demo classes. Hello students welcome to pankaj sir chemistry channel !!about this video :salt analysis 7 | basic radicals 4 | dry tests । class 12 | supertrick for basic r. Theory two basic principles of great use in the analysis are: (i) the solubility product; and (ii) the common ion effect. when ionic product of a salt exceeds its solubility product, precipitation takes place. ionic product of salt is controlled by making use of common ion effect which you have studied in the textbook of chemistry. material. 8. the standard solution is prepared. (b) theory 1. the reaction between kmno4 and mohr’s salt is a redox reaction and the titration is therefore called a redox titration. 2. mohr’s salt is the reducing agent and kmno4 is the oxidizing agent. 3. kmno4 acts as an oxidizing agent in all the mediums; i.e. acidic, basic and neutral medium. 4.

Comments are closed.